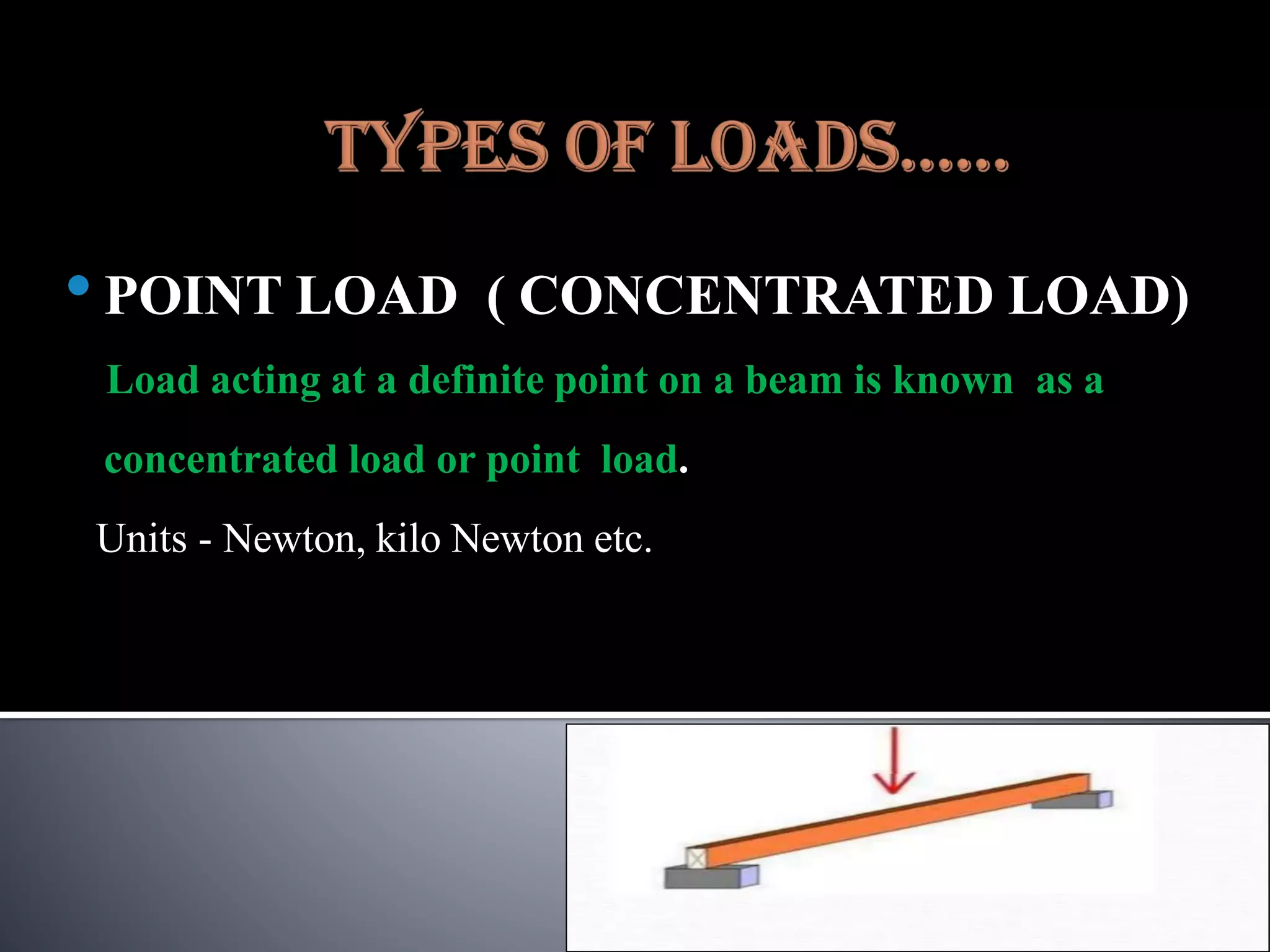
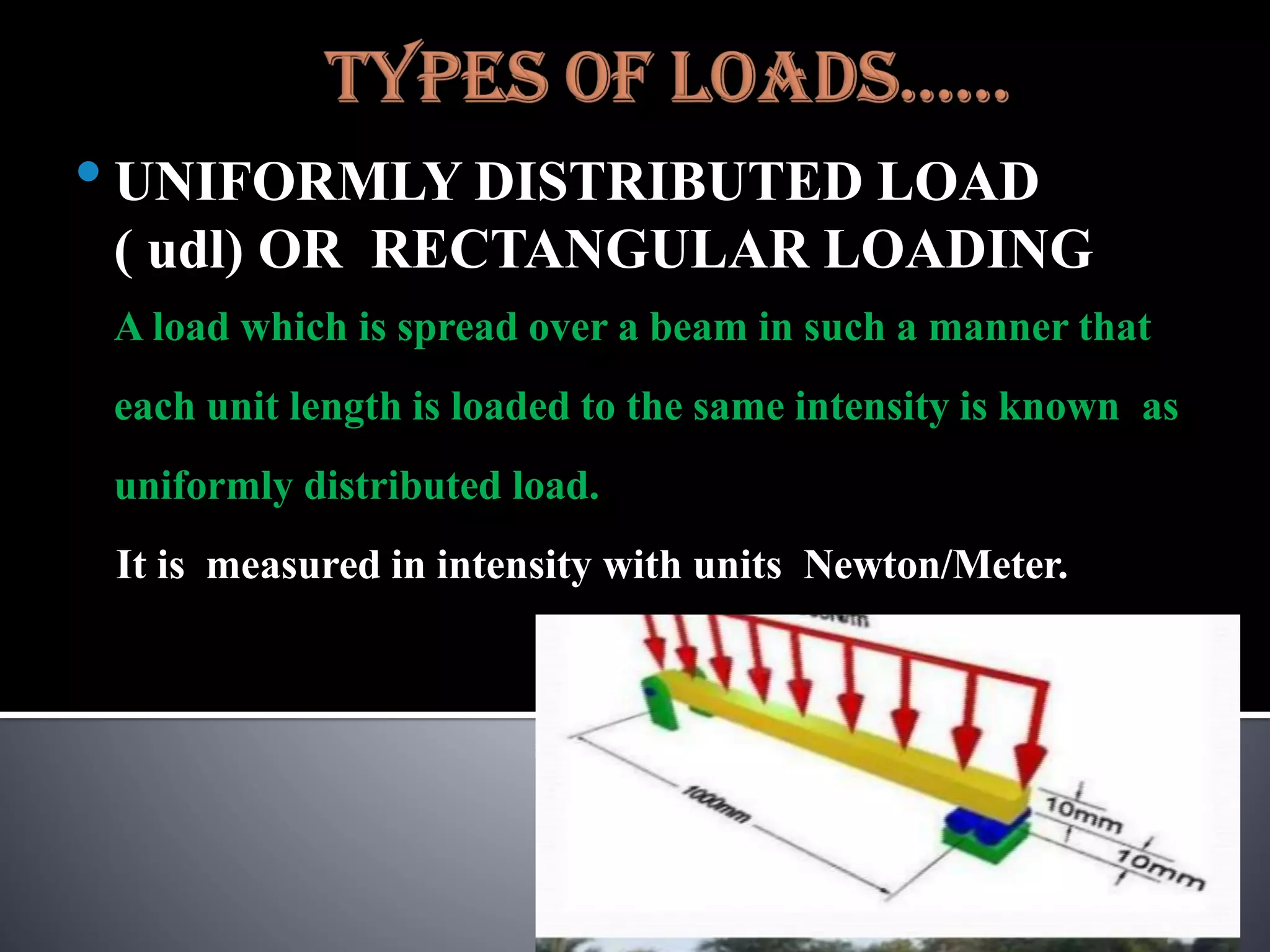
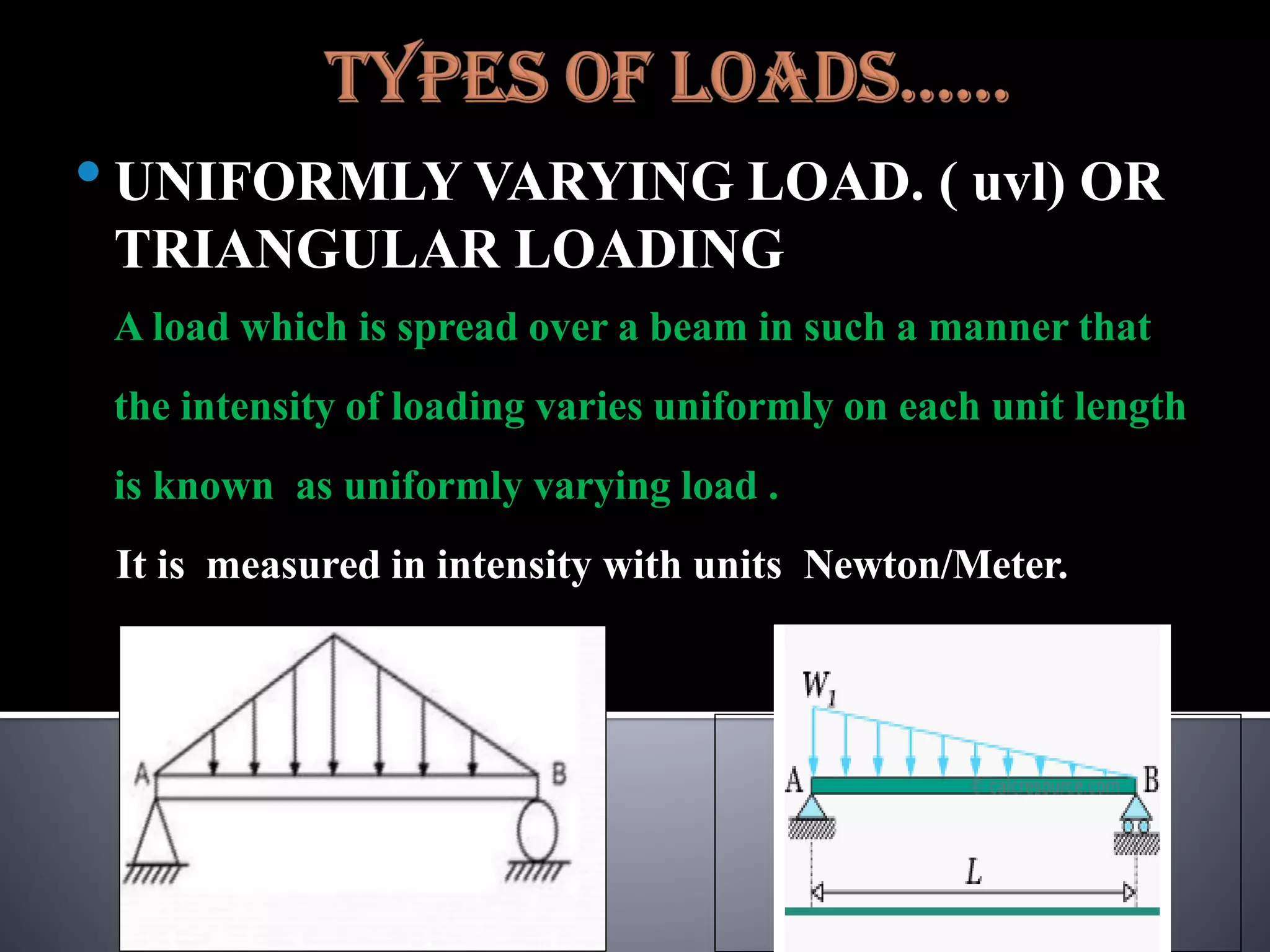
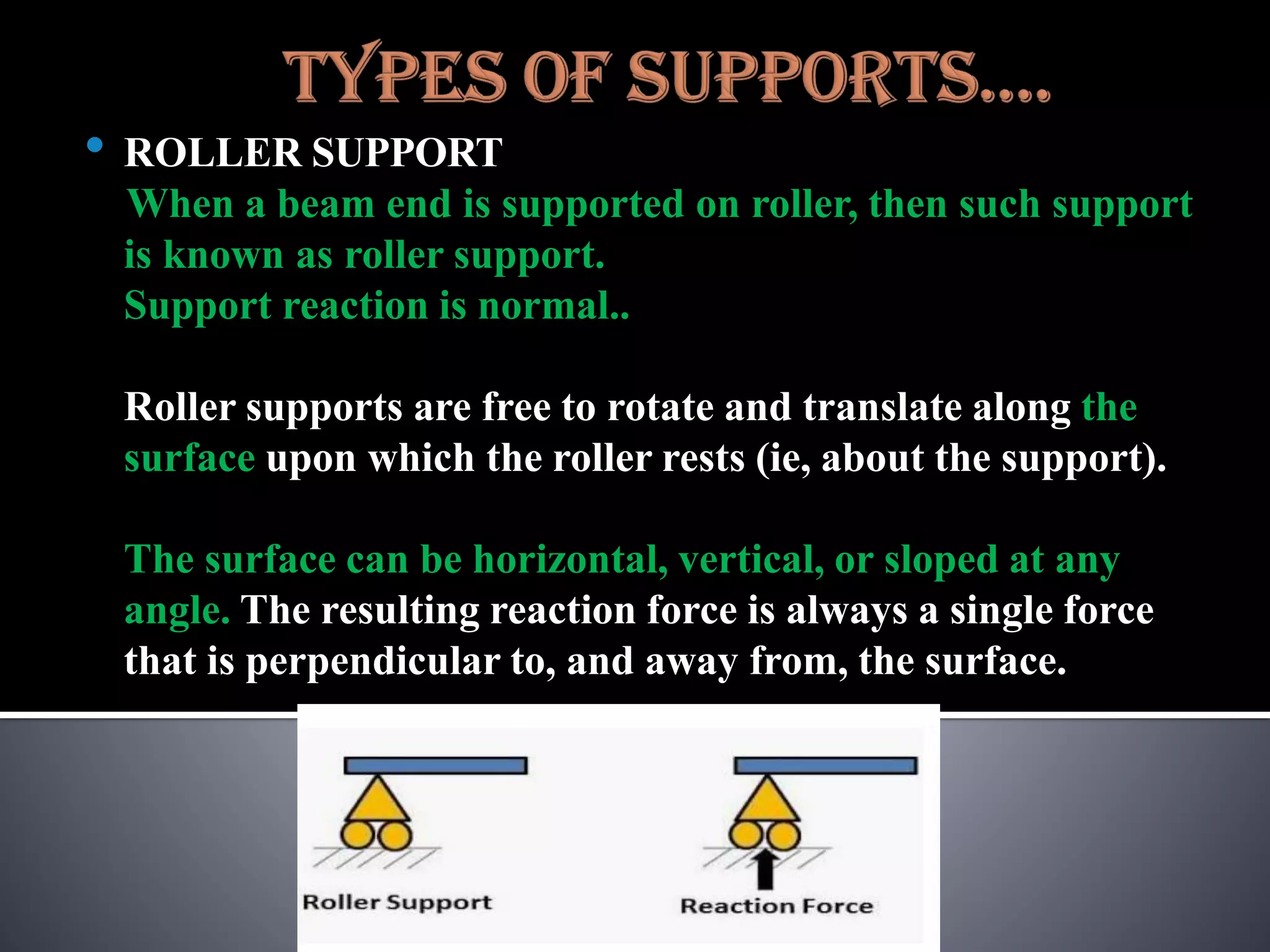
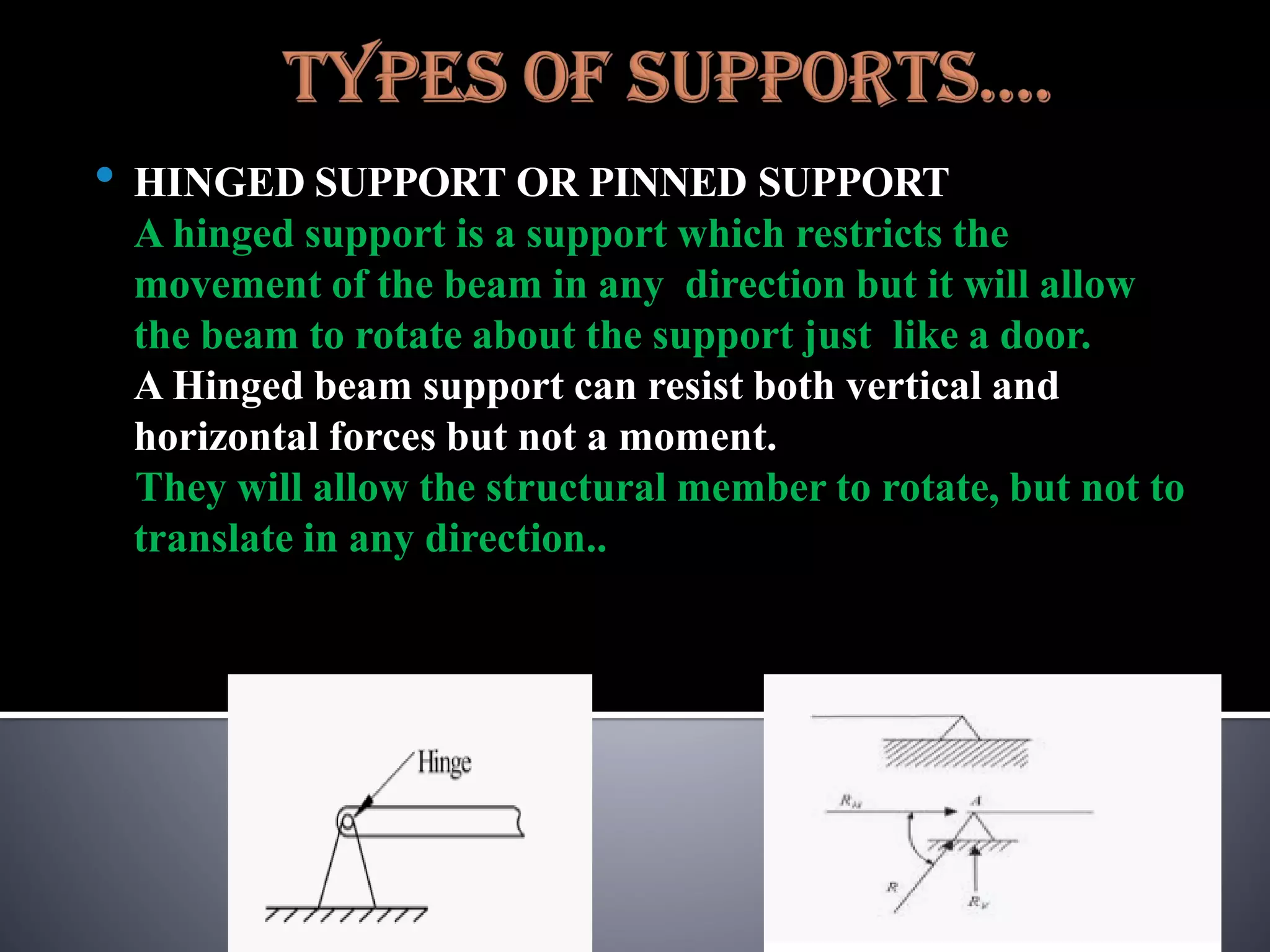
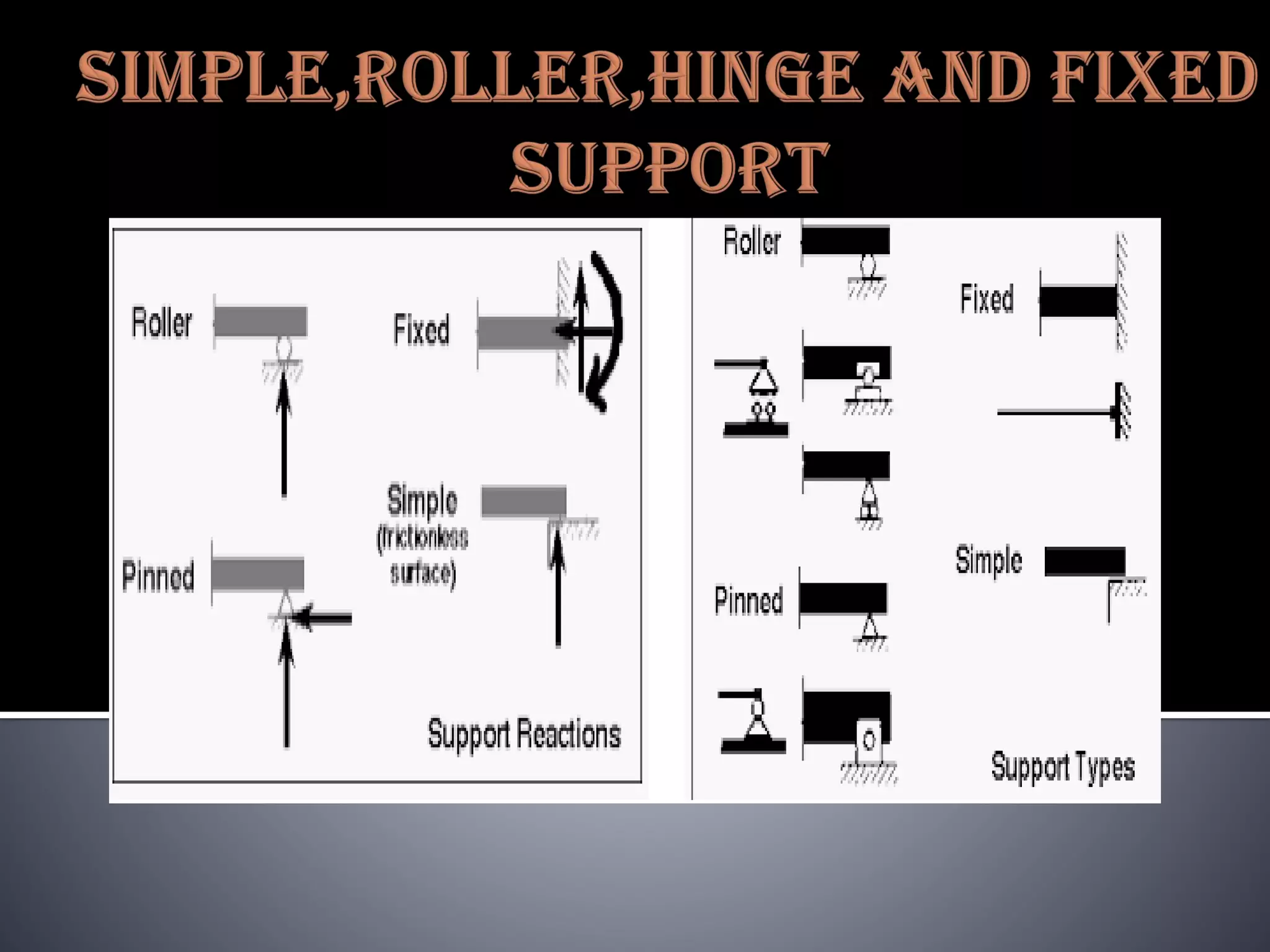
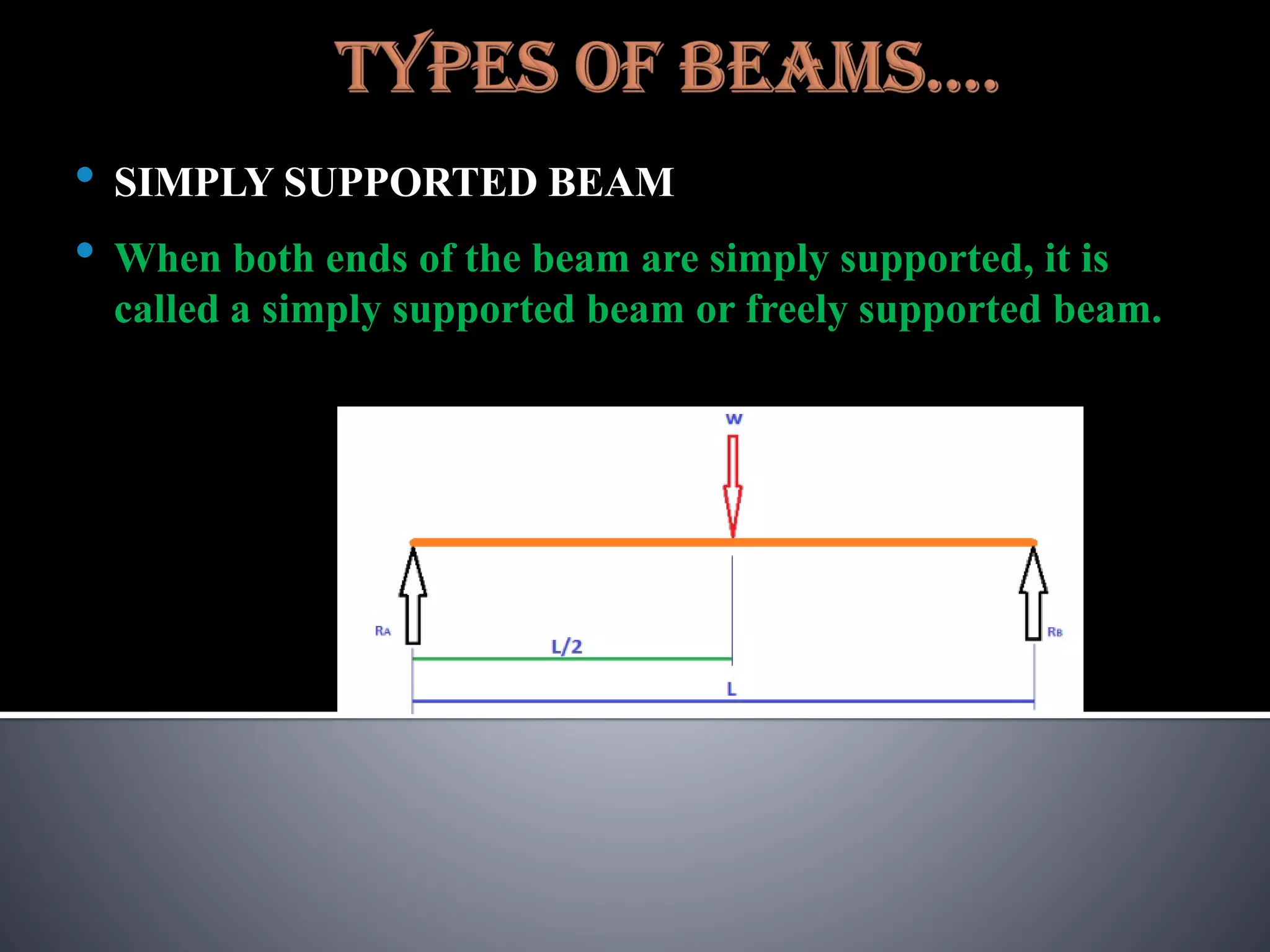
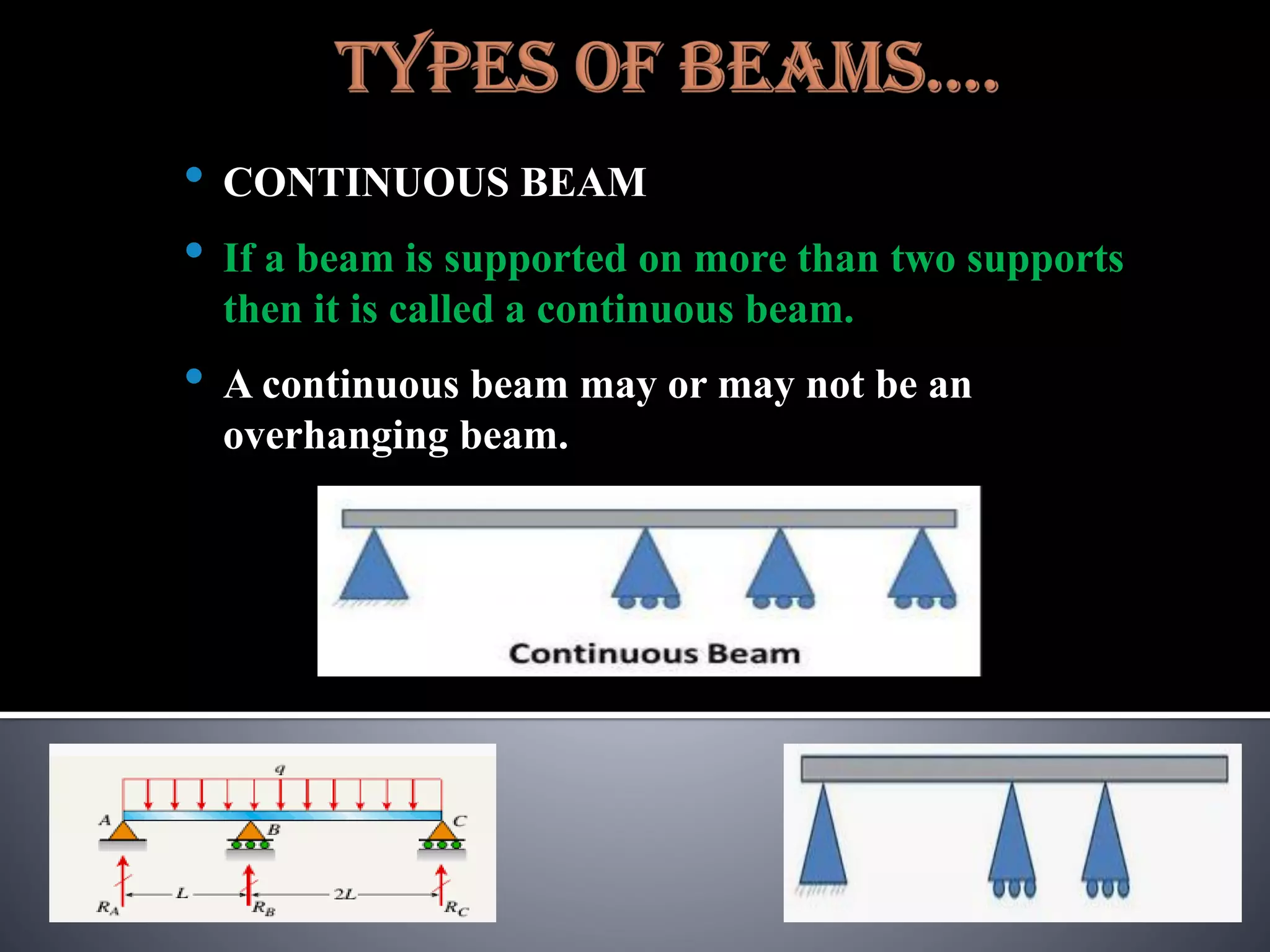
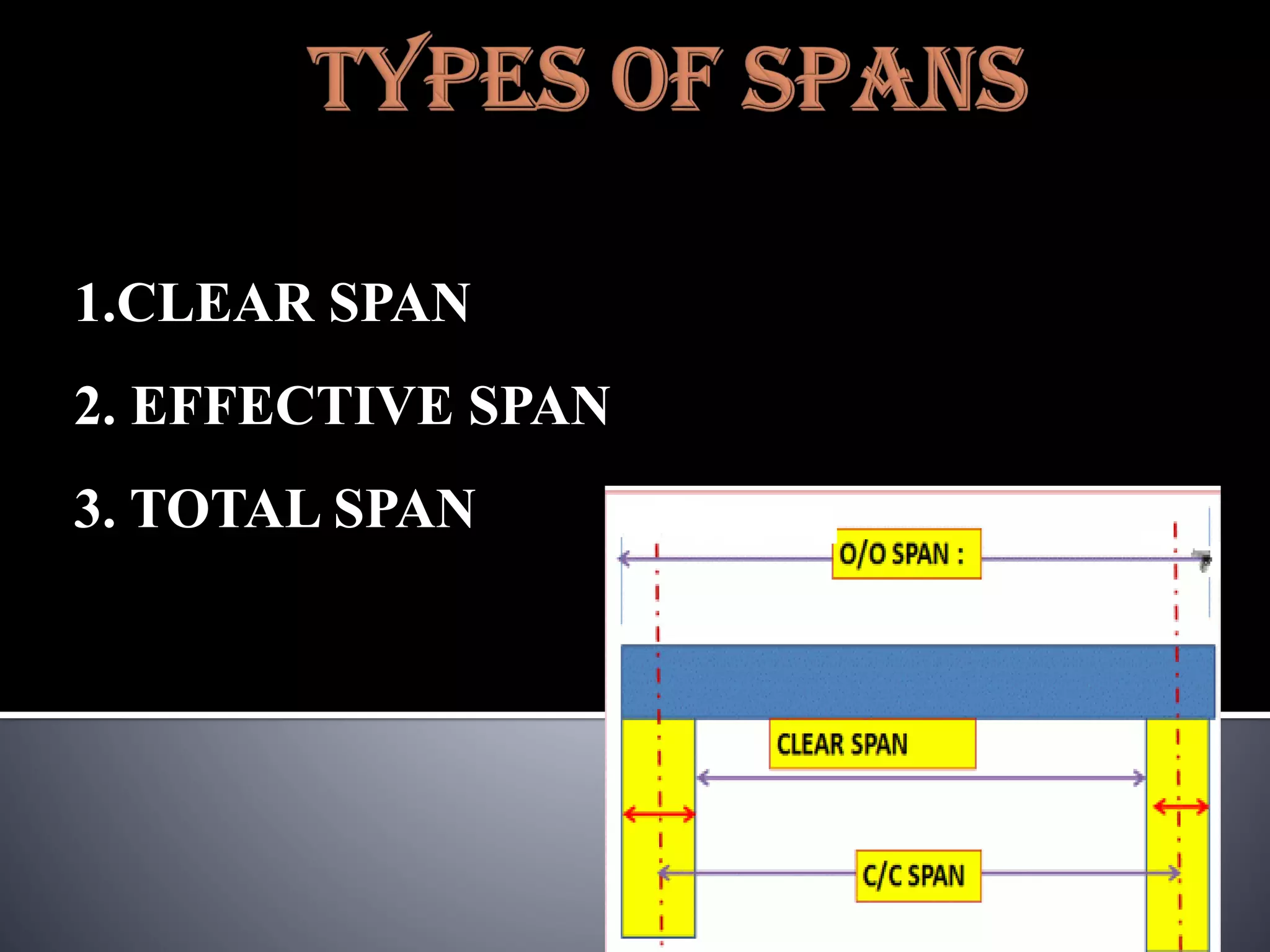
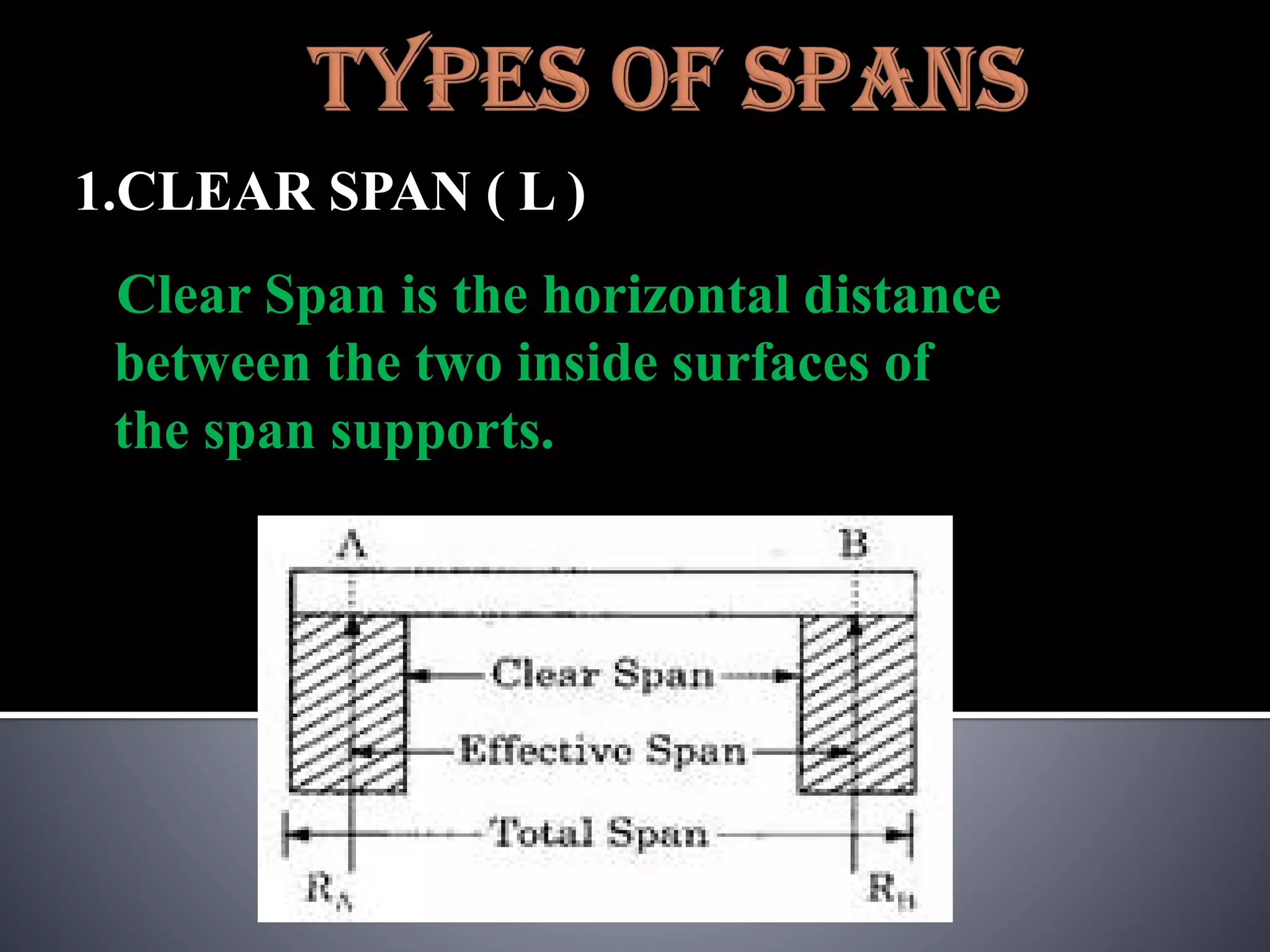
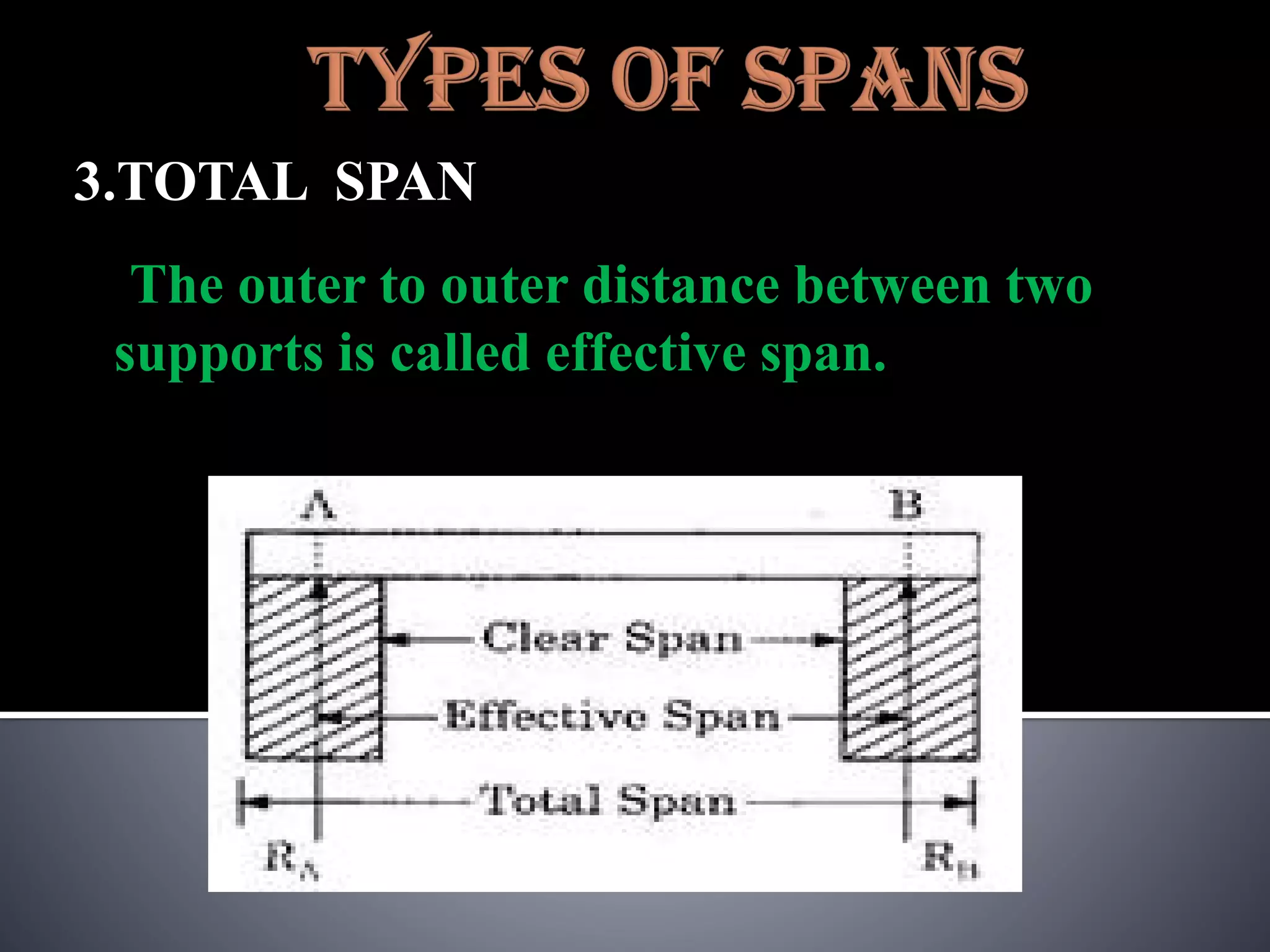
The document discusses various types of loads, supports, beams, and spans that are commonly analyzed in structural engineering. It defines point loads, uniformly distributed loads, uniformly varying loads, and rolling loads. It also describes simple supports, roller supports, hinged supports, and fixed supports. The types of beams covered are simply supported beams, cantilever beams, fixed beams, overhanging beams, continuous beams, and beams with one end hinged and the other end roller supported. Finally, it distinguishes between clear span, effective span, and total span.