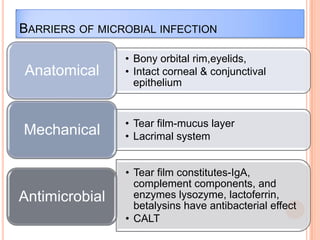
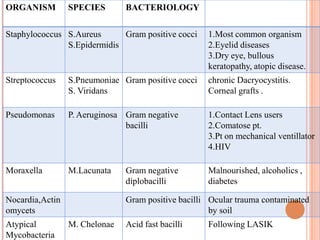
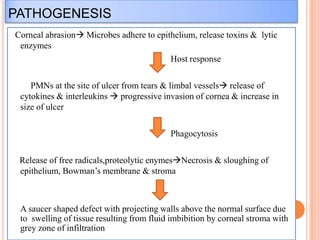
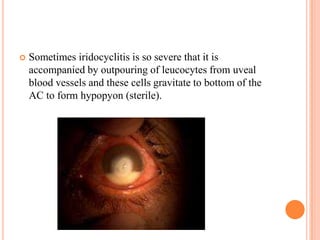
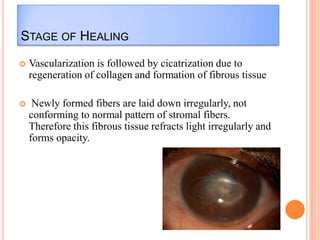
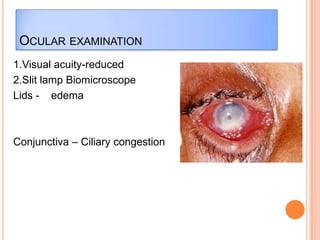
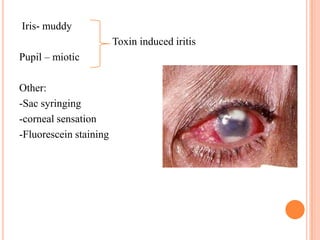
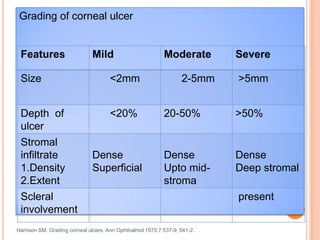
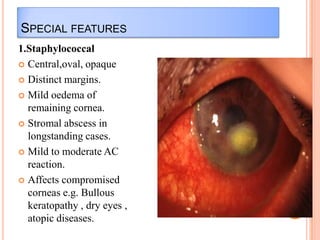
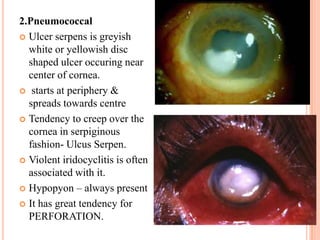
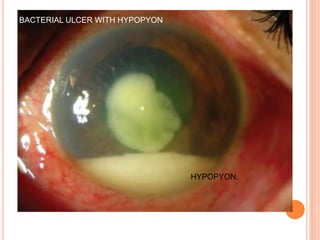
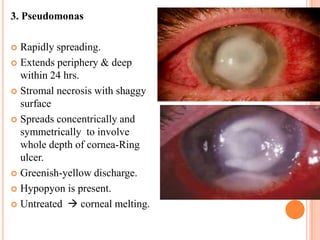
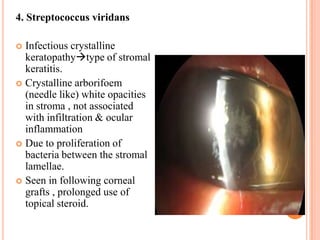
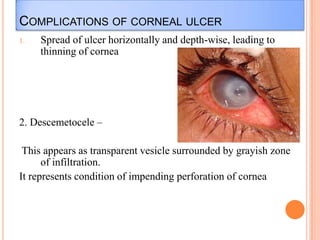
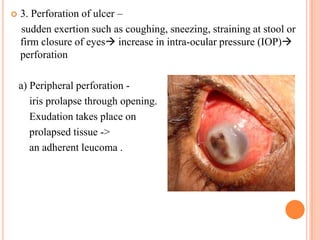
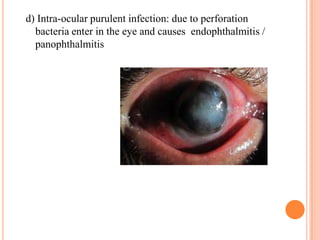
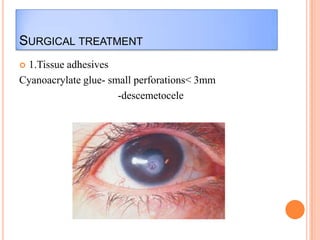
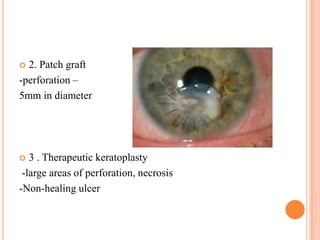
Corneal ulcers occur due to loss of corneal epithelium and inflammation. Bacteria are a common cause and can penetrate breaks in the epithelium. Symptoms include reduced vision, pain, watering and photophobia. Examination reveals the size, depth and borders of the ulcer. Treatment involves topical antibiotics based on smear or culture results along with cycloplegics. Systemic antibiotics may be needed for severe cases. Surgery with tissue adhesives or grafting is used for perforations. Prognosis depends on severity, depth and cause of the ulcer.