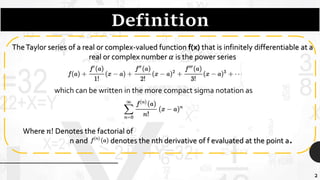
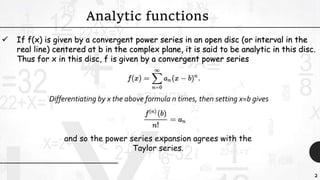
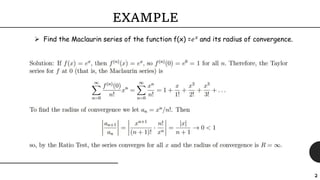
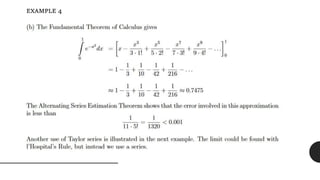
Brook Taylor was an English mathematician who formally introduced the Taylor series in 1715. A Taylor series represents a function as an infinite sum of terms calculated from the function's derivatives at a single point. It can be used to approximate functions by taking a finite number of terms of the Taylor series. The Taylor theorem gives quantitative estimates on the error of such approximations. A function is analytic if it is equal to its Taylor series in an open interval, meaning it can be expressed entirely as the Taylor series within that interval.