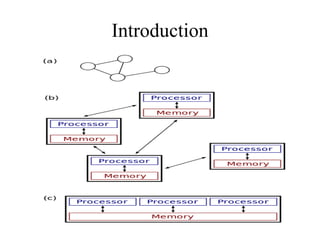
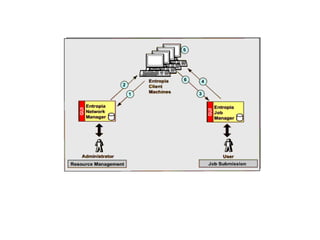
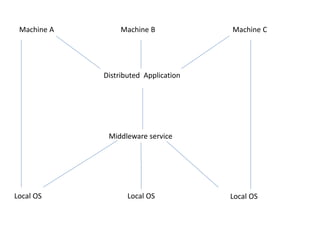
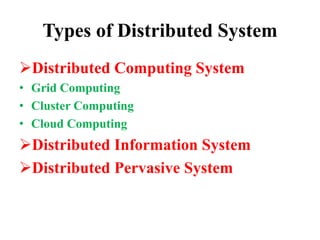
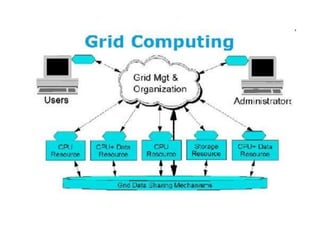
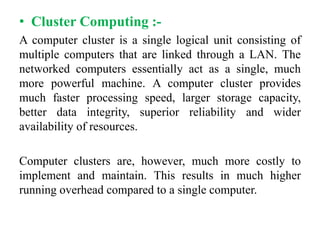
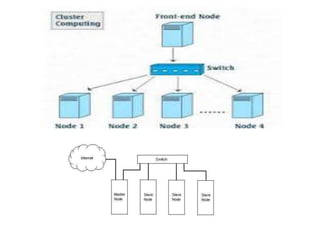
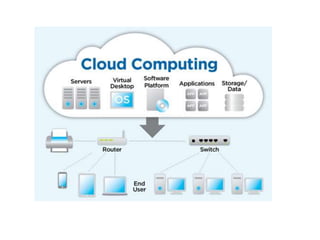
This document provides an overview of distributed computing. It discusses the history and introduction of distributed computing. It describes the working of distributed systems and common types like grid computing, cluster computing and cloud computing. It covers the motivations, goals, characteristics, architectures, security challenges and examples of distributed computing. Advantages include improved performance and fault tolerance, while disadvantages are security issues and lost messages.