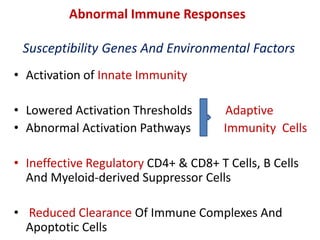
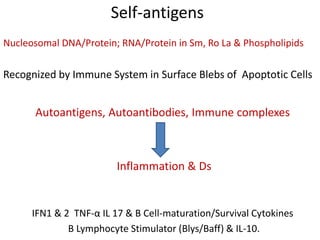
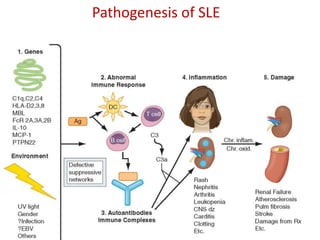
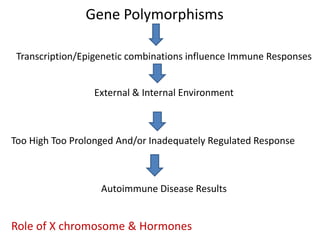
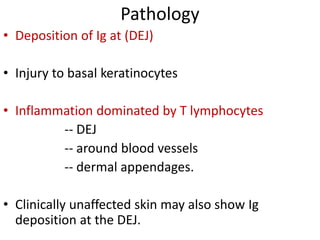
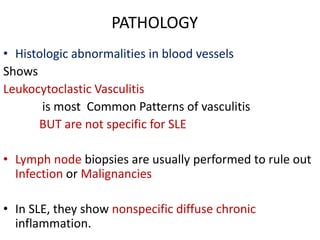
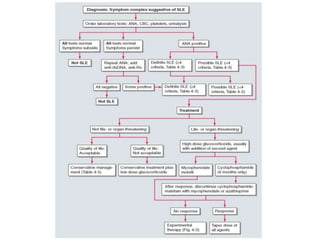
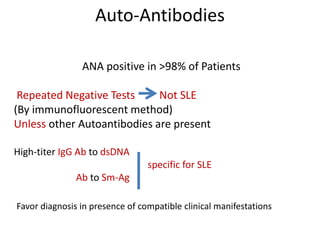
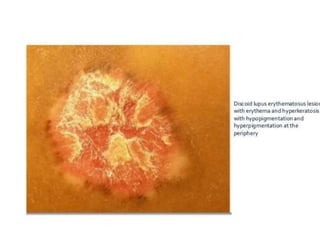
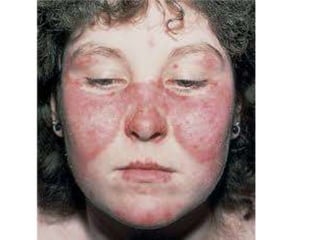
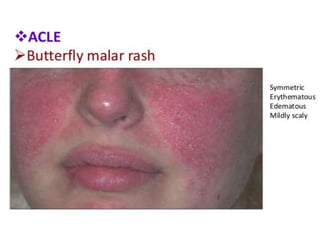
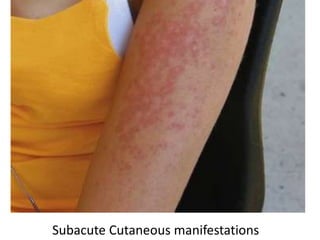
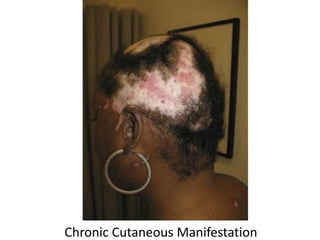
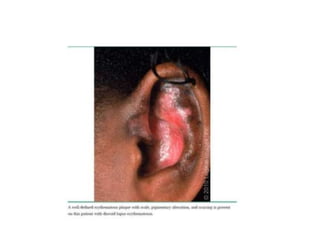
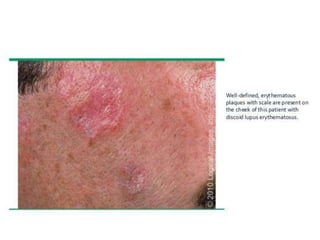
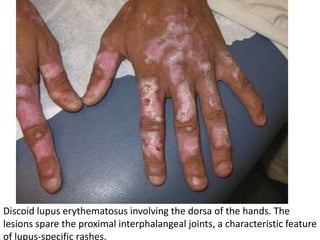
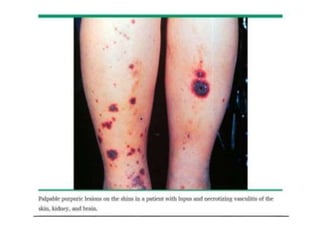
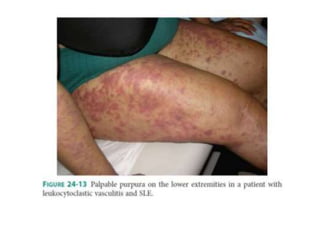
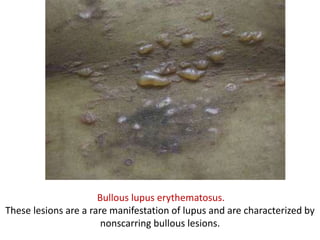
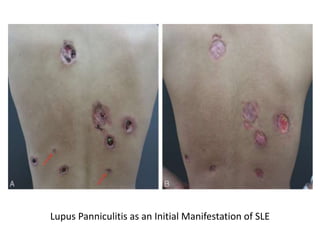
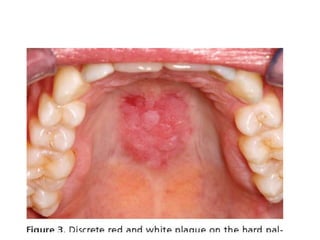
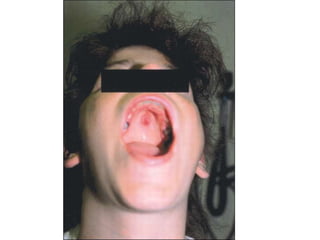
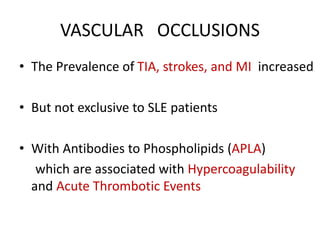
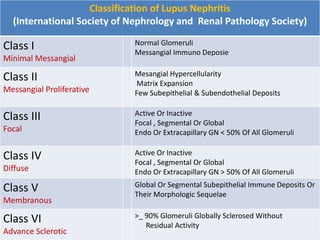
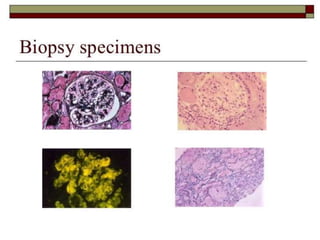
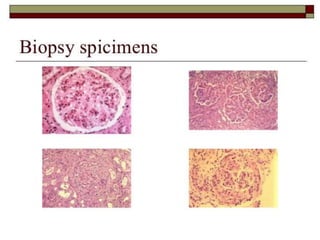
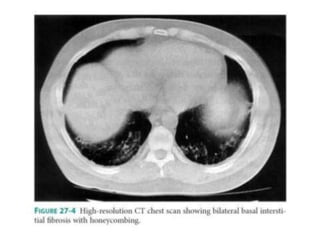
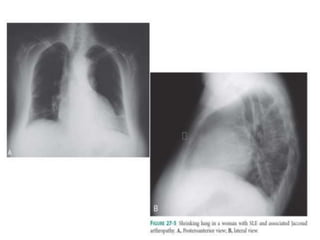
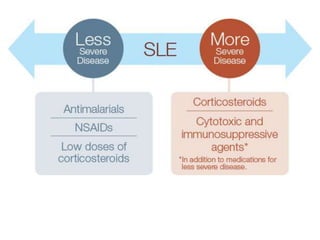
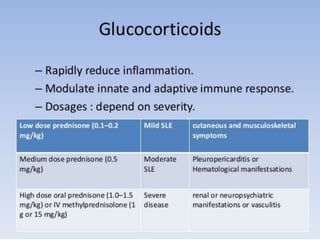
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a multi-gene autoimmune disease caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is characterized by abnormal immune responses that result in inflammation and damage to various organs. Diagnosis requires meeting 4 out of 11 classification criteria relating to clinical symptoms and blood markers. Management aims to induce remission of acute flares, maintain improvements to suppress symptoms, and prevent organ damage. Treatment choices depend on the severity and potential reversibility of manifestations. The goal is controlling symptoms without cure since complete sustained remission is rare.