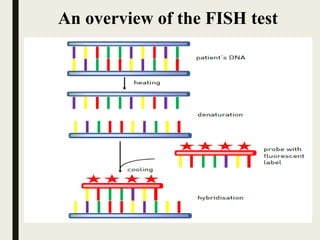
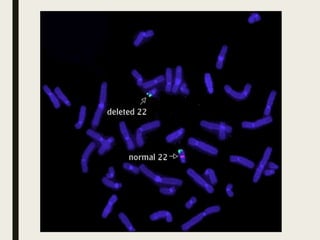
The document discusses the fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) technique, which is used to detect and localize specific DNA sequences on chromosomes using fluorescent probes. It outlines the process of FISH, including probe selection, labeling, tissue fixation, hybridization, and detection, as well as its applications and limitations in genetics and medical diagnostics. Additionally, it introduces variations of the FISH technique, such as fiber FISH, and highlights its advantages for genetic analysis.