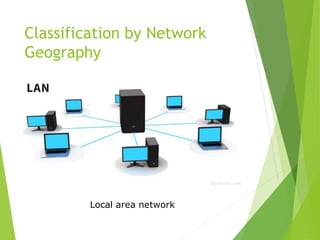
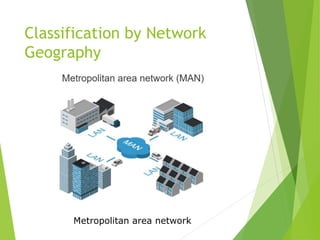
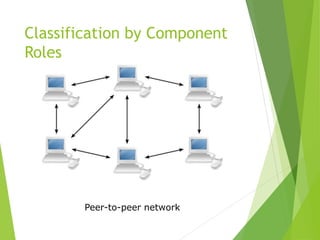
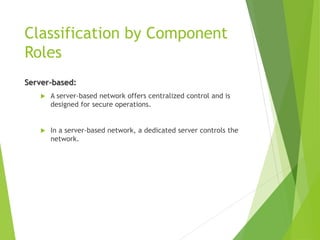
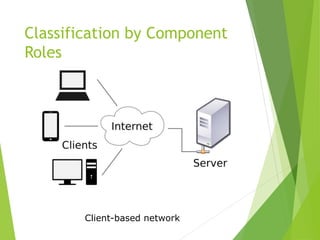
This document provides an introduction to basic network concepts. It defines what a computer network is, discusses the need for networks to enhance communication, share resources, and facilitate centralized management. It also covers different types of network classifications, including by geography (LAN, MAN, WAN) and by component roles (peer-to-peer, server-based, client-based).