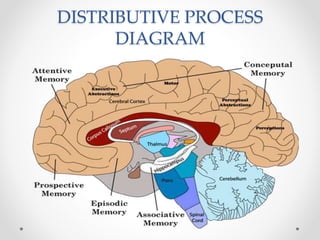
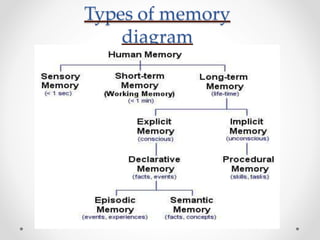
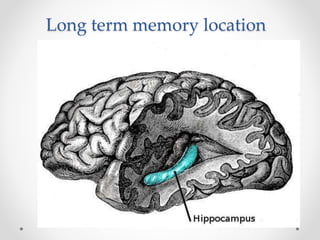
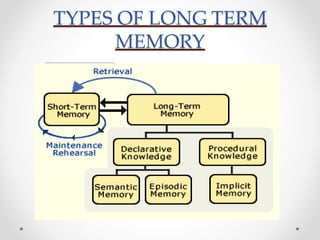
The document provides an overview of human memory, explaining the processes involved in encoding, storing, and retrieving information. It describes three types of memory: sensory, short-term, and long-term memory, with subcategories like implicit and explicit memory. Factors affecting memory are also discussed, including health, age, and meaningfulness of material.