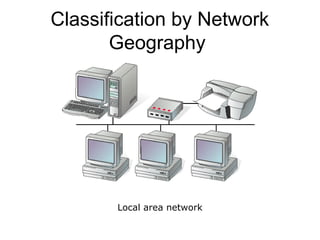
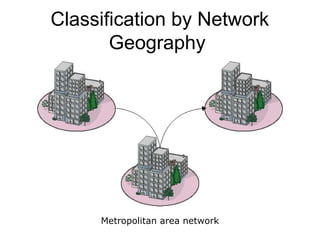
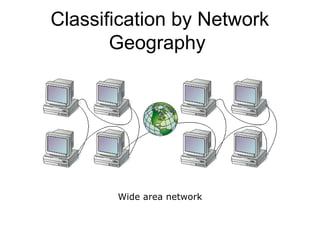
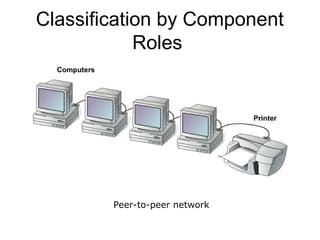
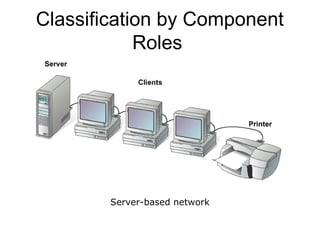
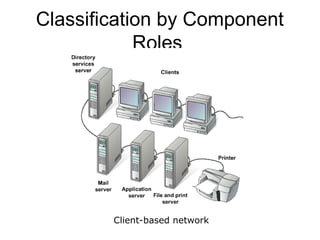
This document introduces basic network concepts, emphasizing the need for networks to enhance communication, share resources, and enable centralized management. It describes various classifications of networks, including Local Area Networks (LAN), Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), and Wide Area Networks (WAN), as well as different roles such as peer-to-peer, server-based, and client-based networks. The essential purpose of networks is highlighted as facilitating effective communication and resource sharing among connected computing devices.