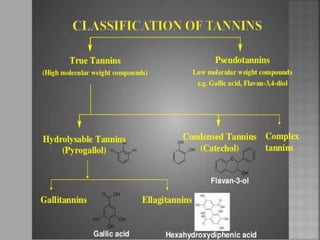
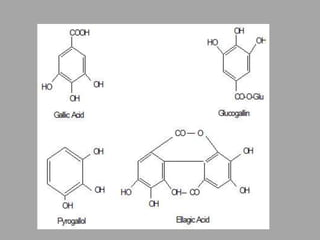
Tannins are polyphenolic substances found in various plants, useful in industries such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals due to their astringent properties. They are classified into hydrolysable and condensed tannins based on their chemical nature and behavior during distillation, with examples including gallotannin and catechin. Various extraction methods and identification tests, such as the gelatin test and goldbeater's skin test, are employed to isolate and confirm the presence of tannins in drugs.