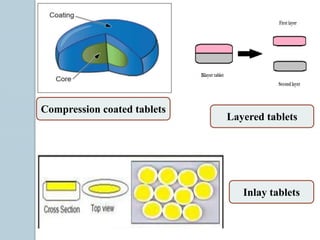
The document provides a comprehensive overview of pharmaceutical tablets, including their classification, formulation, granulation processes, and the role of excipients. It details the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of tablets, as well as the various types, such as compressed, enteric coated, and chewable tablets. Additionally, it highlights the importance of ingredient selection in formulation and the methods of tablet granulation.