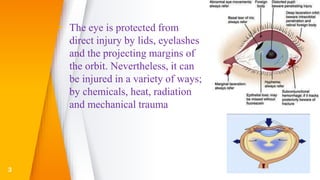
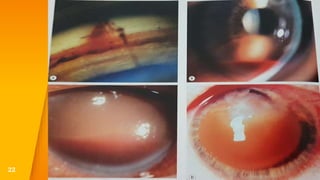
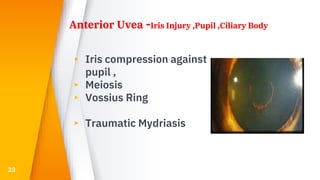
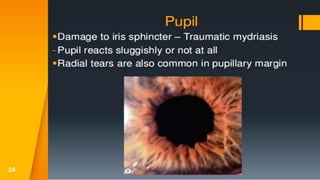
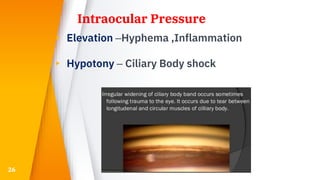
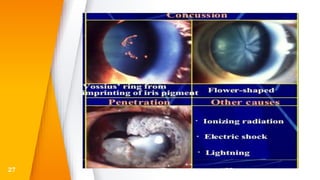
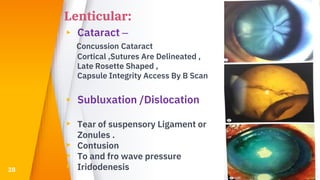
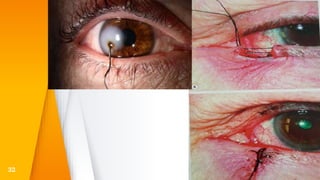
This document discusses various types of ocular trauma, including:
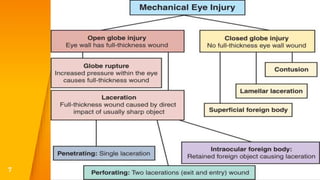
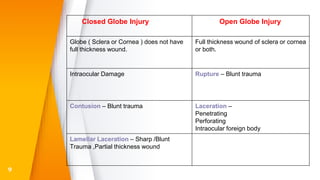
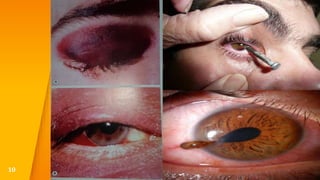
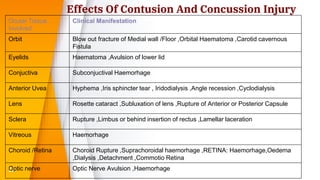
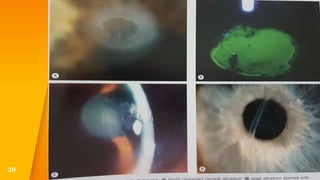
- Closed globe injuries like corneal abrasions, hyphema, iridodialysis, and cataracts caused by blunt trauma.
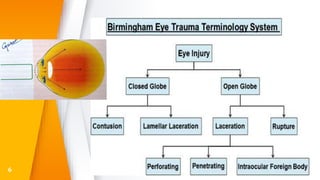
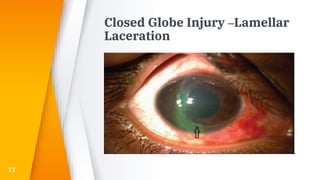
- Open globe injuries which have a full thickness wound of the sclera or cornea.
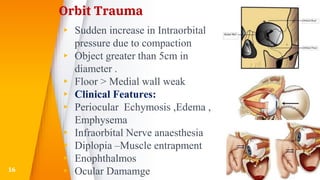
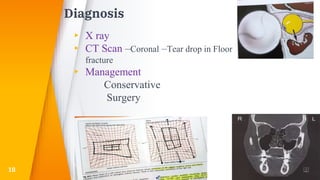
- Orbital fractures from blows to the eye socket, which can cause complications like diplopia.
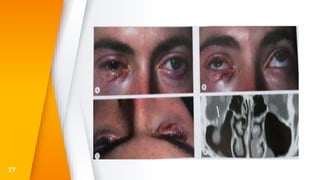
- Eyelid trauma such as periocular hematomas and lacerations, which need to be evaluated to rule out injuries to the globe or orbit.
- The importance of a detailed history and prompt evaluation and treatment of ocular injuries is emphasized to prevent vision loss.