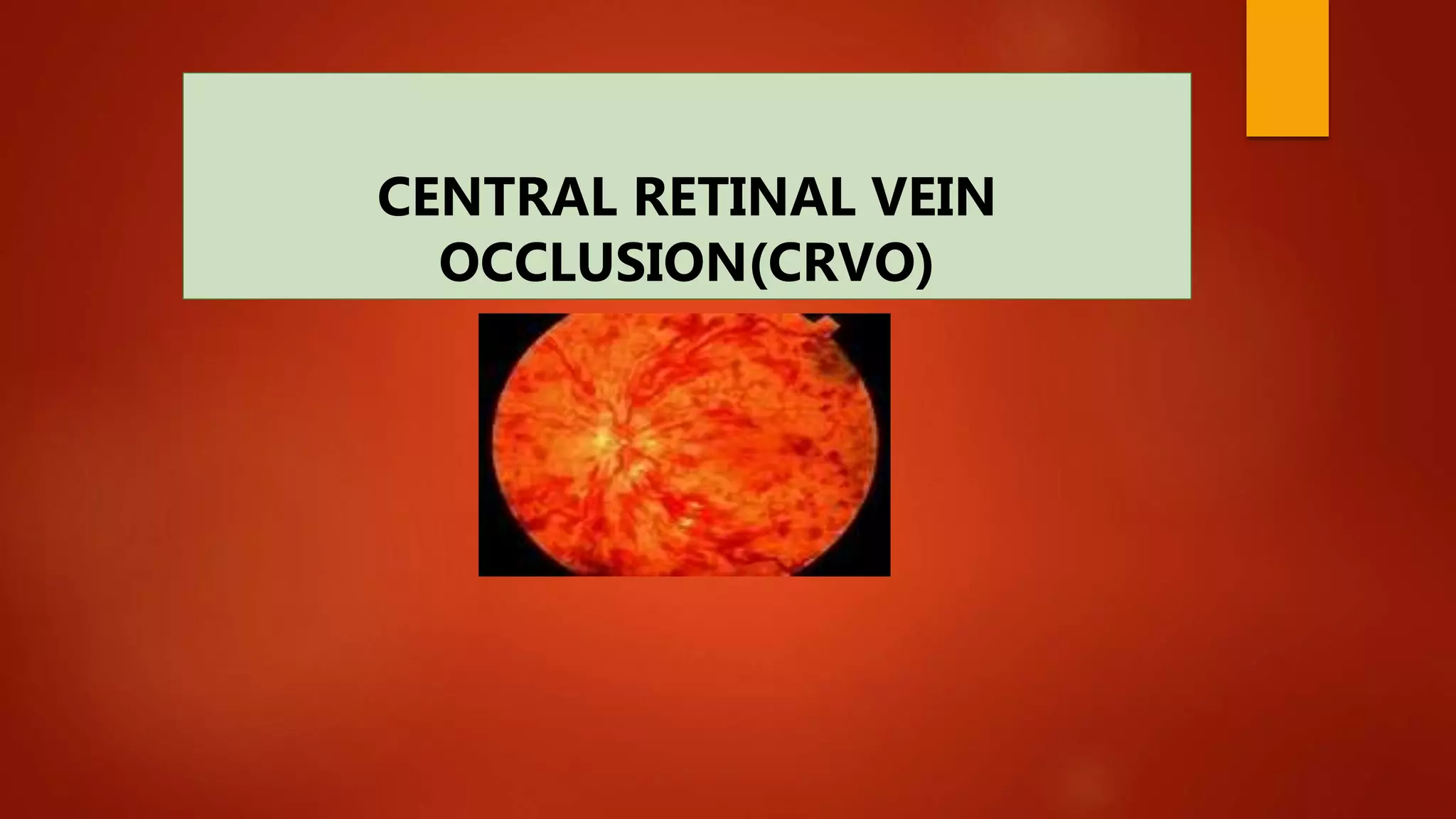
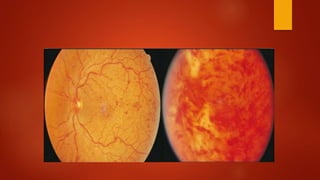
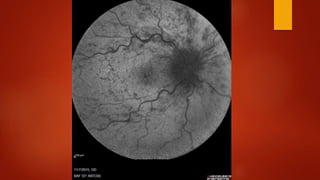
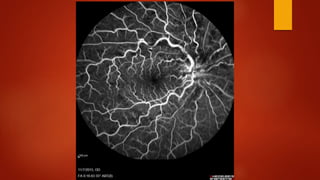
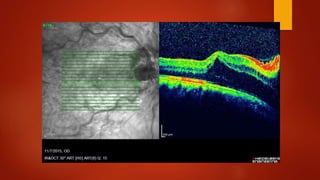
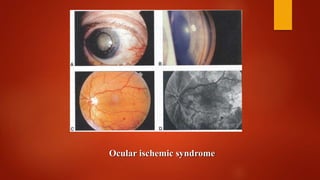
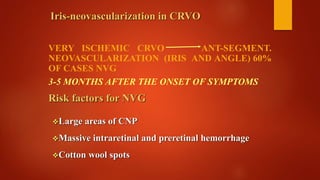
Central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) occurs when there is a thrombus in the central retinal vein, blocking blood flow and oxygen to the retina. It is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. CRVO can be non-ischemic or ischemic depending on the extent of blood flow reduction. Risk factors include hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and certain blood disorders. Current treatments focus on managing complications like macular edema with anti-VEGF drugs and neovascularization with laser therapy or surgery. Prognosis is generally poor for ischemic CRVO without treatment. Close monitoring is needed to detect complications and guide further management.