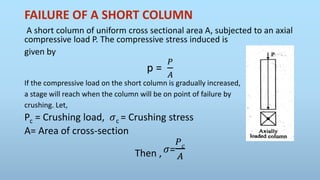
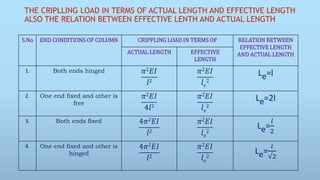
This presentation summarizes key aspects of columns for engineering. It defines a column as a structural member subjected to axial compression. It classifies columns as short, medium, or long based on their slenderness ratio. It describes the failure of columns by crushing (for short columns) or buckling (for long columns). Euler's theory of buckling is summarized, which models buckling based on a column's effective length, modulus of elasticity, and moment of inertia. Different effective lengths are defined for varying end conditions. Finally, Rankine's empirical formula is presented as applicable to both short and long columns.