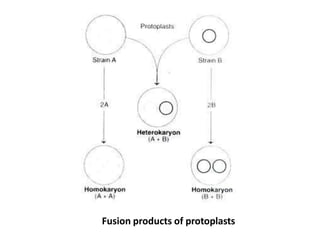
Somatic hybridization involves fusing isolated plant cell protoplasts that have had their cell walls removed. This allows for fusion between species that could not otherwise breed. The key steps are:
1) Fusing protoplasts from two plant species using techniques like PEG or electrofusion.
2) Selecting for hybrid cells that contain genetic material from both parents.
3) Identifying hybrid plants regenerated from the fused cells through chromosome counting and molecular markers.
Somatic hybridization can introduce useful traits like disease resistance and stress tolerance to crops. However, regenerated plants often show genetic instability and not all hybrid combinations are viable.