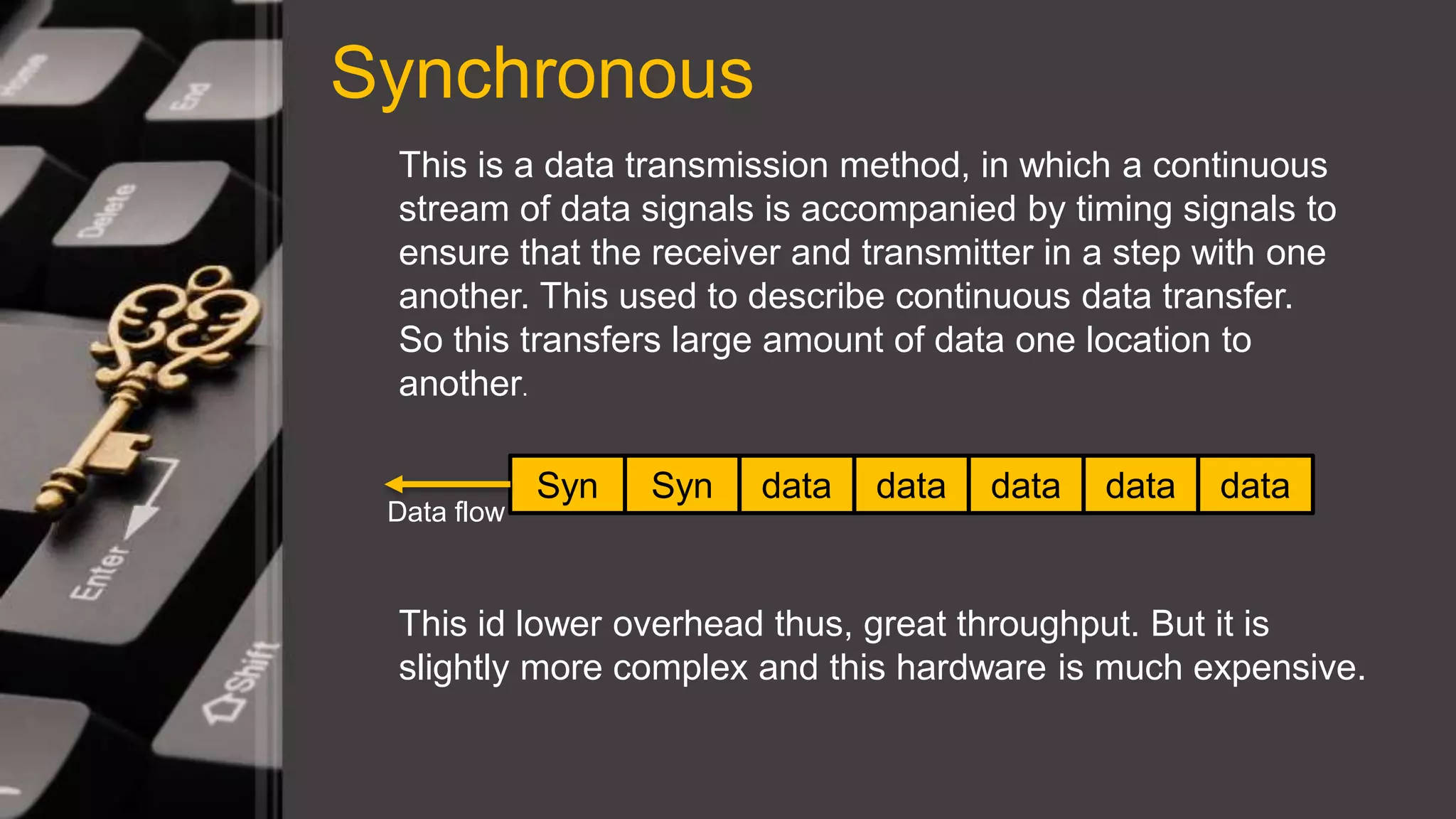
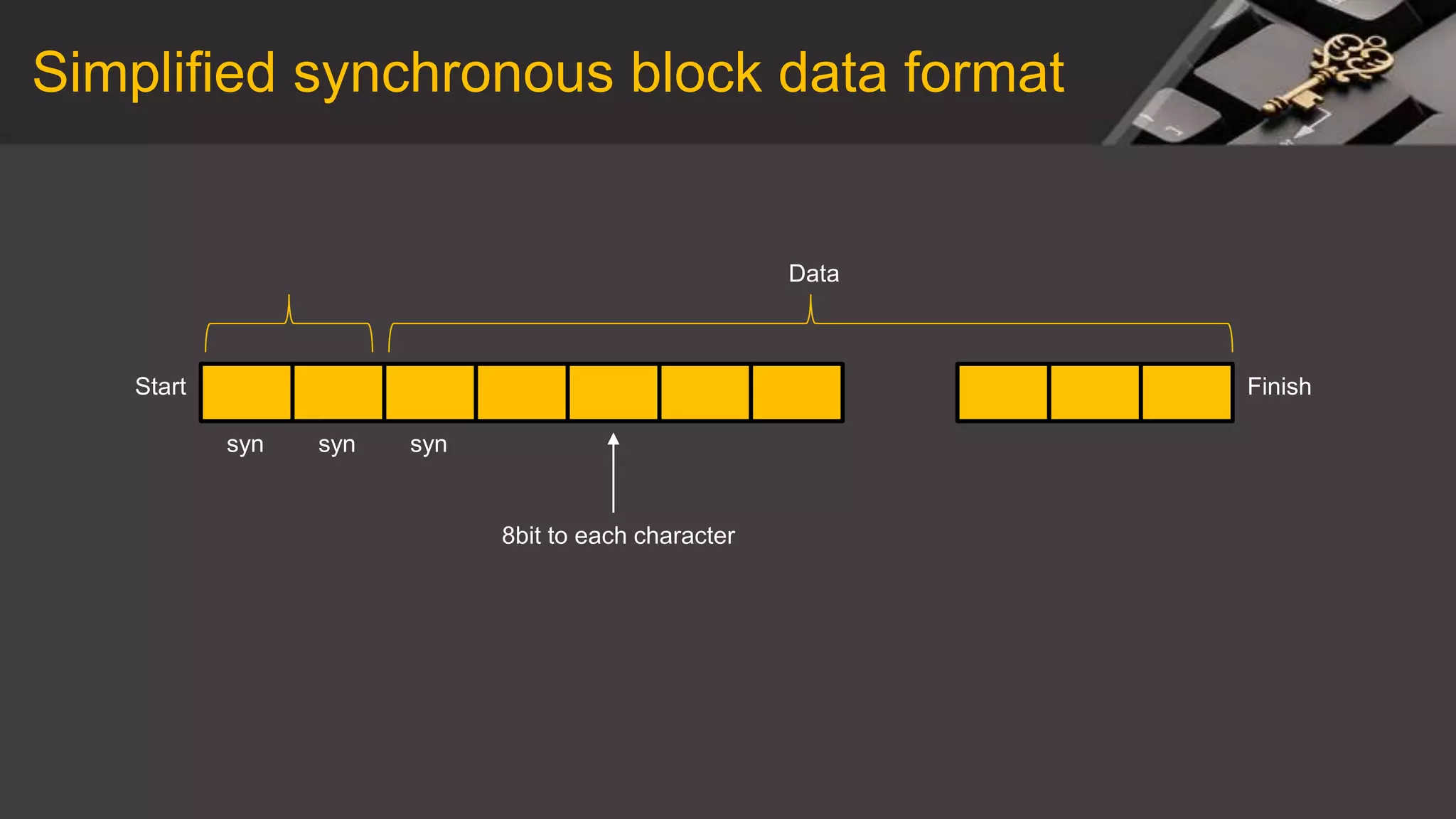
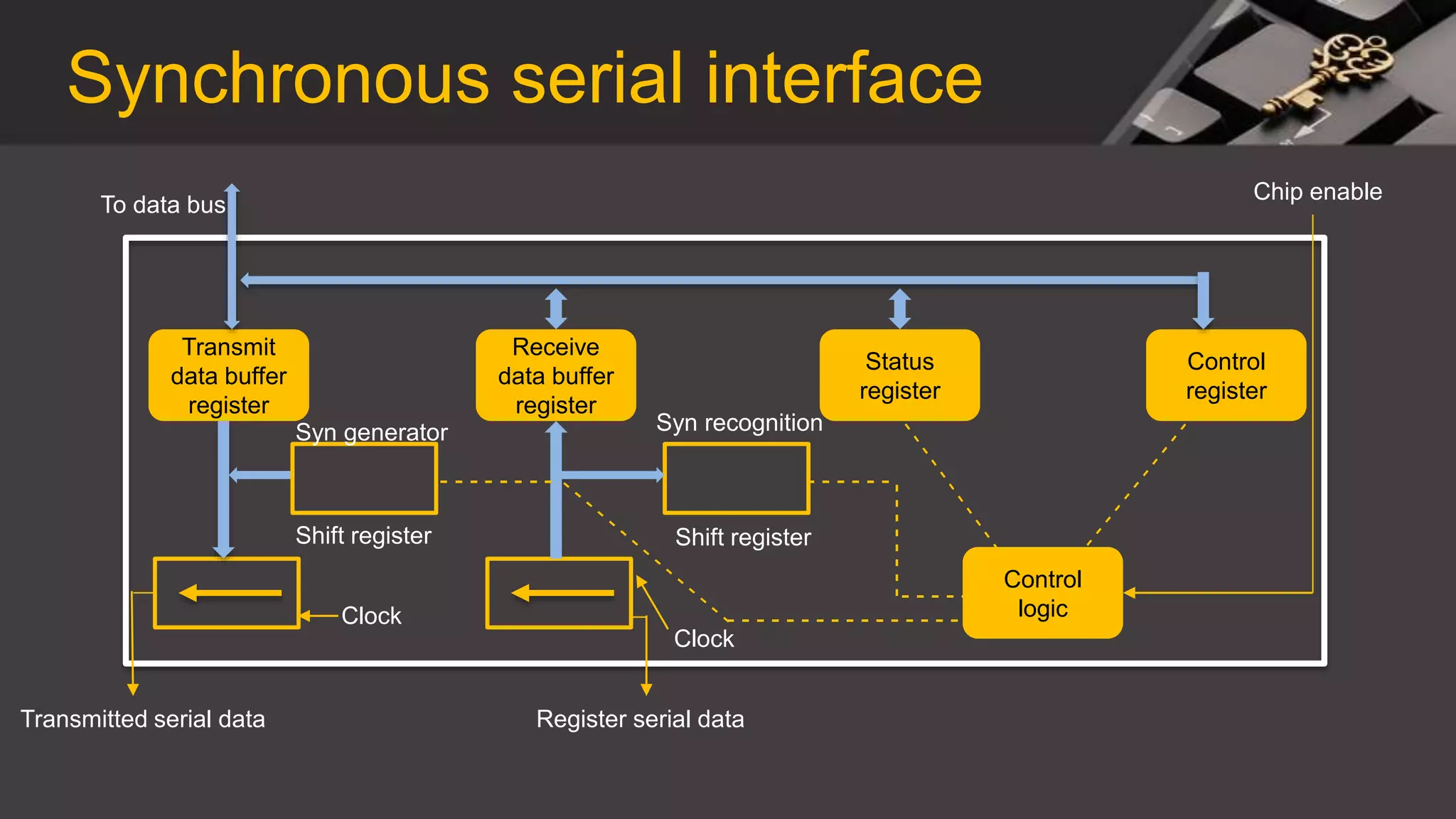
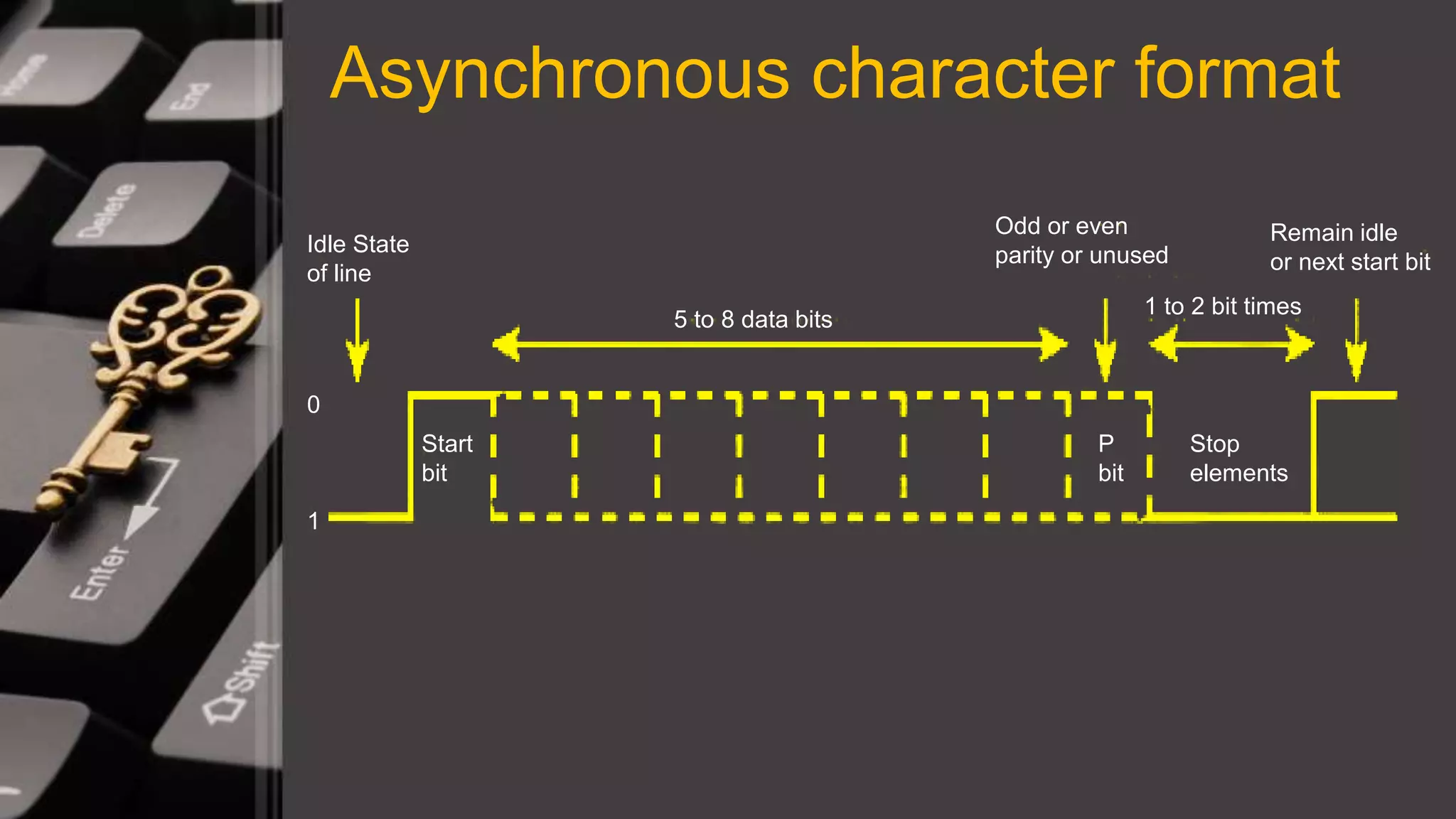
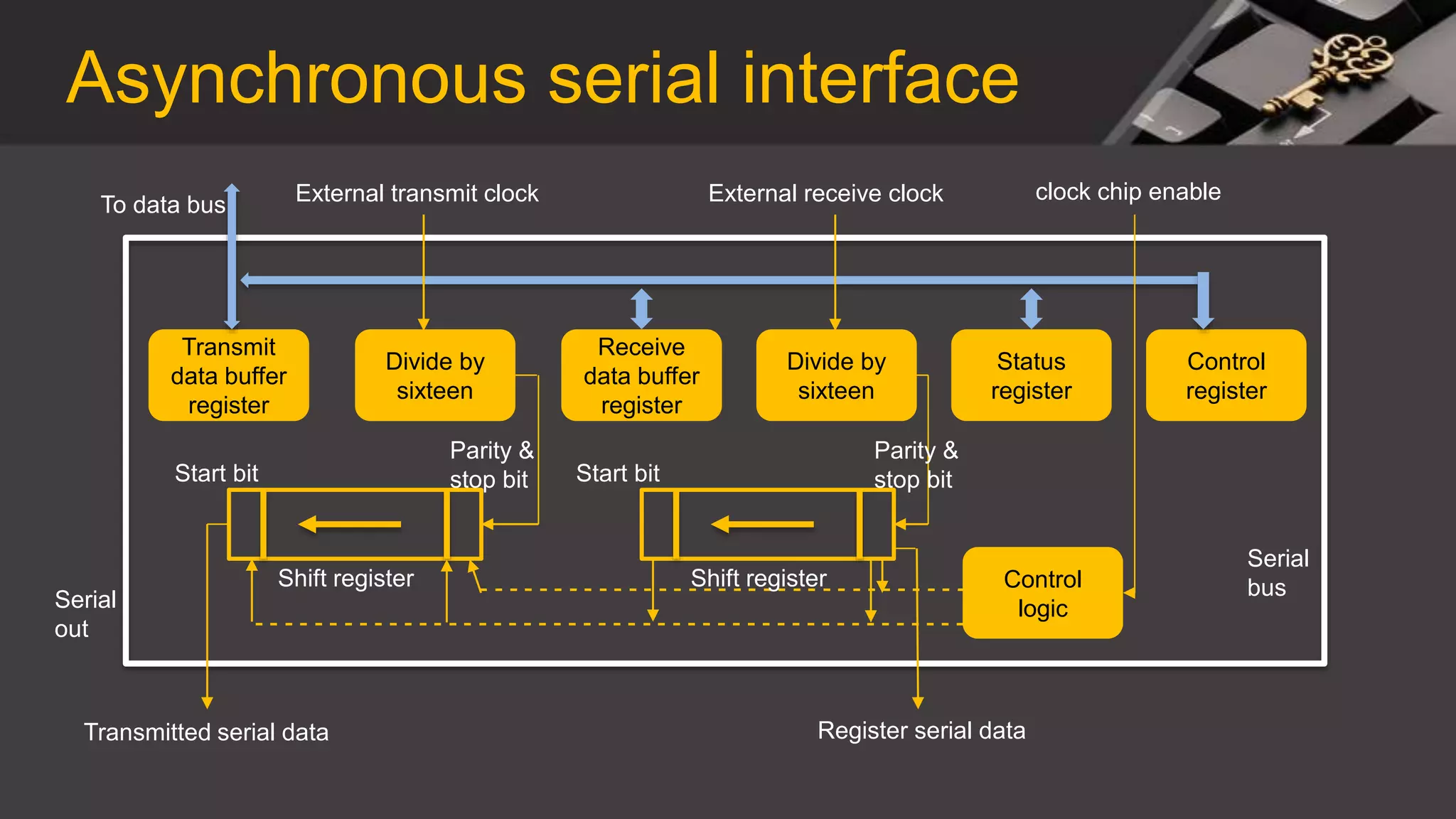
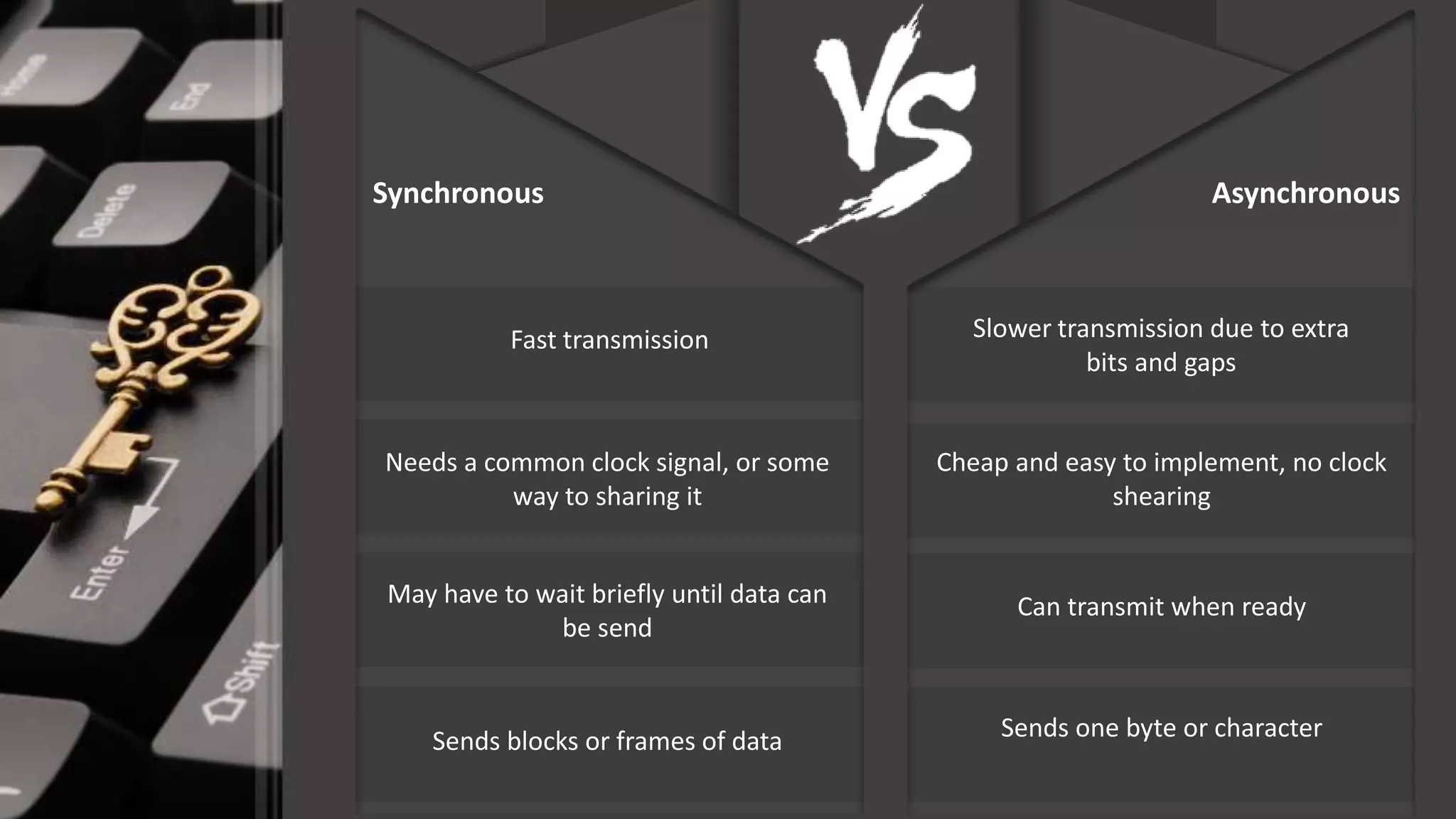
This document discusses synchronous and asynchronous data transmission methods. Synchronous transmission uses timing signals to ensure the receiver and transmitter stay synchronized during continuous data transfer, allowing for high throughput but requiring more complex hardware. Asynchronous transmission encodes each character with start and stop bits, making it slower but cheaper to implement without a shared clock. Both methods are compared in terms of speed, overhead, complexity and cost.