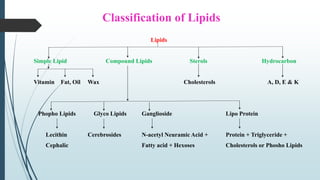
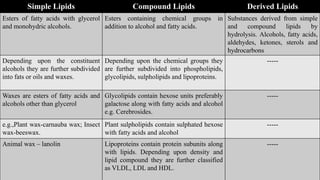
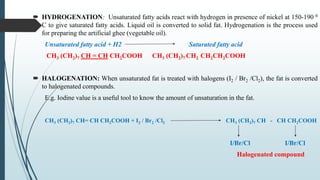
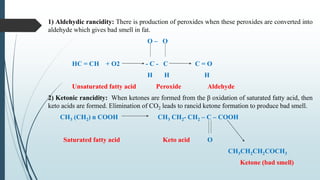
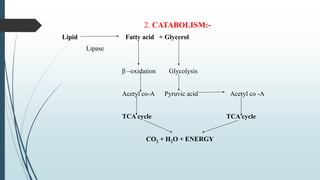
The document provides information about lipids including their definition, functions, classification, properties and metabolism. It defines lipids as compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents and on hydrolysis yield fatty acids. Lipids include simple lipids like fats and oils, compound lipids like phospholipids and glycolipids, and derived lipids like fatty acids. They serve important functions like energy storage, structure of cell membranes, and as signaling molecules. The document also discusses lipid hydrolysis, saponification, hydrogenation and rancidity.