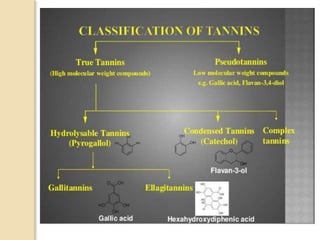
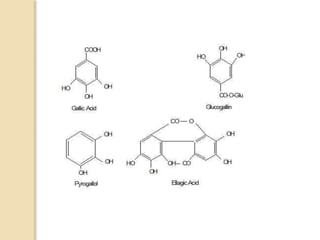
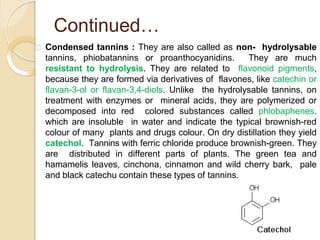
Tannins are polyphenolic substances found in plants, primarily used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries for their antiseptic properties and roles in leather tanning and dyeing. They are classified into hydrolysable (e.g., gallo tannin, ellagi tannin) and condensed tannins (e.g., proanthocyanidins), with different chemical behaviors and extraction methods. Detection tests for tannins include the gelatin test, goldbeater’s skin test, and tests with ferric chloride, among others.