Embed presentation

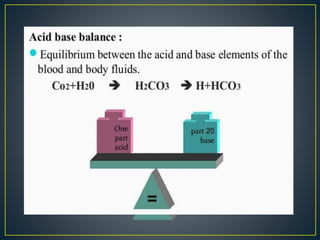
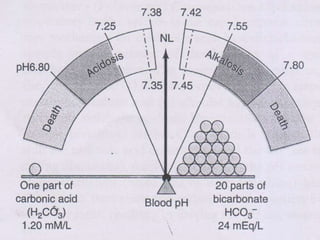

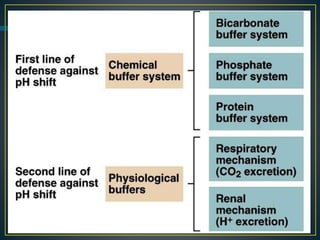

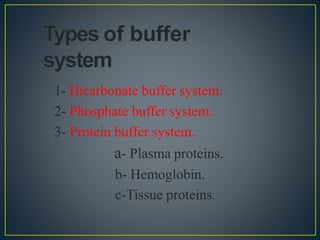

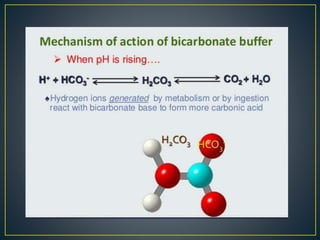
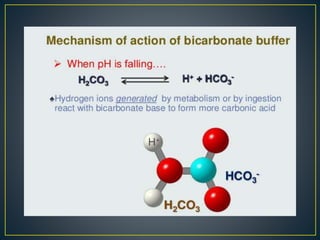


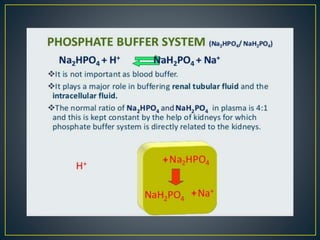



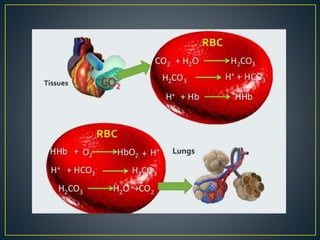
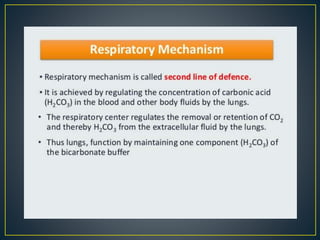
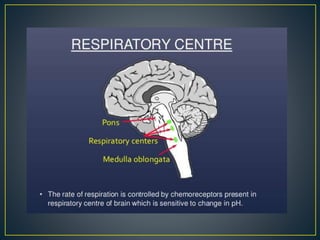

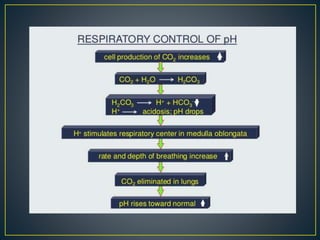
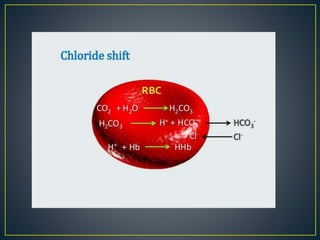



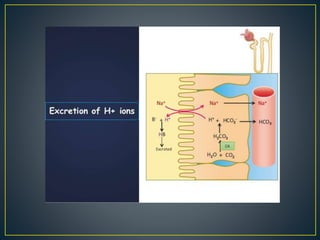
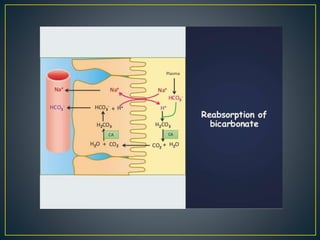
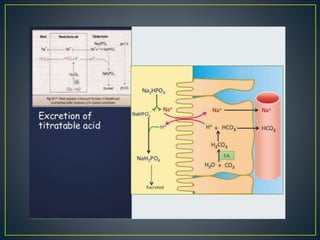
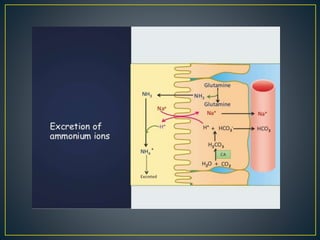



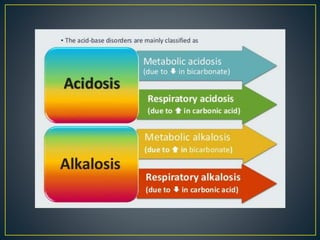
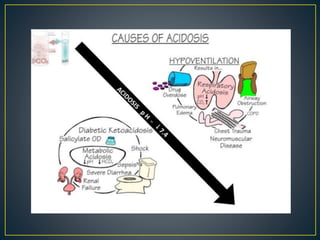
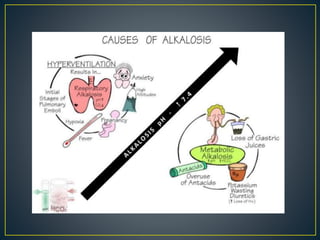



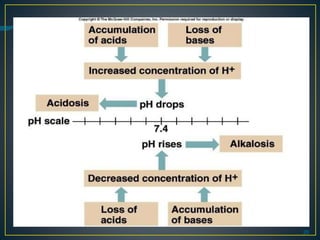

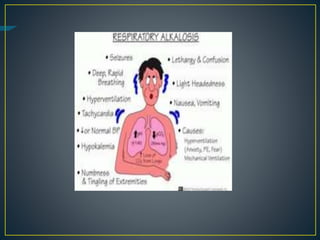


The document discusses the concepts of acids, bases, buffers, and pH levels, as well as the body's three mechanisms for maintaining acid-base balance: buffering, respiratory compensation, and metabolic compensation. It defines buffers as solutions that prevent significant changes in hydrogen ion concentration and outlines various buffer systems, including the bicarbonate, phosphate, and protein buffer systems. Additionally, it briefly mentions conditions such as respiratory and metabolic acidosis and alkalosis.











































