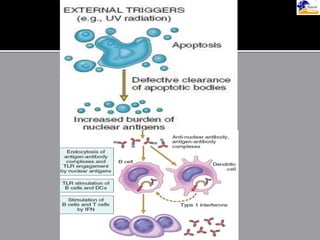
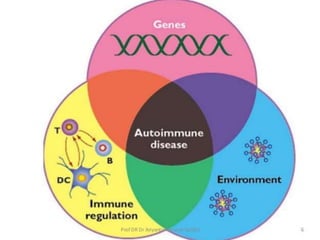
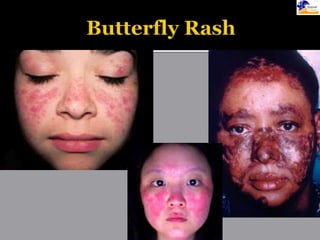
This document discusses systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues and organs. It causes inflammation and damage to many different body systems. SLE is more common in women and typically presents between ages 15-25. Symptoms can include rashes, joint pain, fatigue, and organ involvement. Diagnosis involves evaluating symptoms, signs, and antibody tests. Treatments include medications like NSAIDs, antimalarials, steroids, and immunosuppressants to reduce symptoms and prevent organ damage. Complications can affect many organs but most commonly involve the kidneys, heart, and lungs. With treatment, 5-year survival rates are over 85%.