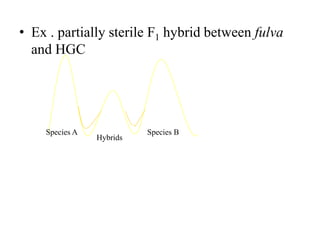
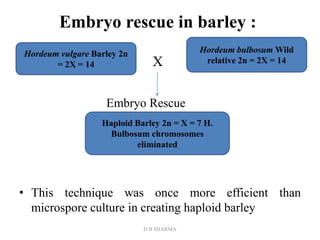
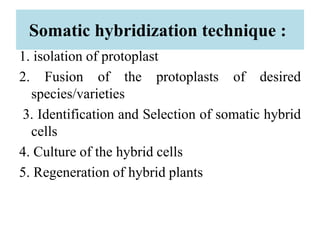
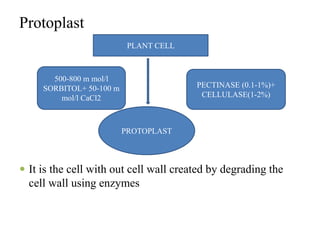
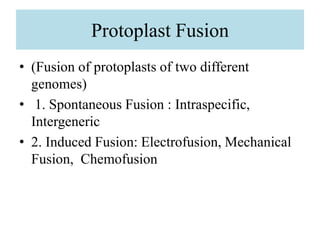
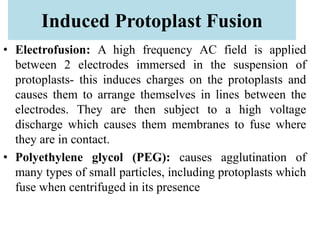
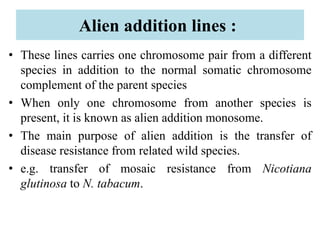
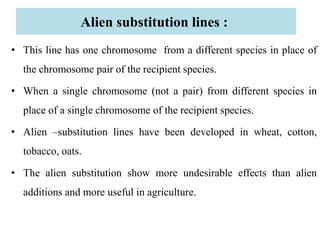
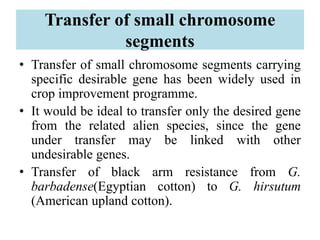
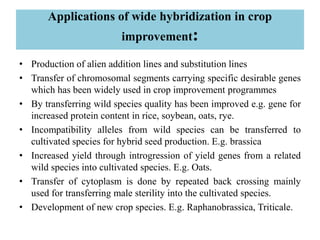
This document provides information on genetic incongruity and techniques for overcoming barriers in distant plant hybridization. It defines genetic incongruity as evolutionary divergence between two taxa that results in gene incompatibility. Techniques discussed include embryo rescue, somatic hybridization, alien addition/substitution lines, and transferring small chromosome segments. Applications in crop improvement involve transferring traits like disease resistance, yield, and hybrid seed production from wild species. Challenges include sterility, incompatible crosses, and linkage of undesirable genes.