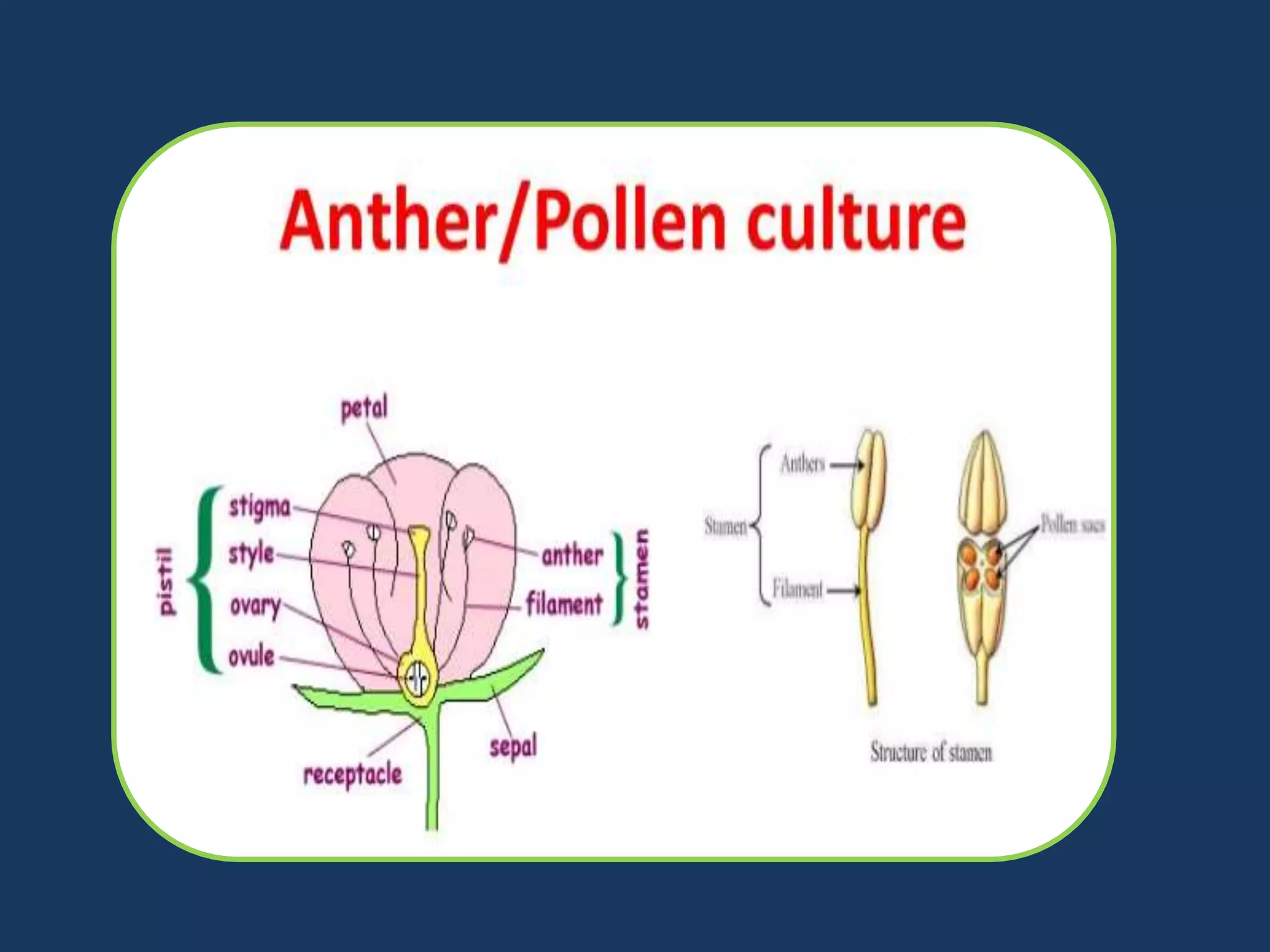
Anther culture is an in vitro technique used to produce haploid plants from male gamete cells. Haploid cells contain only one set of chromosomes. The first report of anther culture was in the 1970s, while the first natural occurrence of haploids was observed in 1922 in Datura plants. Anthers containing microspores are cultured on nutrient media supplemented with hormones and sugars. Depending on the species, haploid plants or callus can regenerate from the cultured anthers within 3-8 weeks. Haploid plants are useful for breeding programs as they can be doubled to generate fertile, homozygous plants in one generation.