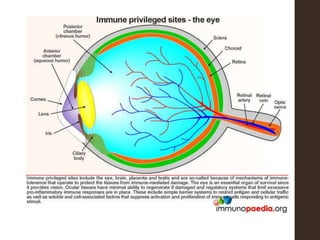
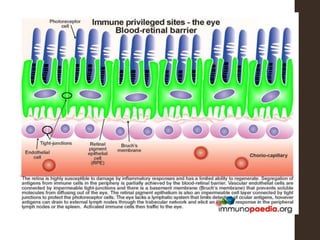
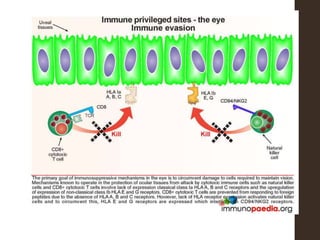
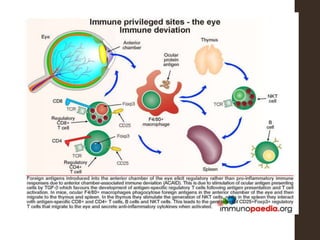
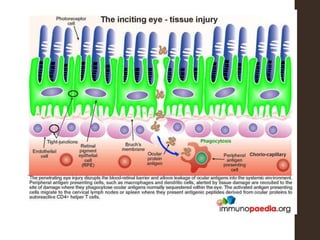
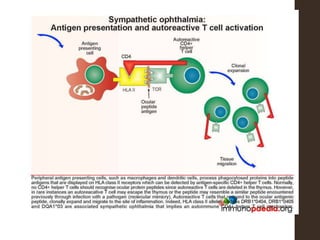
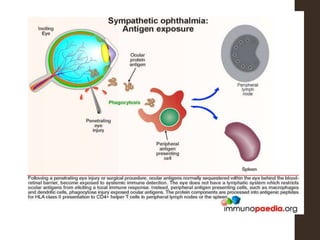
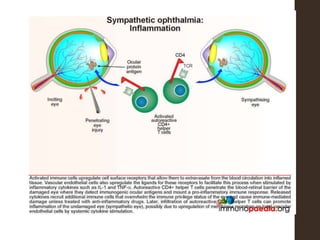
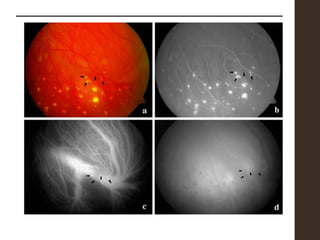
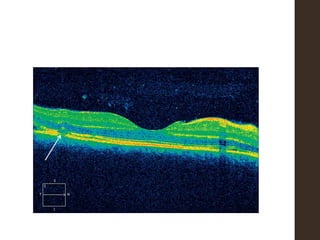
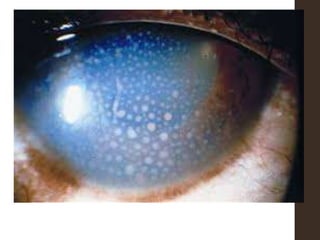
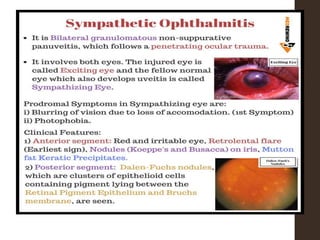
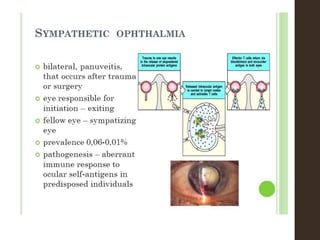
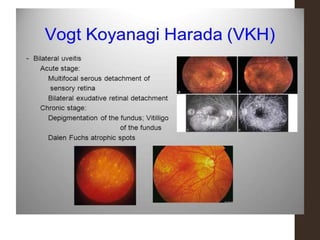
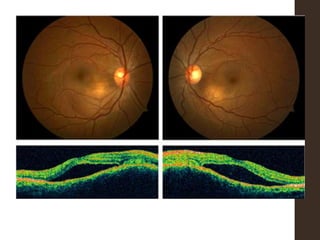
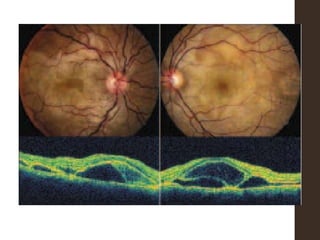
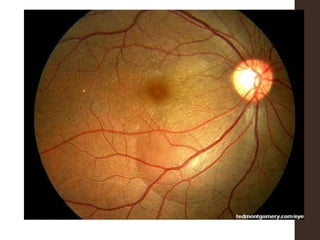
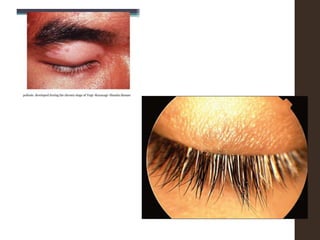
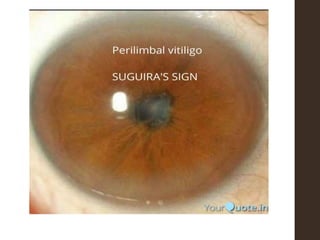
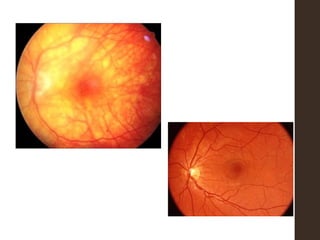
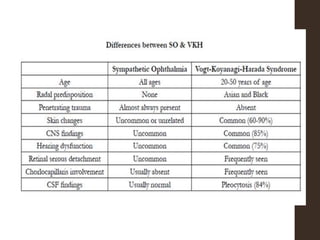
Sympathetic ophthalmia is a rare bilateral granulomatous panuveitis that occurs after trauma or surgery to one eye. It results from an immune response against ocular antigens that spreads from the injured eye to the other eye. The main symptoms are blurred vision, pain, and photophobia in the uninjured eye. Treatment involves high-dose oral corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to prevent vision loss in both eyes. Prompt diagnosis and treatment usually leads to a good visual prognosis.