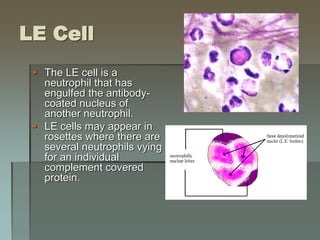
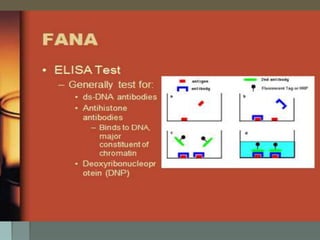
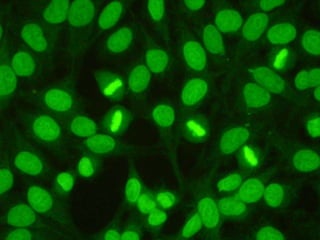
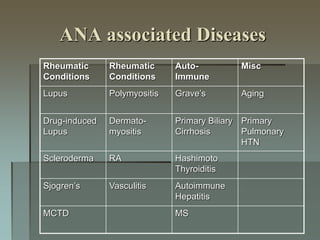
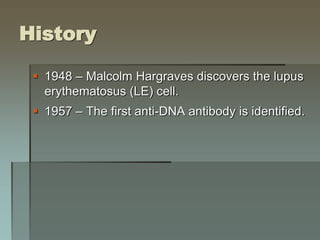
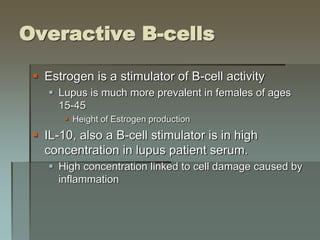
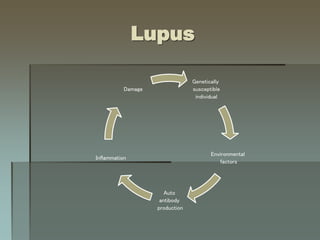
Lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues and organs. It was first described in the 10th century but key advancements in understanding the disease only occurred in the late 19th and 20th centuries with identification of diagnostic markers and classification criteria. Lupus disproportionately affects women and can involve multiple organ systems, with a wide range of potential symptoms. Diagnosis is based on evaluating clinical features and lab tests for autoantibodies and applying classification criteria from medical organizations.














































![AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY (ACR)
CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSIS OF SLE
Serositis (Pleurisy, pericarditis)
Oral ulcers
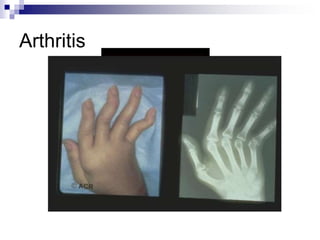
Arthritis
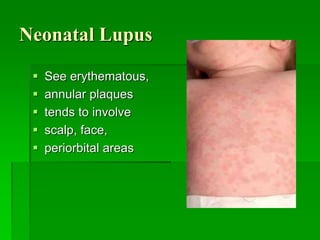
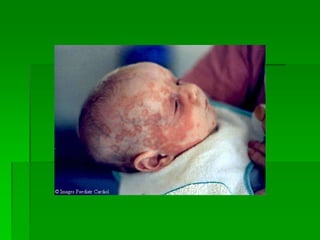
Photosensitivity
Blood disorders (Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia)
Renal involvement
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
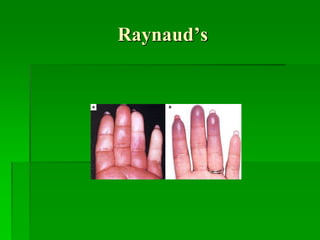
Immunologic phenomena [false-positive Rapid Plasma Reagin
(RPR)]
Neurologic disorder
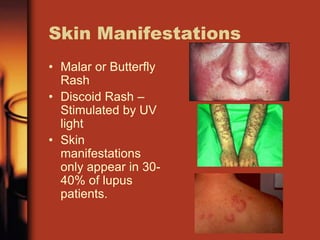
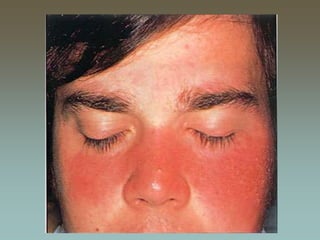
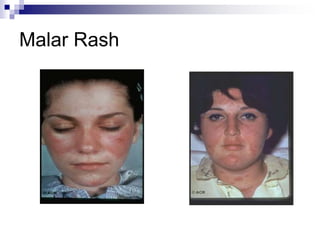
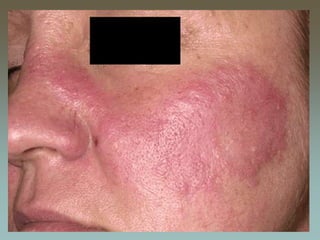
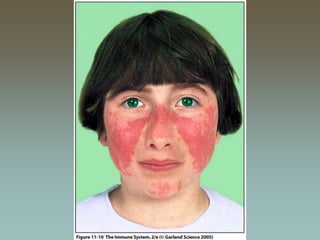
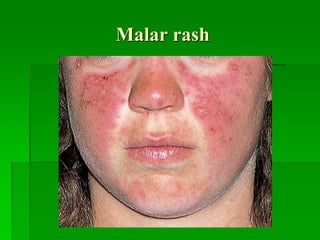
Malar rash
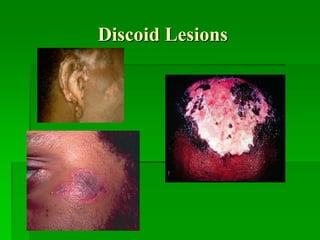
Discoid rash](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slea-190729061234/85/systemic-lupus-erythematosus-63-320.jpg)