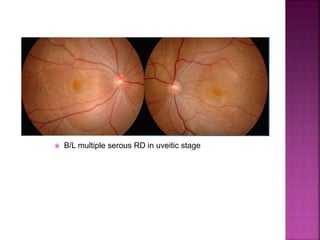
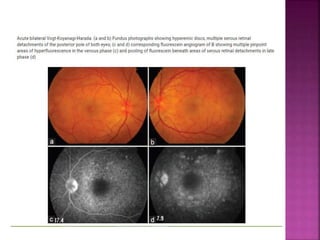
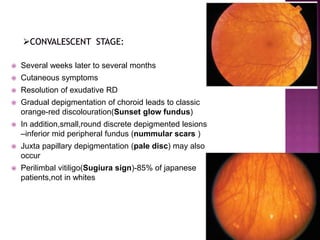
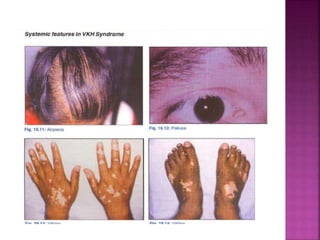
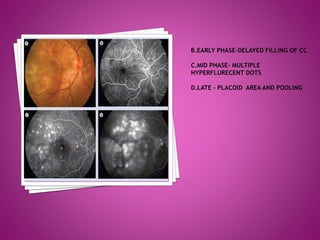
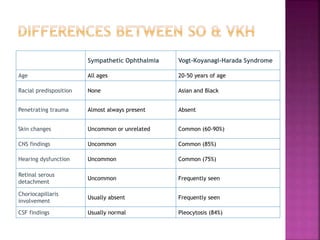
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease is a multisystem autoimmune disorder that commonly affects the eyes, skin, brain and inner ears. It is characterized by granulomatous panuveitis with exudative retinal detachments in the eyes. The disease is most common in Asian and Hispanic populations between 20-50 years of age. The cause is unknown but believed to be a cell-mediated autoimmune reaction against melanocytes. Diagnosis is based on clinical features including retinal detachments, neurological signs, skin changes and investigations such as fluorescein angiography and lumbar puncture. Treatment involves high-dose corticosteroids with immunosuppressants to prevent recurrences




























![ Immunosupprasants
Cyclosporine, 5 mg/kg/ day
Tacrolimus 0.1–0.15 mg /kg /day
Cytotoxic Agents[10,42]
Azathioprine, 1–2.5 mg/kg/ day
Mycophenylate mofetil, 1-3 g/day
Cyclophosphamide 1–2 mg/ kg/ day
Chlorambucil 0.1 mg/kg/day with adjustment of dose every 3
weeks up to a maximum of 18 mg/day](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vkh-180111061432/85/Vkh-36-320.jpg)


