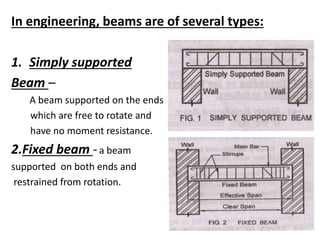
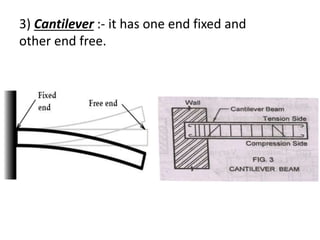
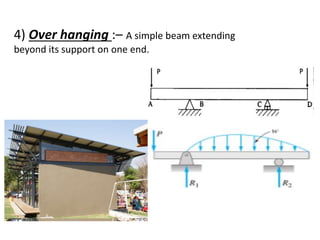
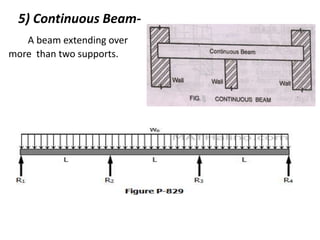
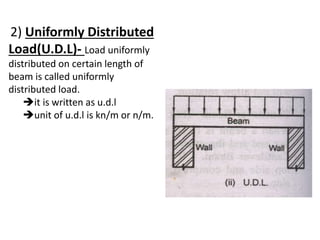
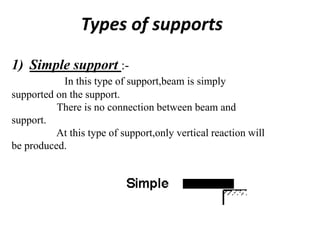
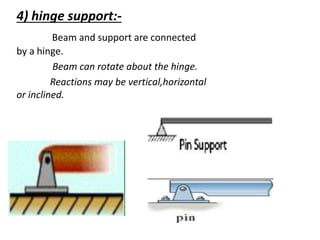
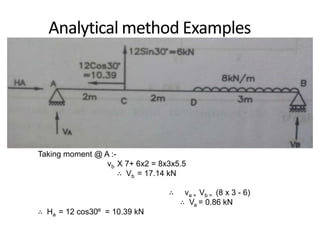
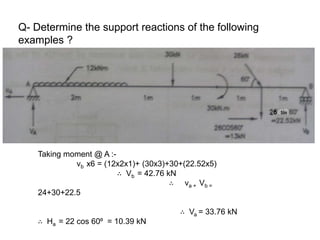
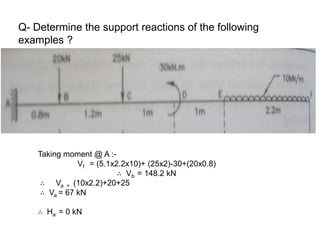
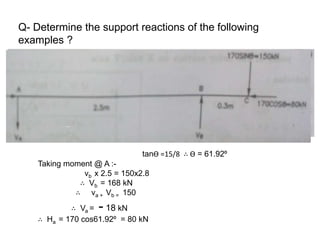
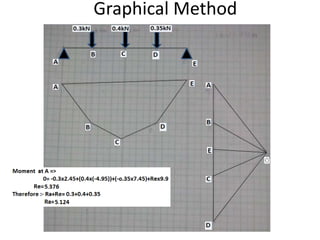
The document discusses the mechanics of solids, particularly focusing on support reactions relevant to beams in structural engineering. It covers various types of beams, loads, and supports, detailing how they interact and the methods available for calculating support reactions. The introduction highlights the importance of understanding these concepts for effective building design and includes examples and analytical methods for determining support reactions.