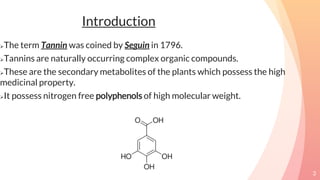
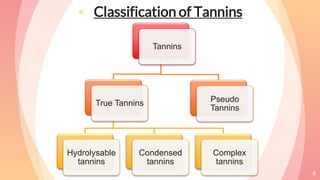
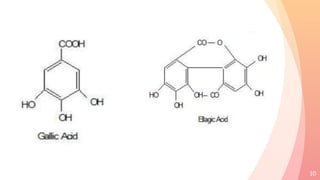
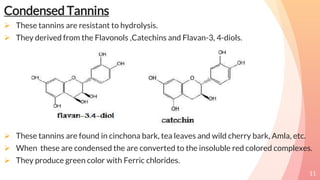
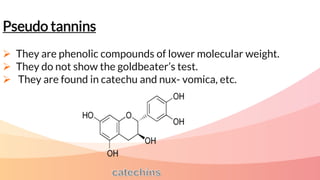
Tannins are complex organic compounds that are secondary metabolites of plants. They have high medicinal properties and are classified as hydrolysable tannins, condensed tannins, or pseudo tannins. Hydrolysable tannins can be hydrolyzed by acids or enzymes to produce gallic or ellagic acid, while condensed tannins are resistant to hydrolysis. Tannins have various medicinal and biological properties including stopping hemorrhage, precipitating proteins, and acting as antioxidants. Common identification tests for tannins include the gelatin test, Goldbeater's skin test, and phenazone test.