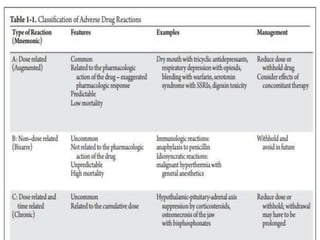
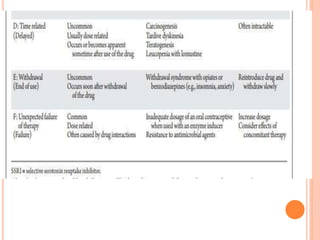
This document discusses adverse drug reactions (ADRs), their classification and monitoring. It defines an ADR as an unintended effect of a drug that occurs at normal dosages. ADRs are classified into types A-H based on mechanisms and timing. Factors that increase risk of ADRs include polypharmacy, age, drug characteristics, and genetic predispositions. ADRs are detected through pre-marketing clinical trials, post-marketing surveillance programs, and healthcare professional reporting. Vigilant monitoring of at-risk patients can help identify ADRs.