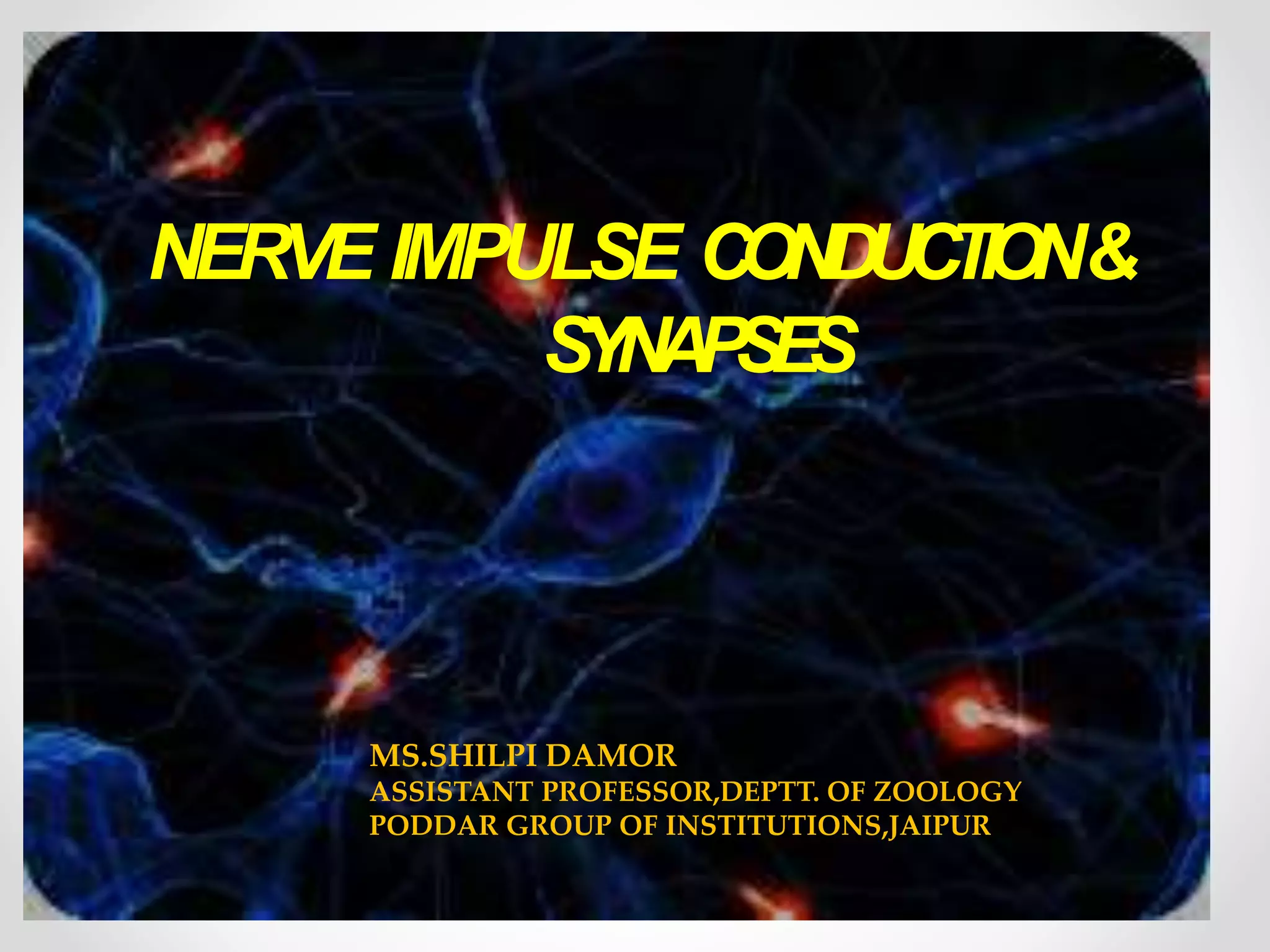
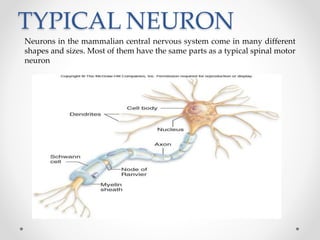
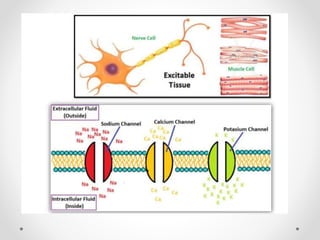
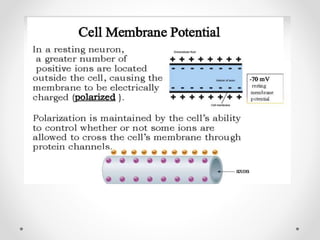
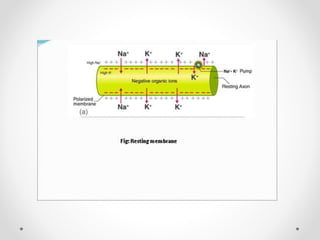
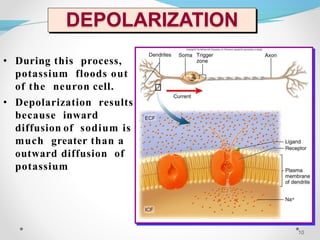
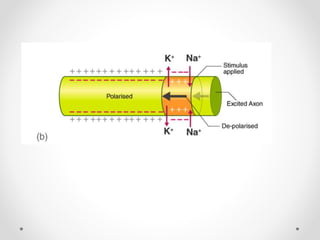
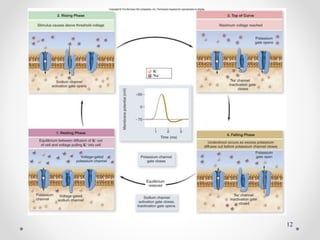
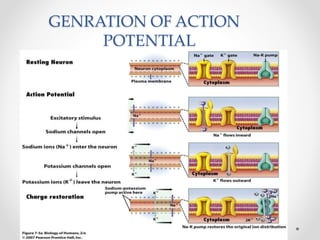
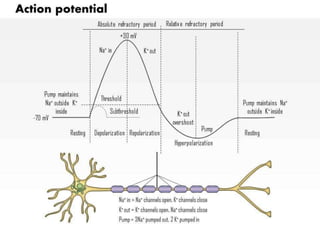
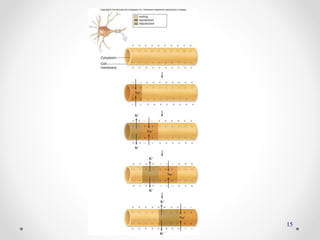
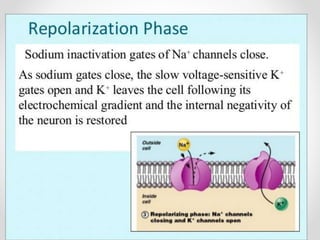
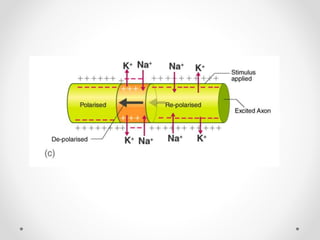
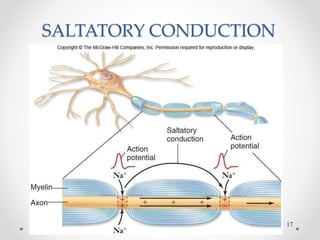
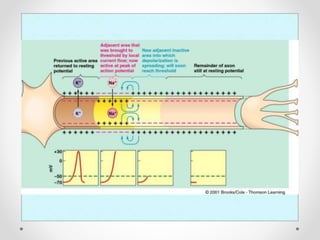
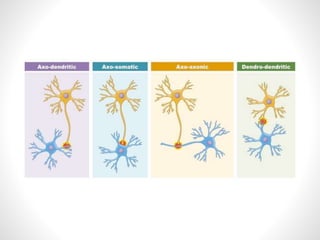
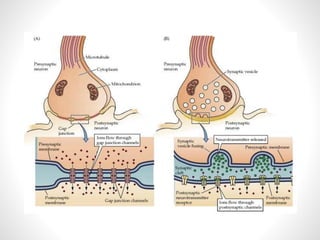
The document discusses nerve impulse conduction and synapses, outlining the structure and function of neurons, including resting potential, action potential, and synaptic transmission. It explains how action potentials propagate along axons and differentiate between types of synapses, such as electrical and chemical synapses. Additionally, it covers critical concepts like synaptic delay, fatigue, and summation within synaptic transmission.