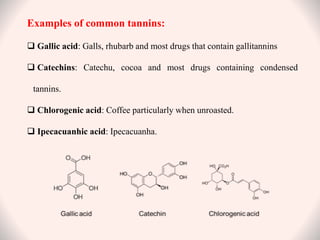
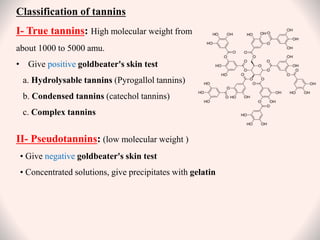
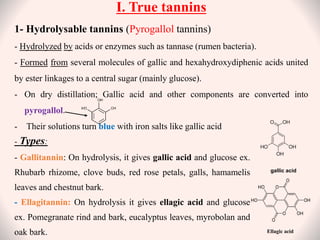
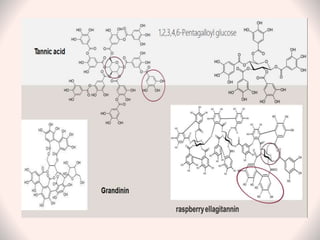
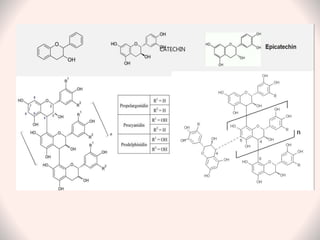
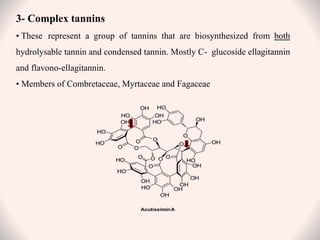
Tannins are naturally occurring polyphenolic compounds found in many plants that have astringent properties. They are secondary plant metabolites that bind and precipitate proteins. There are three main classes of tannins: hydrolysable tannins, condensed tannins, and complex tannins. Hydrolysable tannins contain gallic acid and can be hydrolyzed to release gallic acid. Condensed tannins are polymeric flavan-3-ols that produce catechol upon dry distillation. Tannins have various uses as astringents, antioxidants, and in treating diarrhea, burns, and heavy metal poisoning due to their protein-precipitating effects.