Embed presentation
Download to read offline

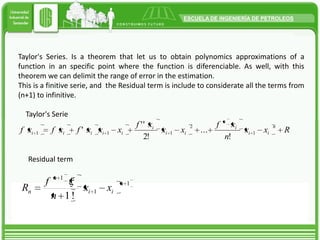


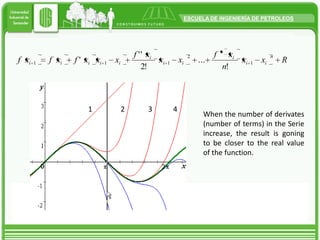
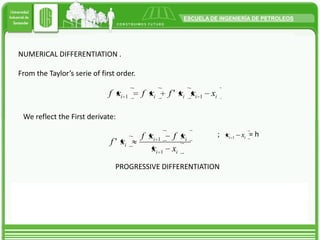
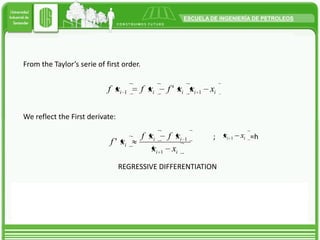

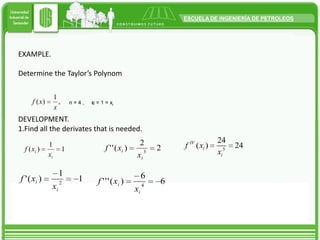

Taylor's approximation theorem allows functions to be approximated by polynomials in a specific point where the function is differentiable. It provides a finite series with a residual term to account for higher order terms. Taylor's series is useful for obtaining close approximations to the real solution of a function by using a finite number of terms. The more derivative terms that are included, the closer the result will be to the actual value of the function at that point.










