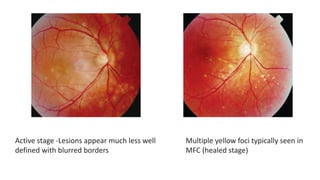
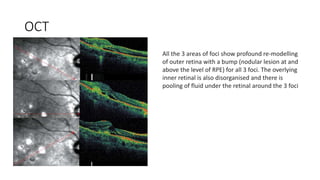
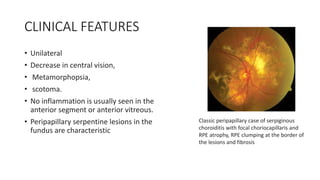
Multifocal choroiditis is a recurrent inflammatory eye condition characterized by small, randomly distributed chorioretinal scars that predominantly affects young to middle-aged females. It can cause decreased vision, photopsia, and scotomas. While fluorescein angiography may not detect active lesions, indocyanine green angiography is highly sensitive for finding new areas of choriocapillaris nonperfusion. Treatment typically involves corticosteroids, though recurrence is common.