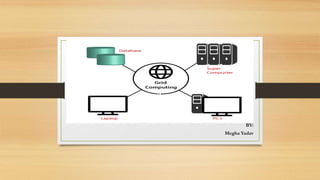
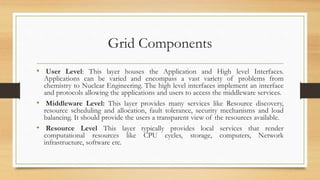
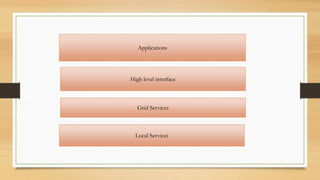
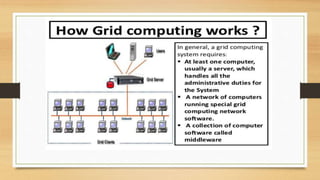
Grid computing interconnects diverse resources like high-performance computers, databases, and instruments from multiple organizations and allows collaborative use. It is characterized by heterogeneity, scalability, adaptability, and security, while operating through a multi-layered structure that includes user-level applications, middleware services, and resource-level components. Despite its advantages such as decentralization and support for heterogeneous systems, grid computing faces challenges like evolving standards and the need for fast interconnects.