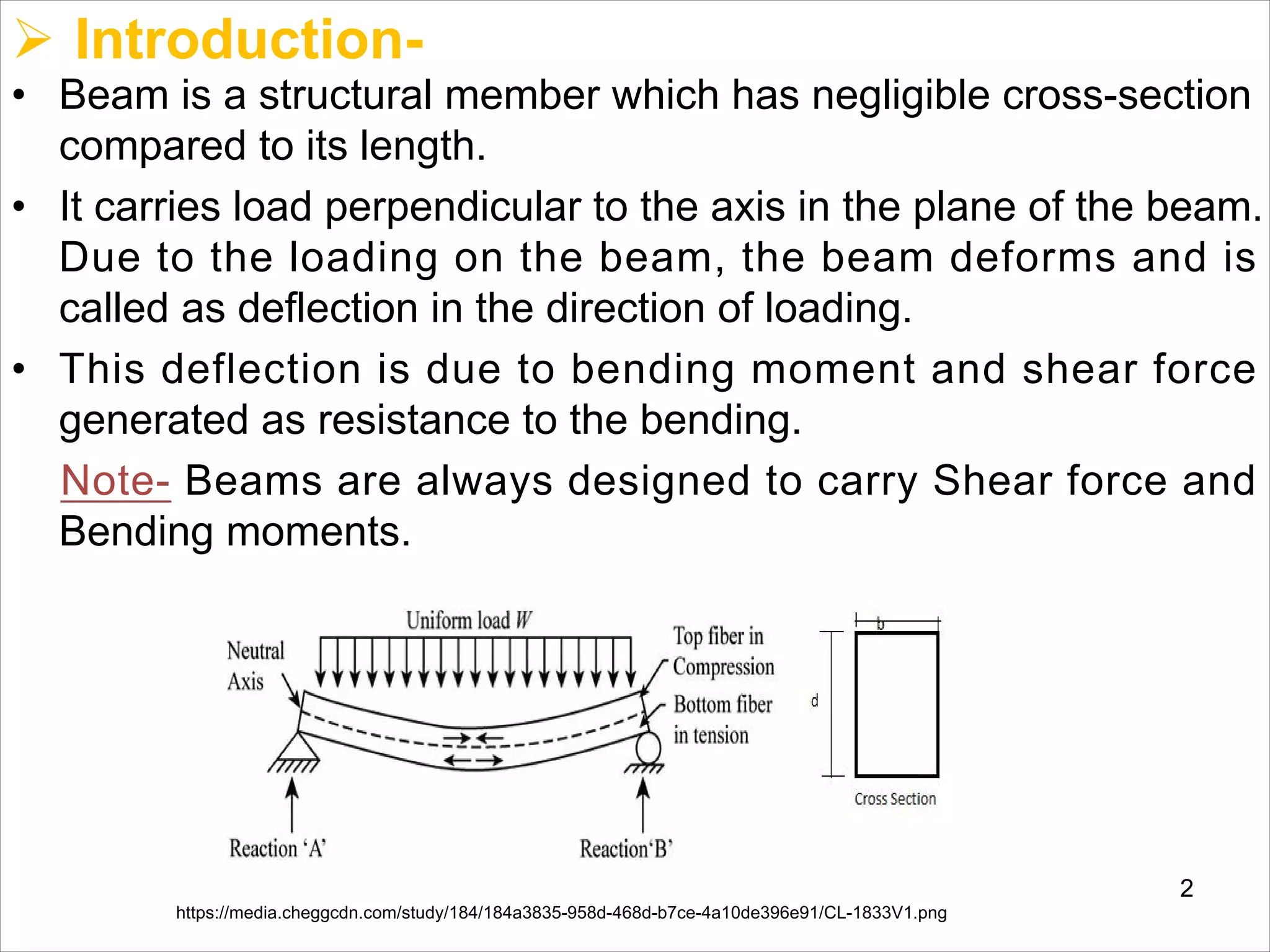
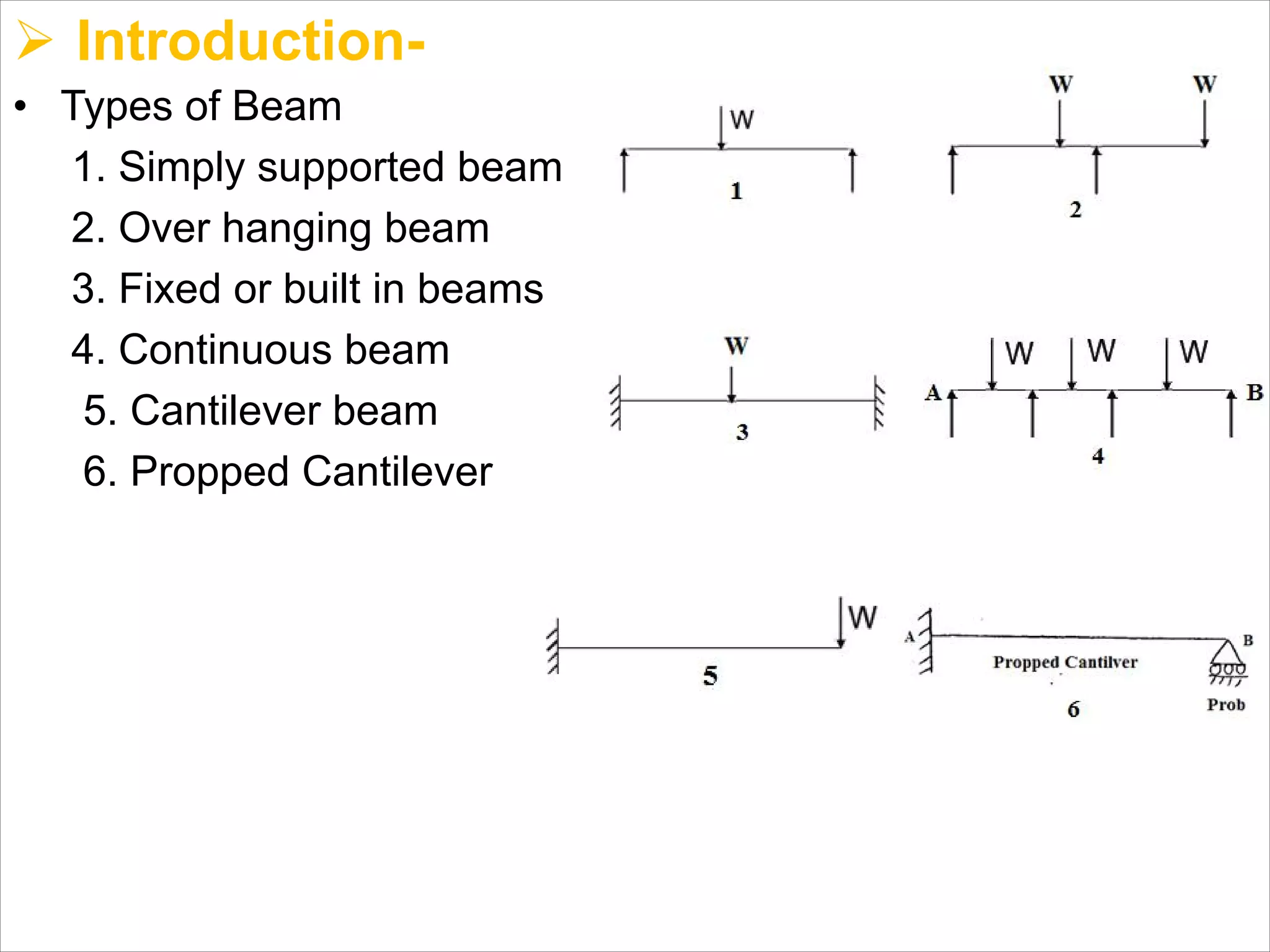
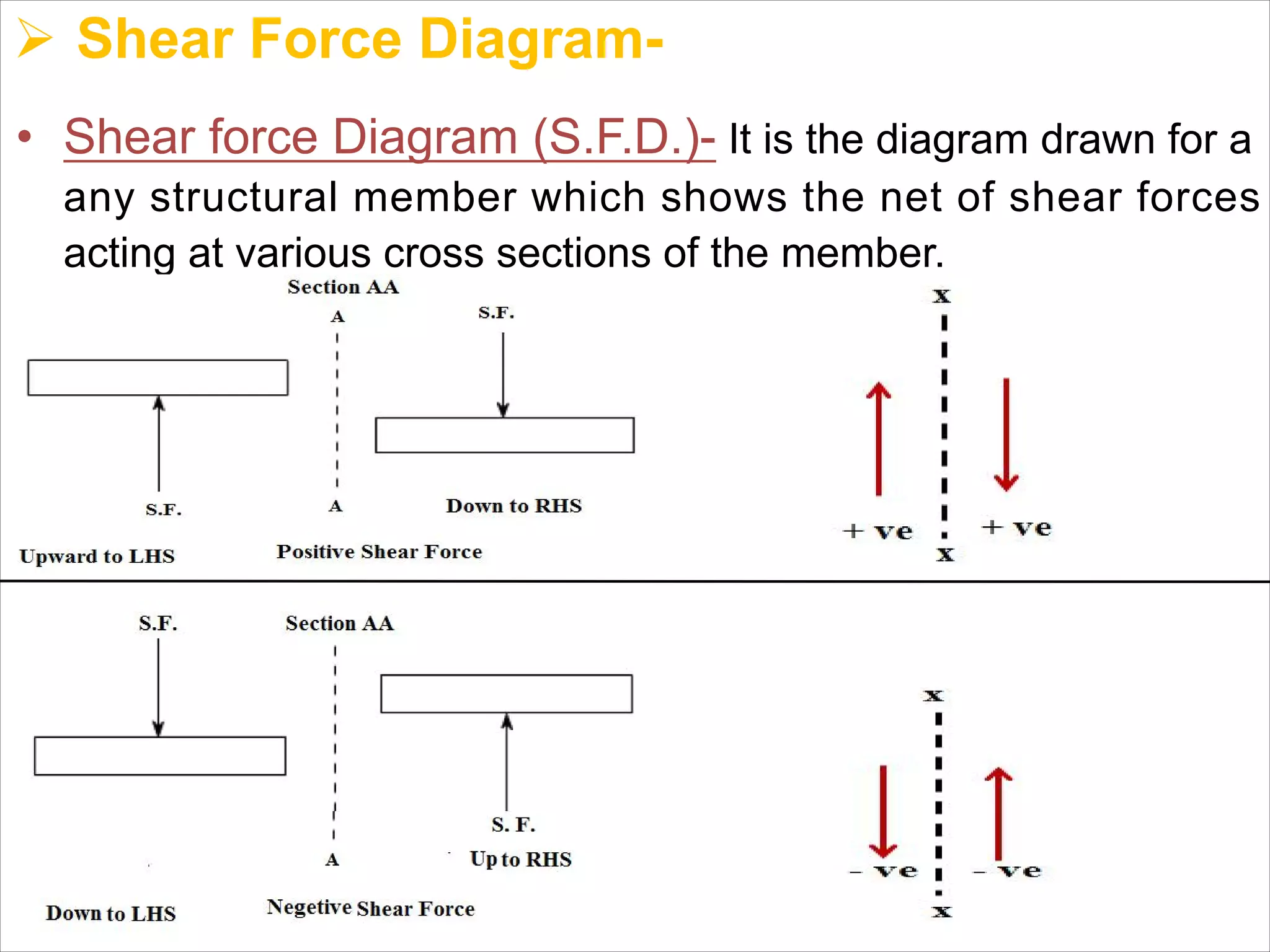
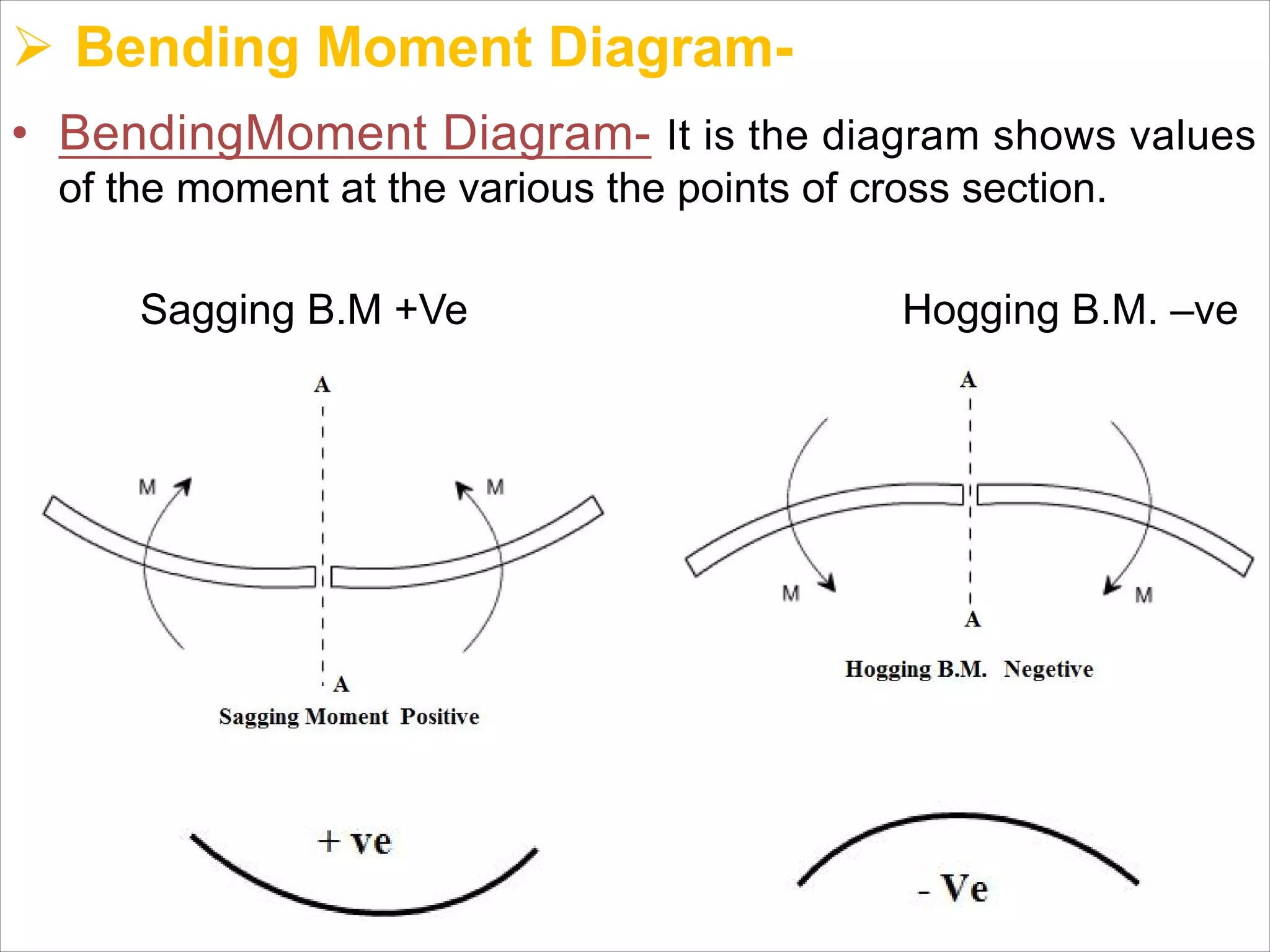
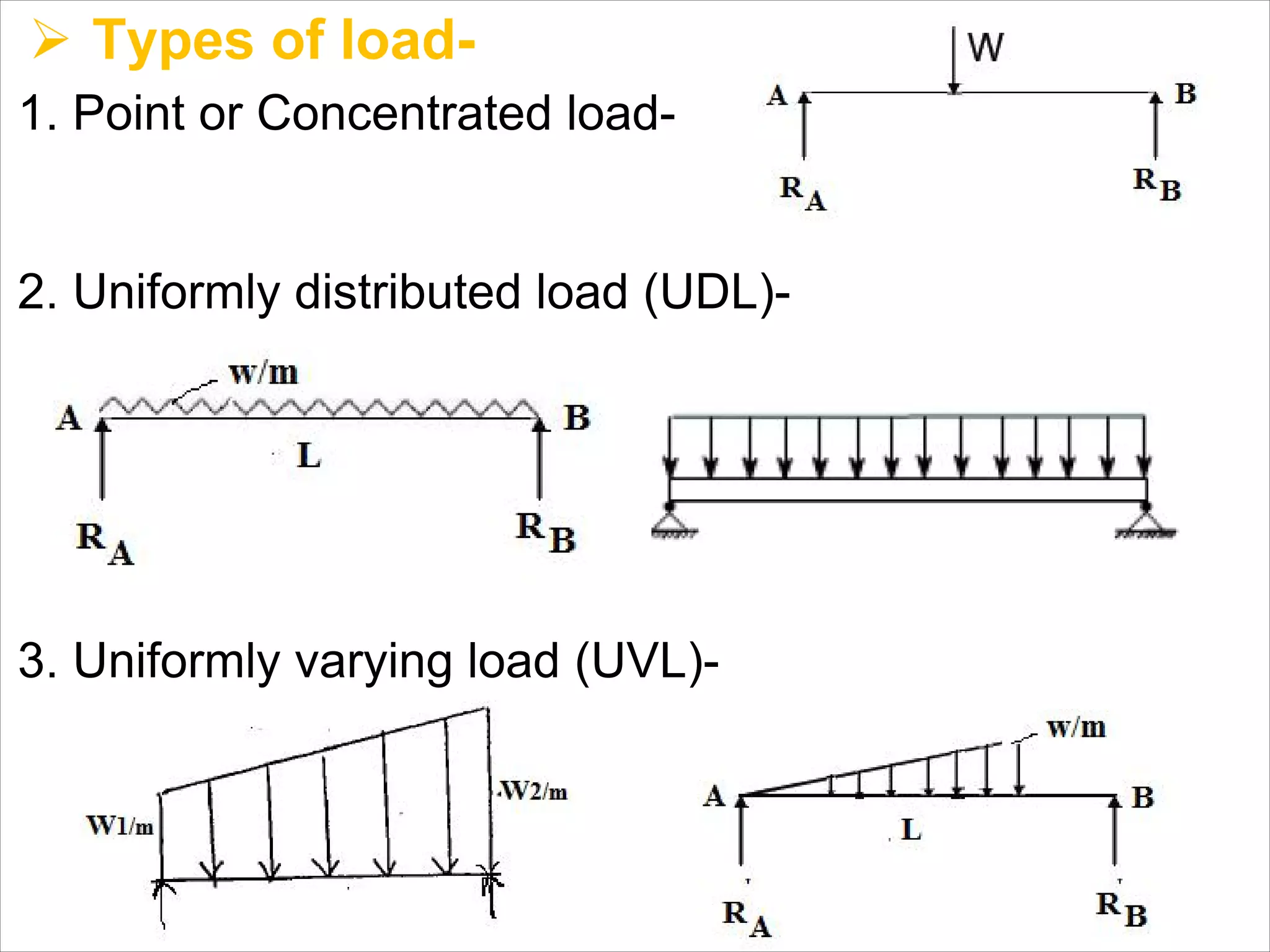
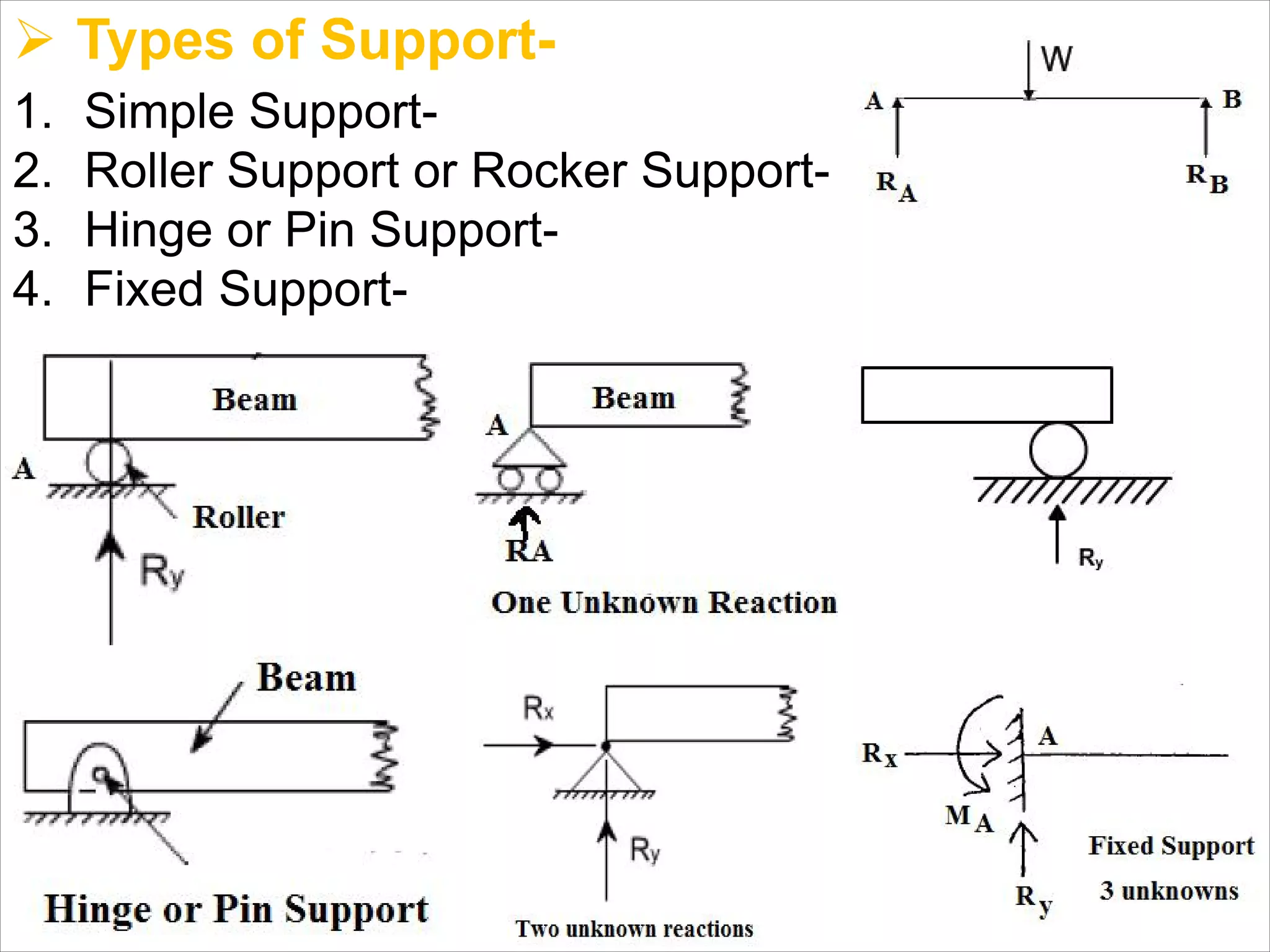
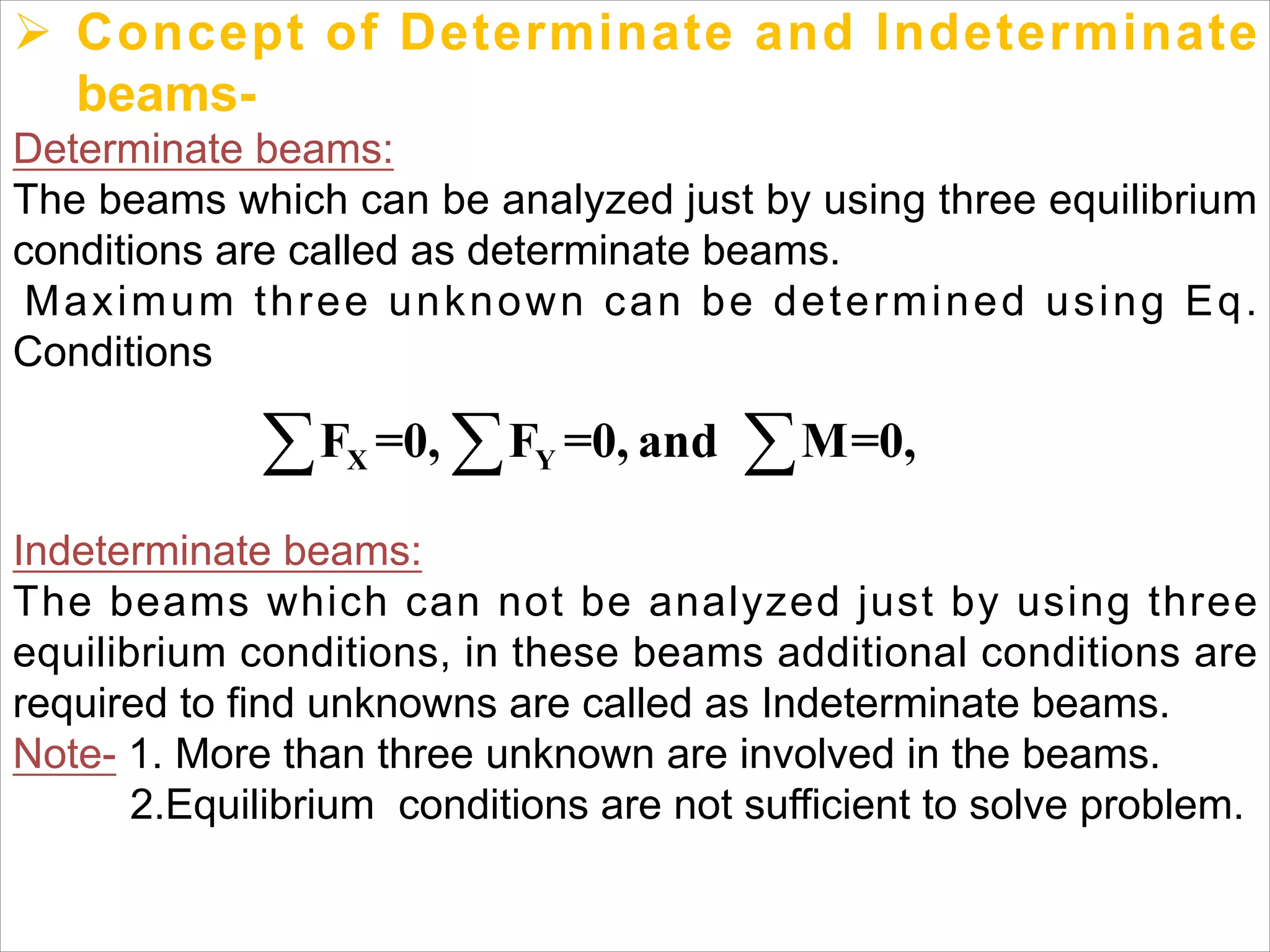
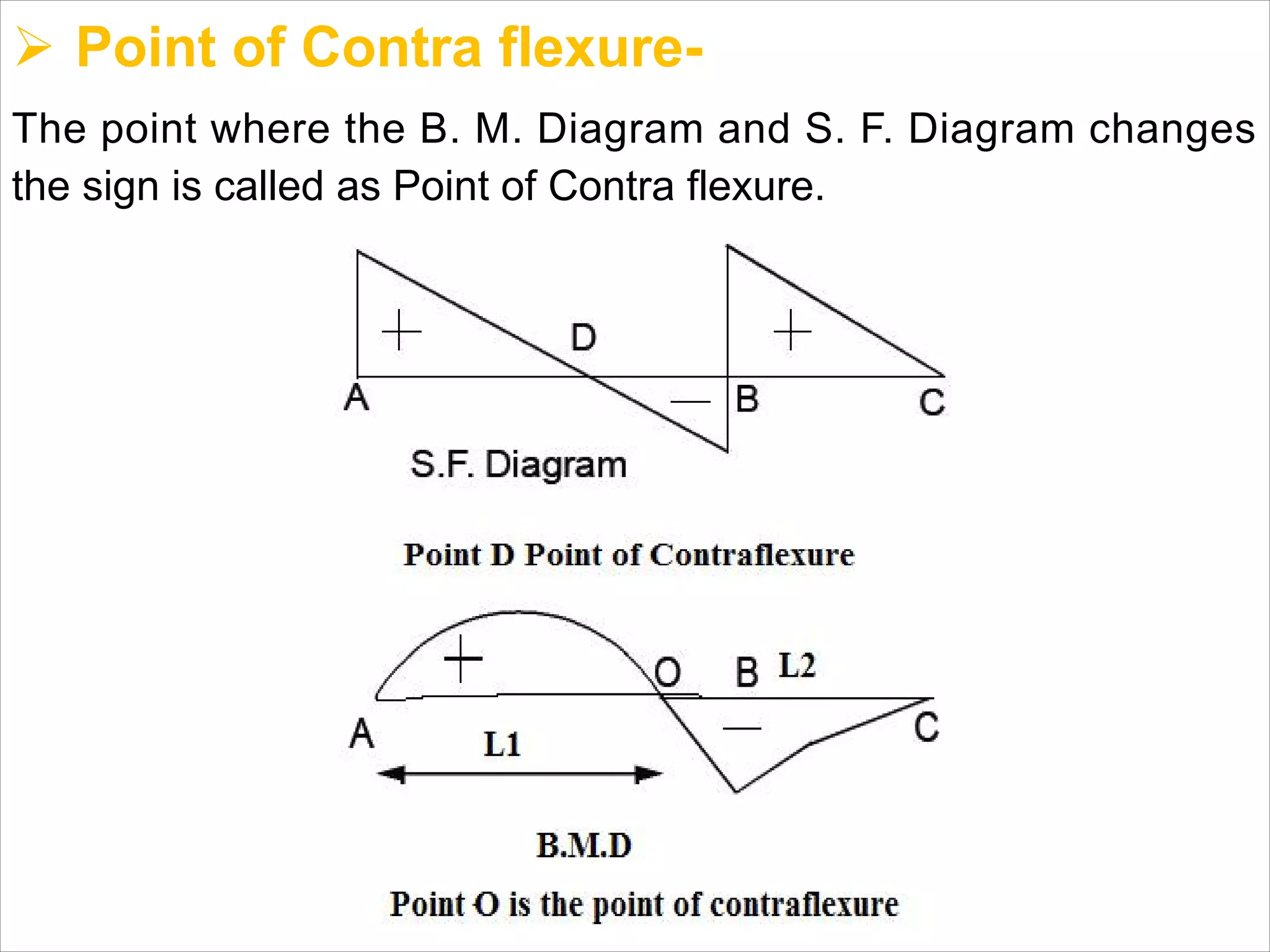
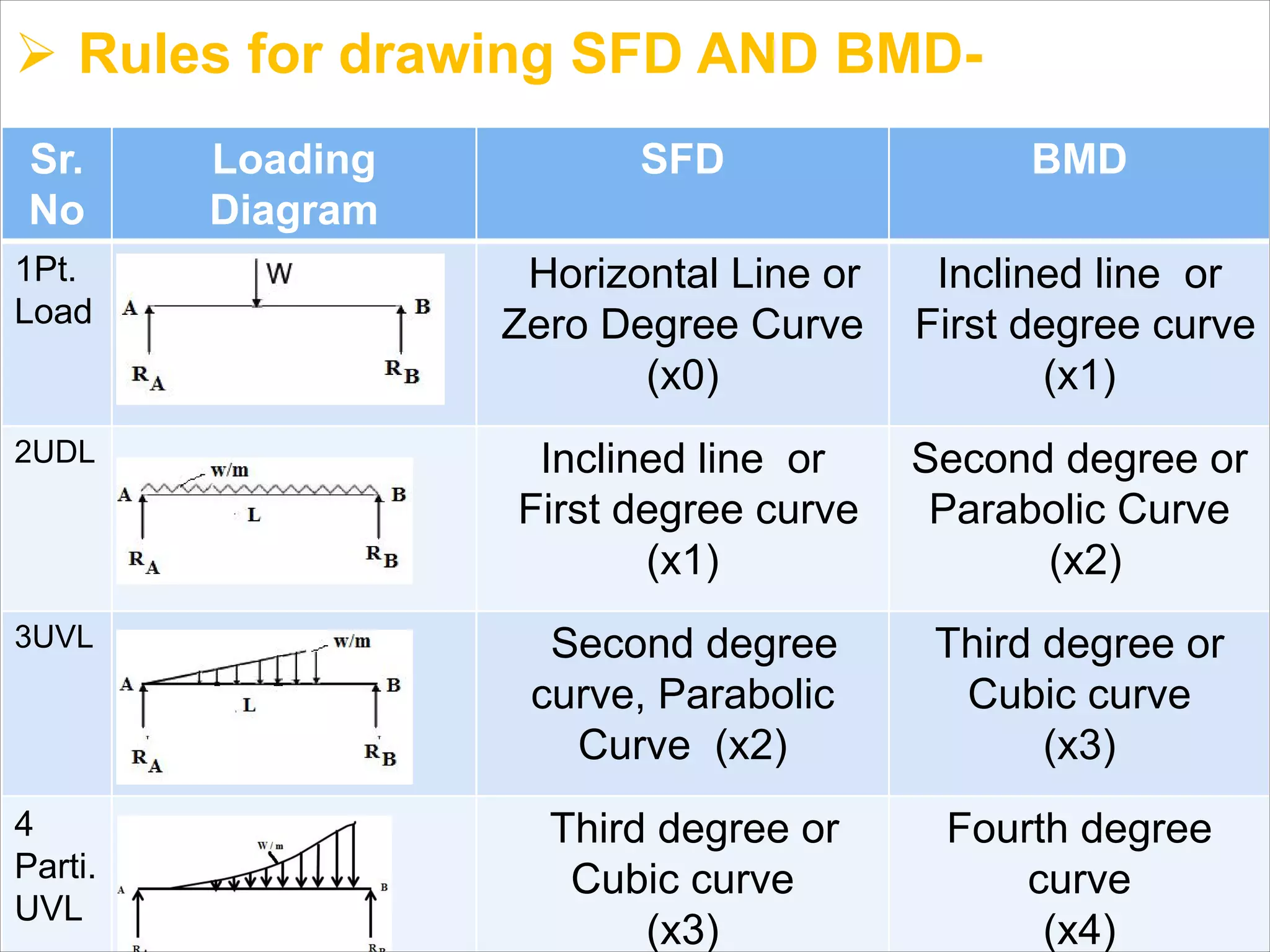
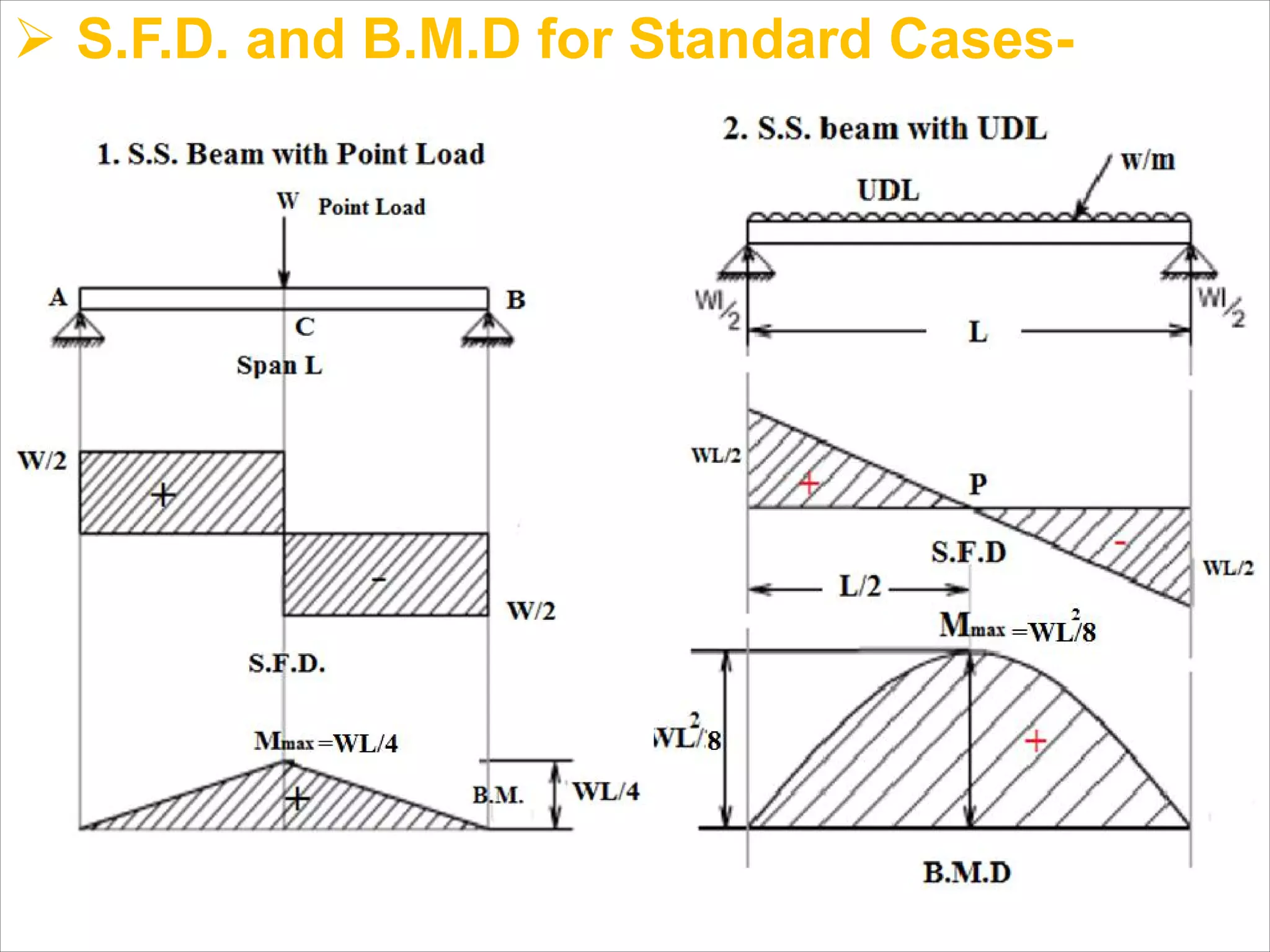
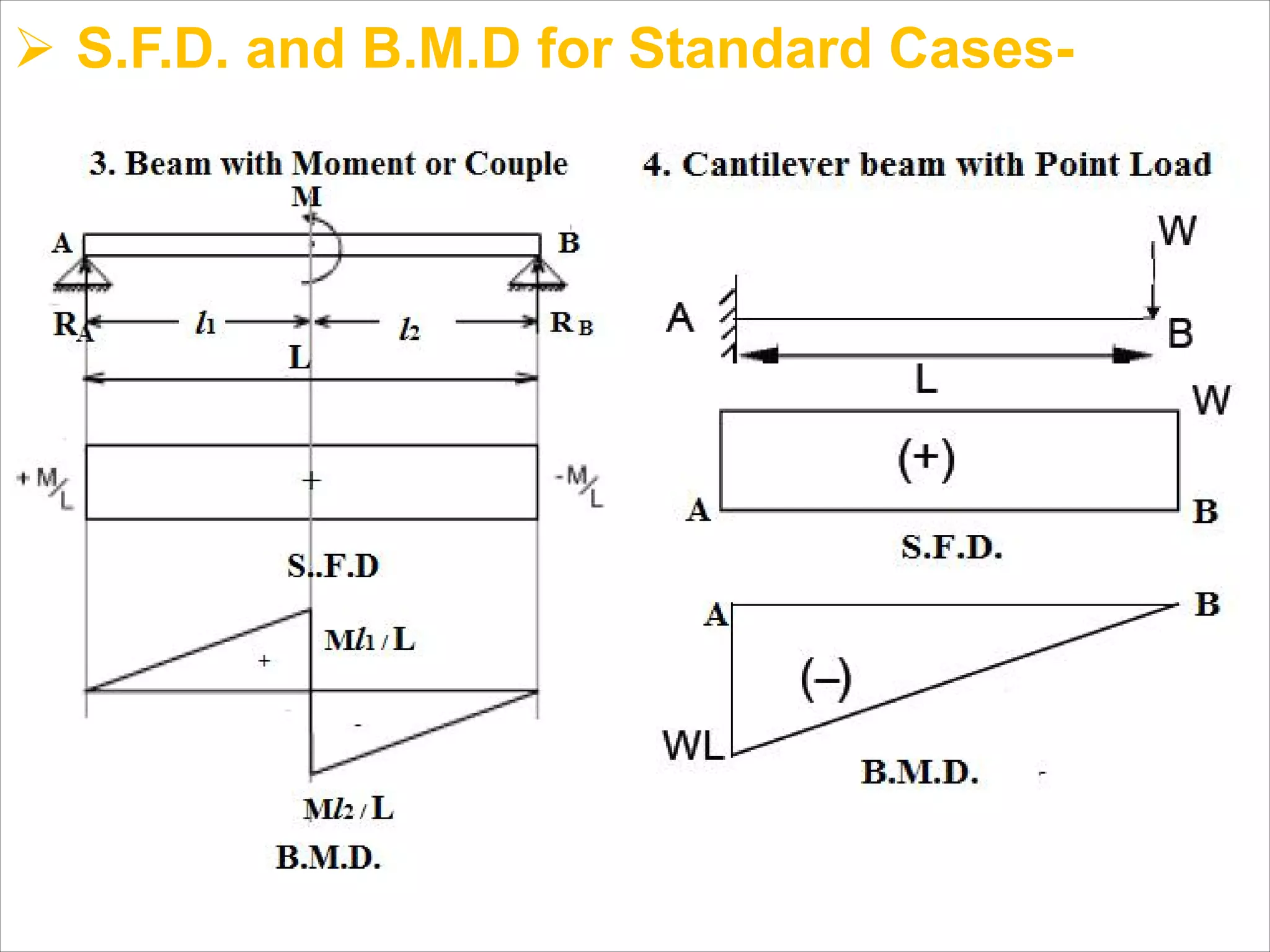
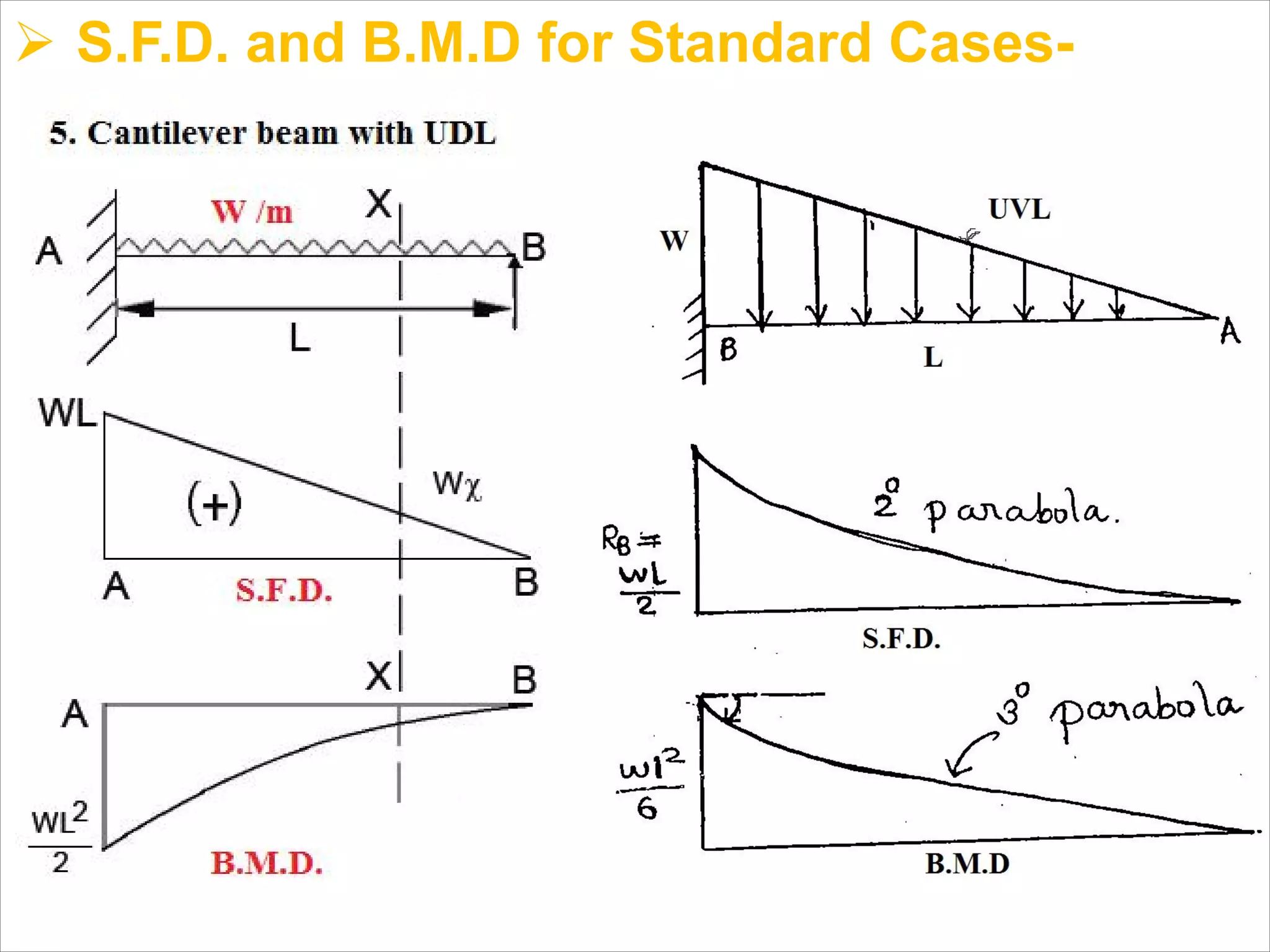
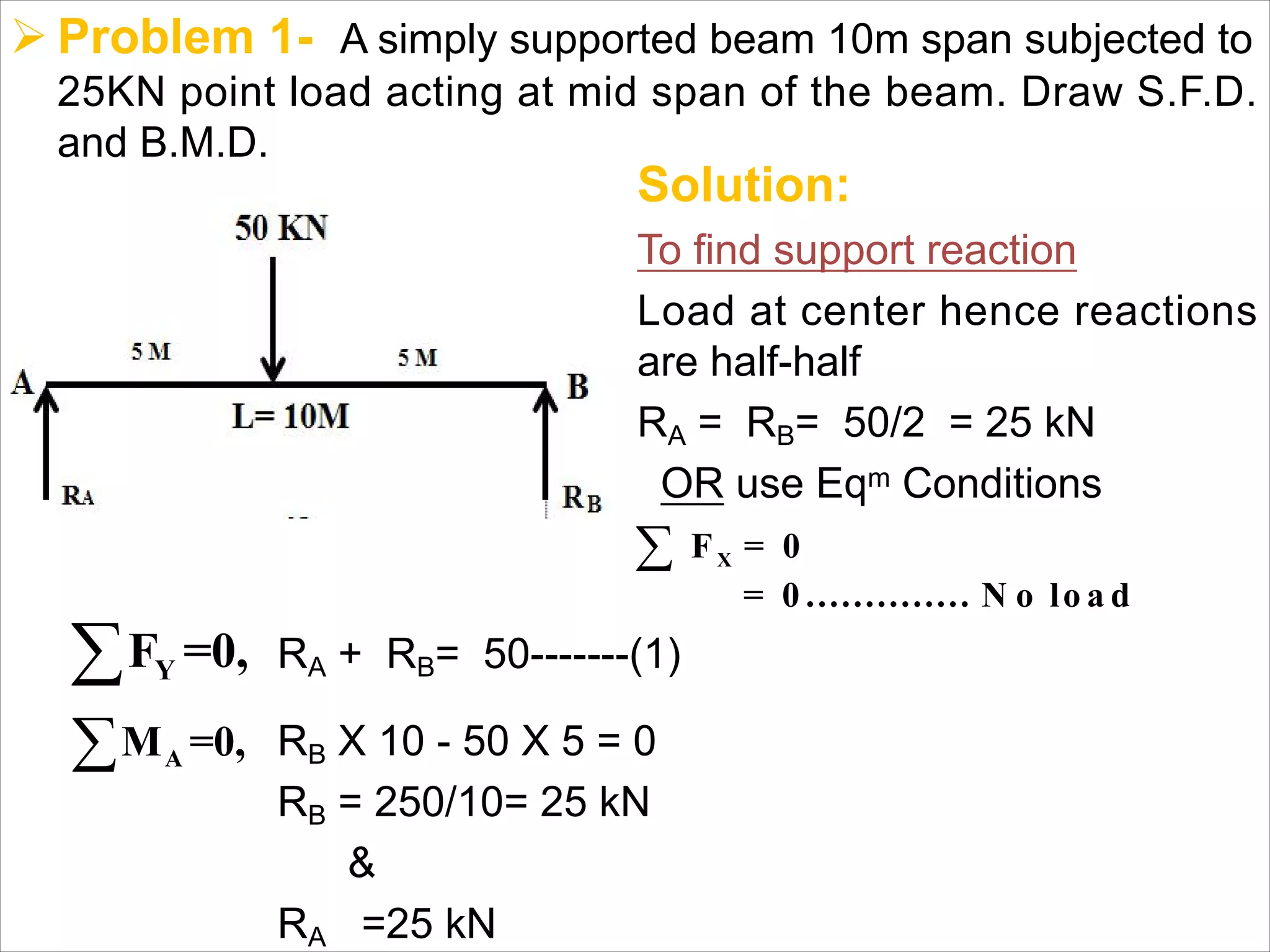
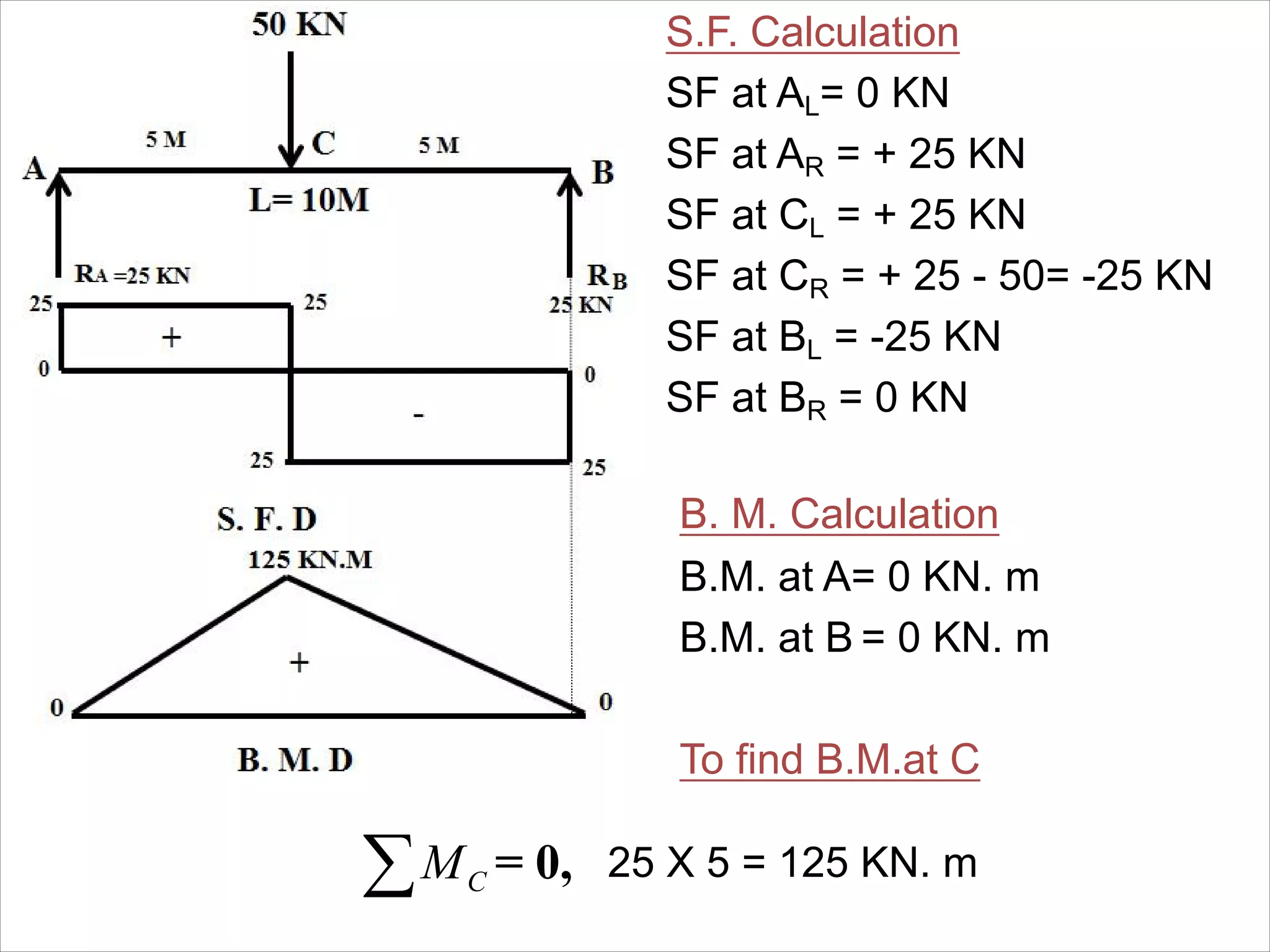
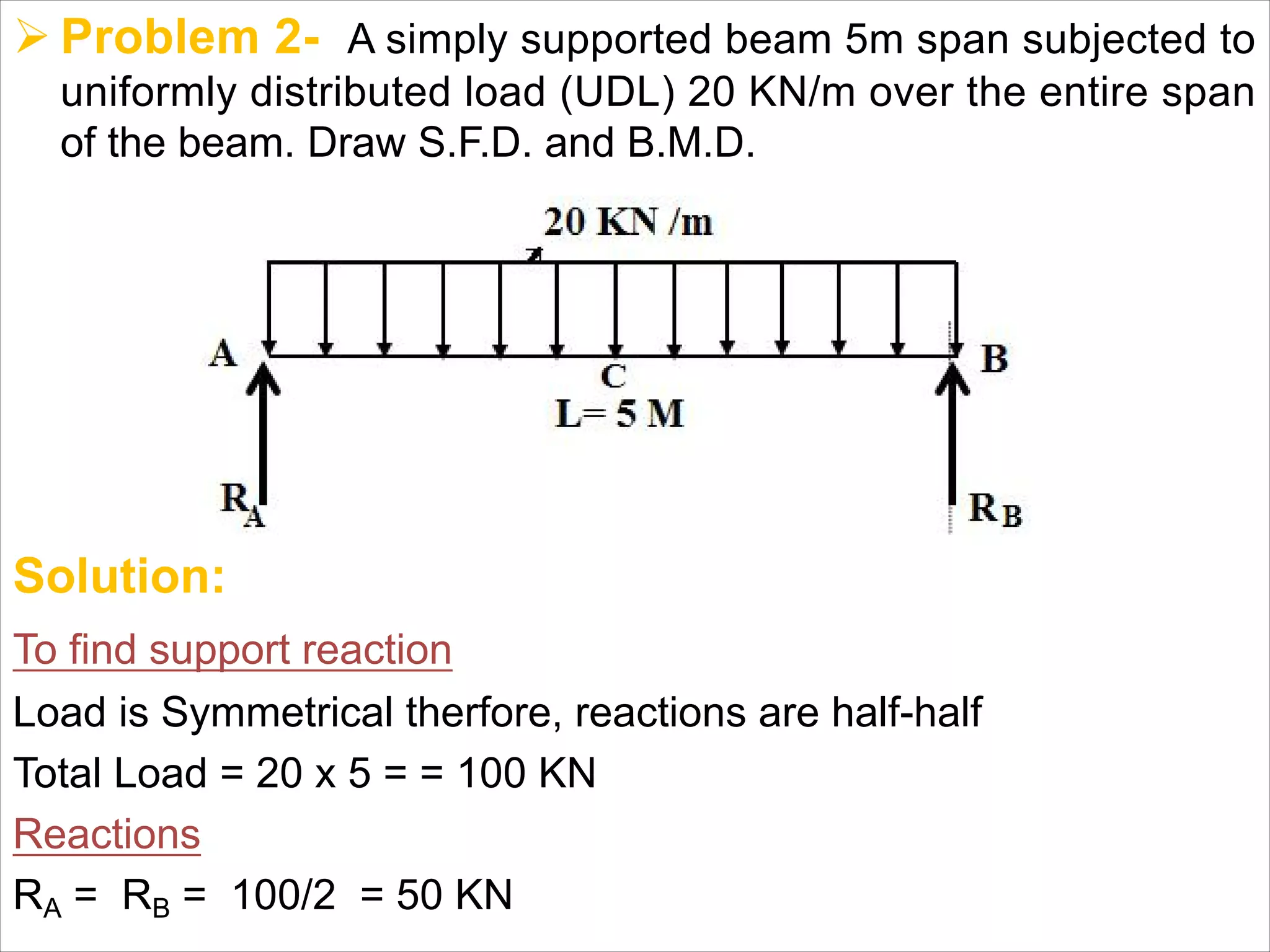
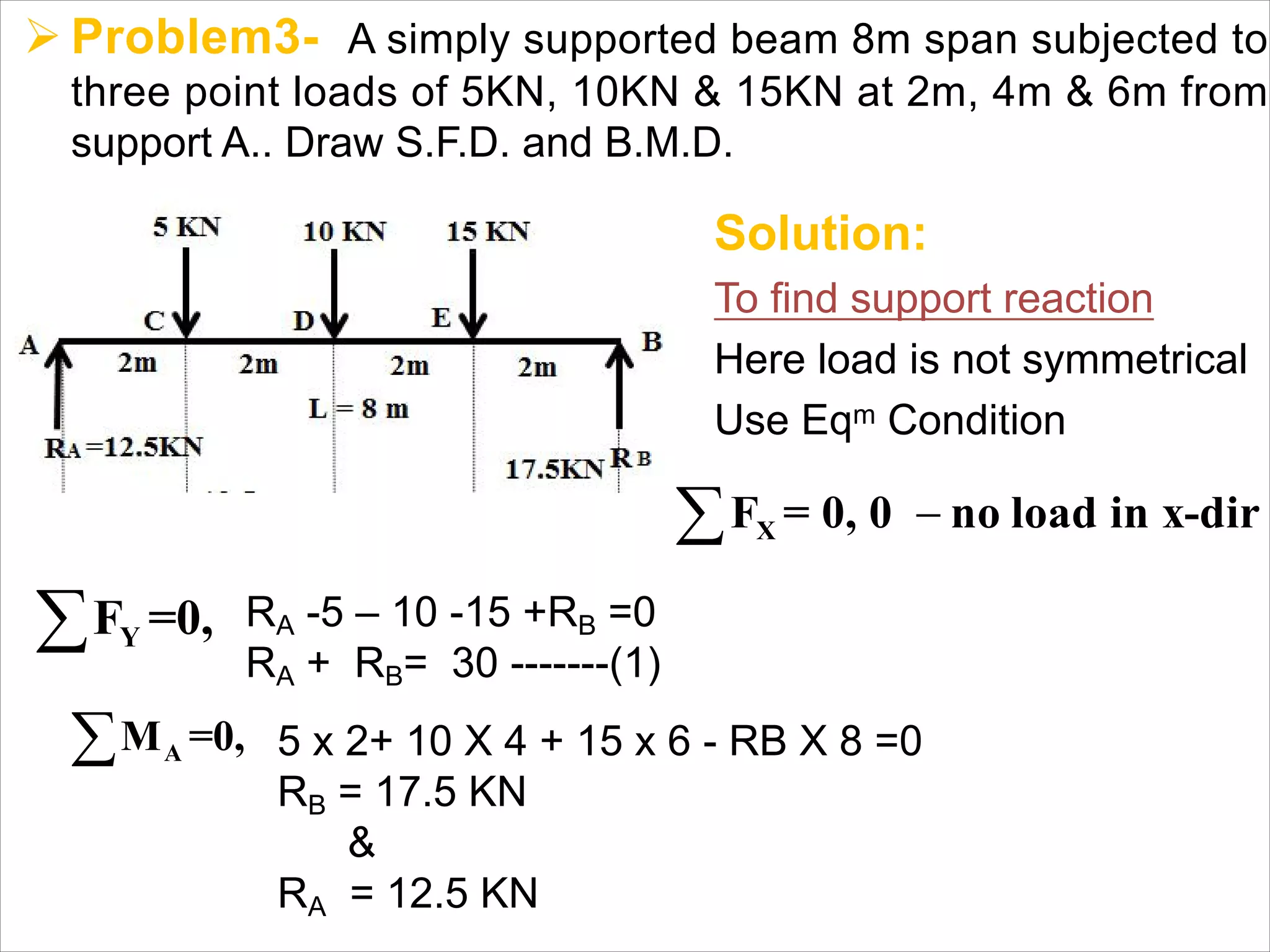
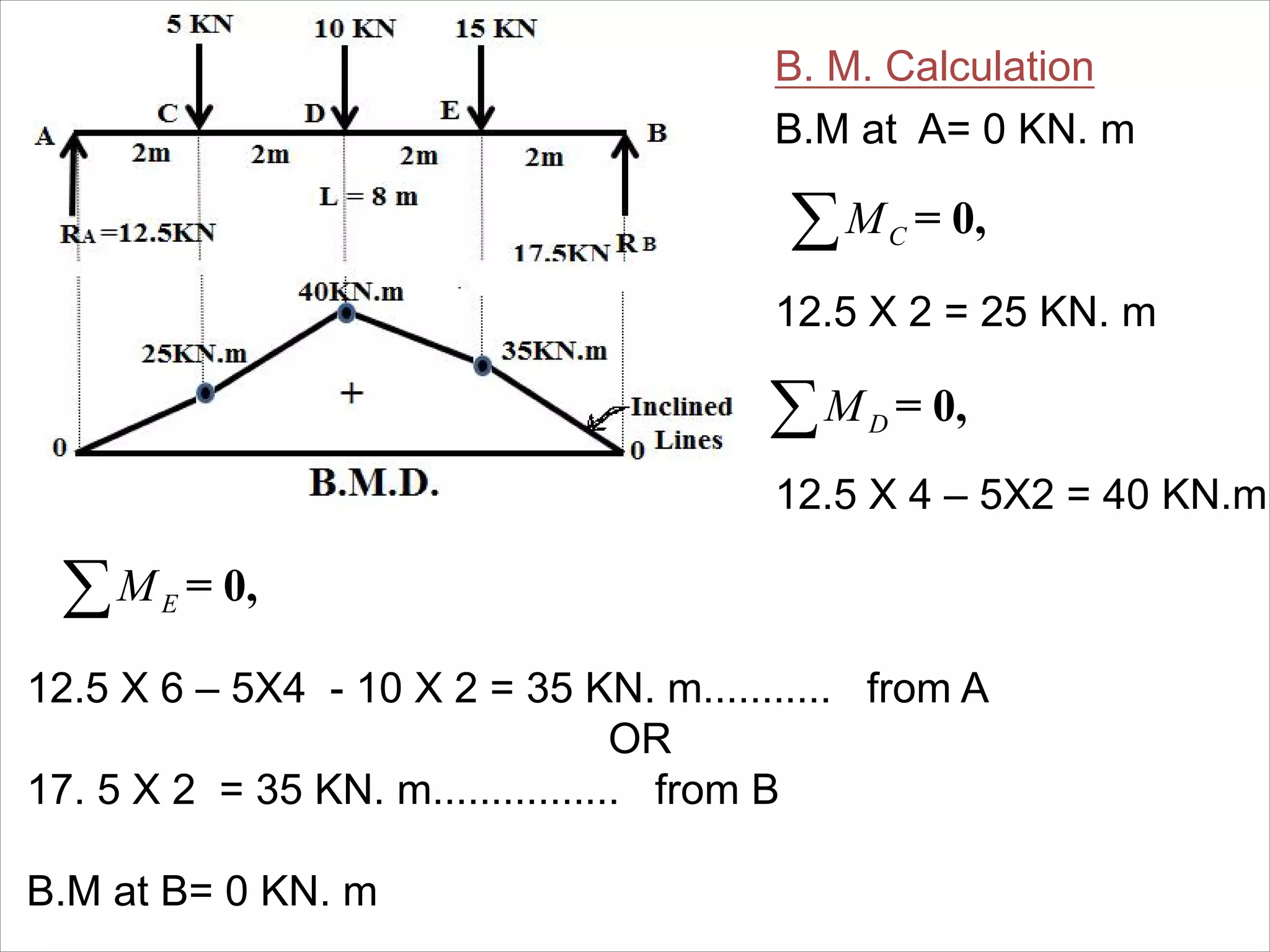
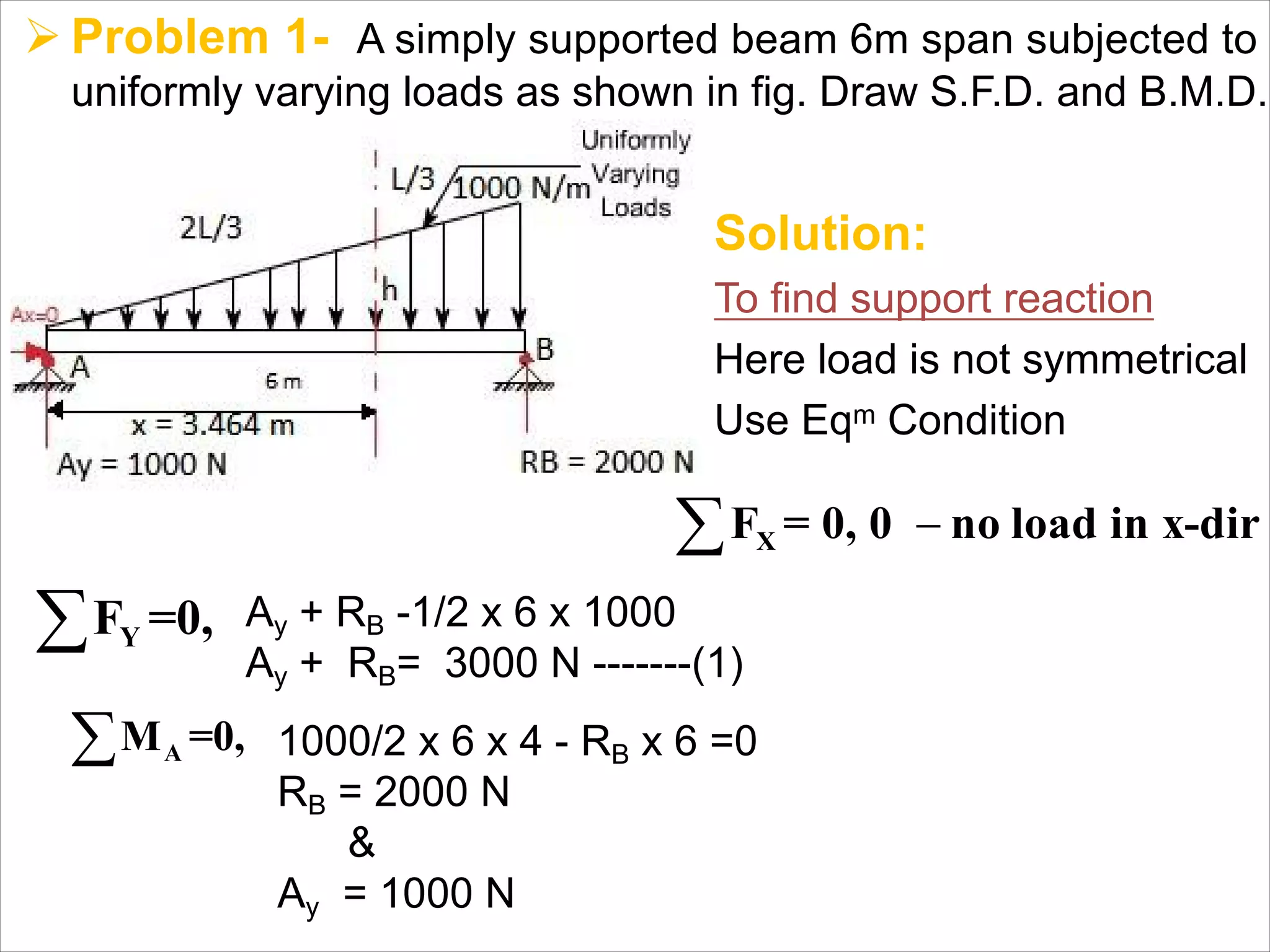
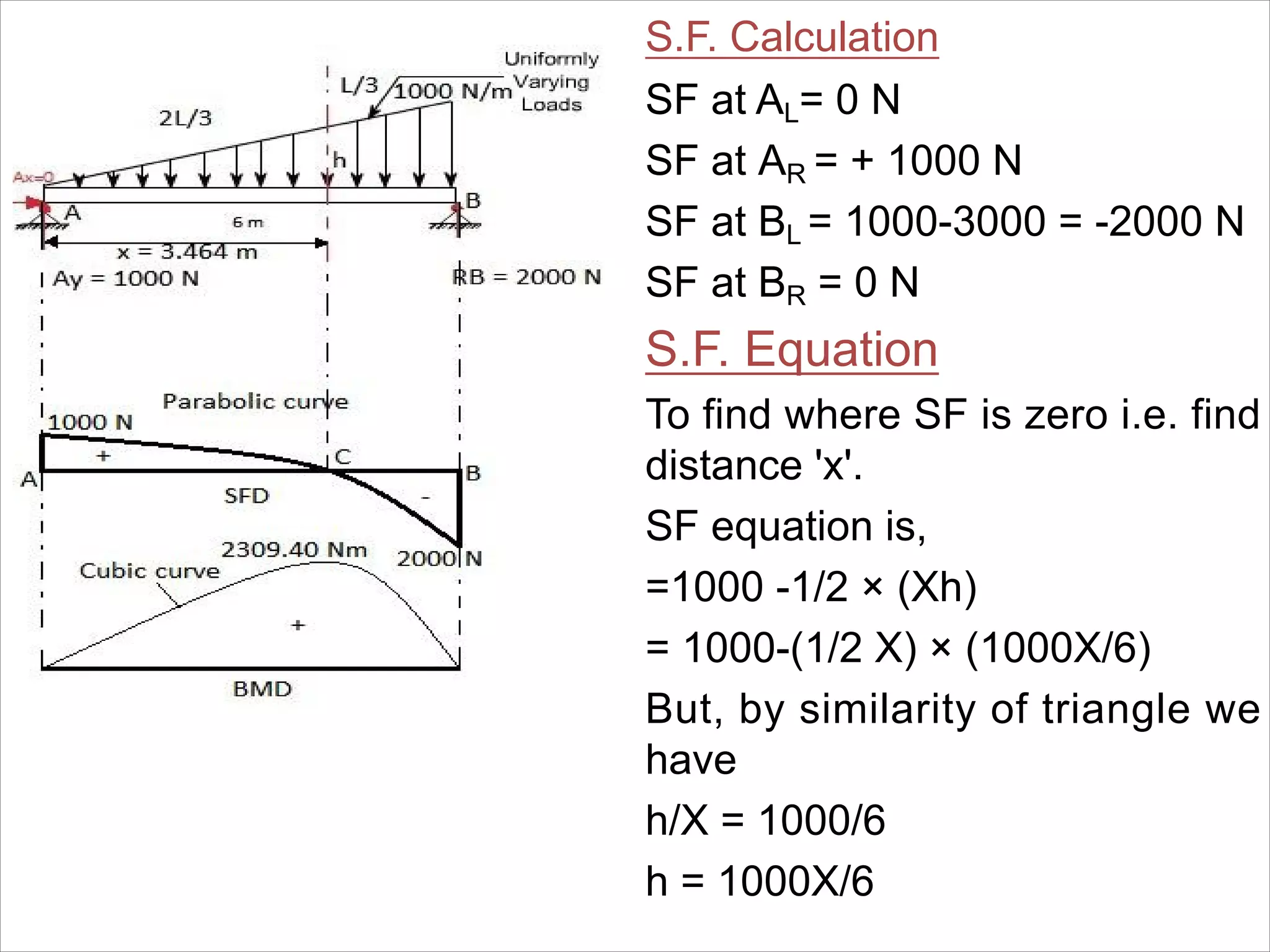
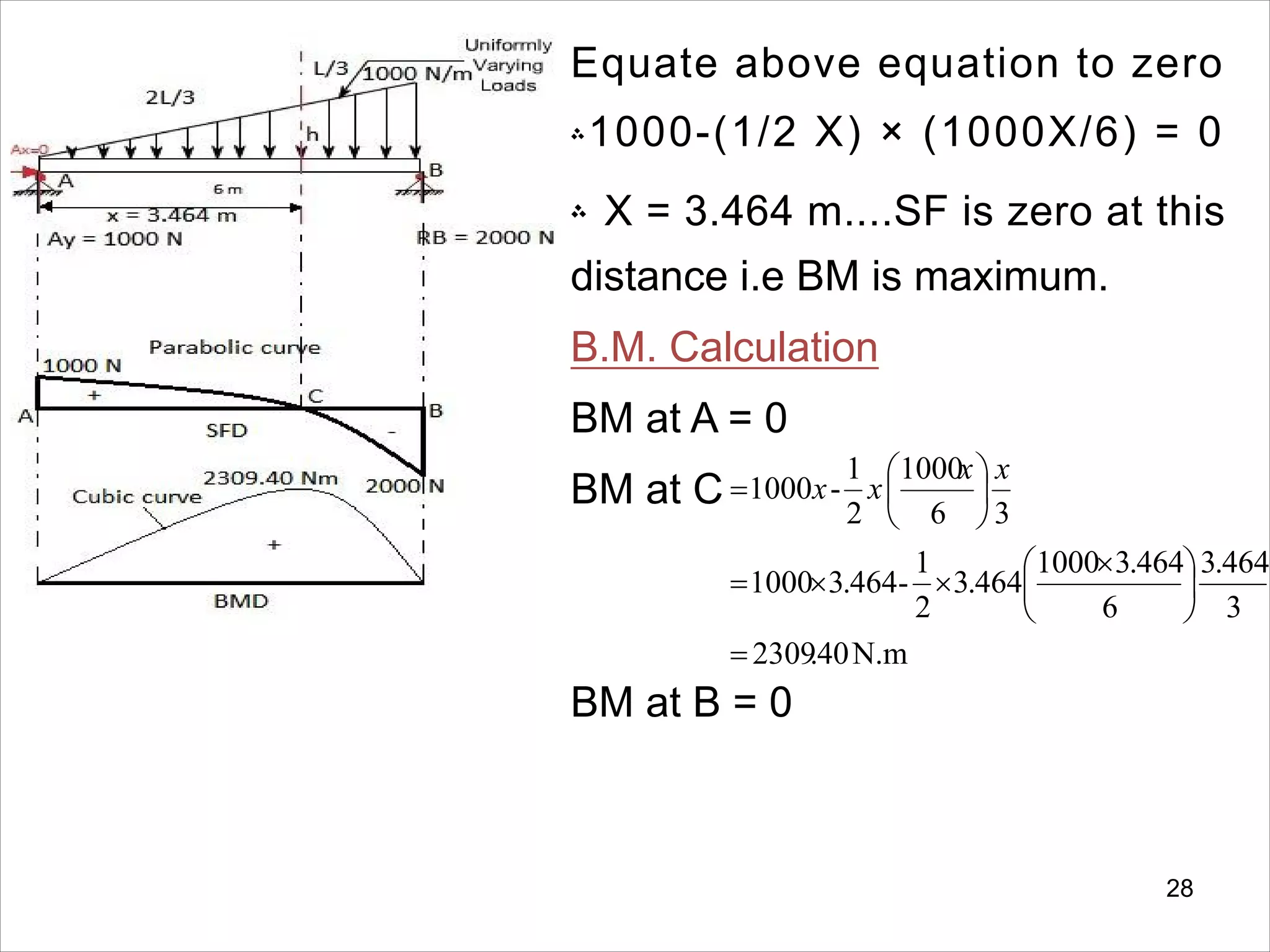
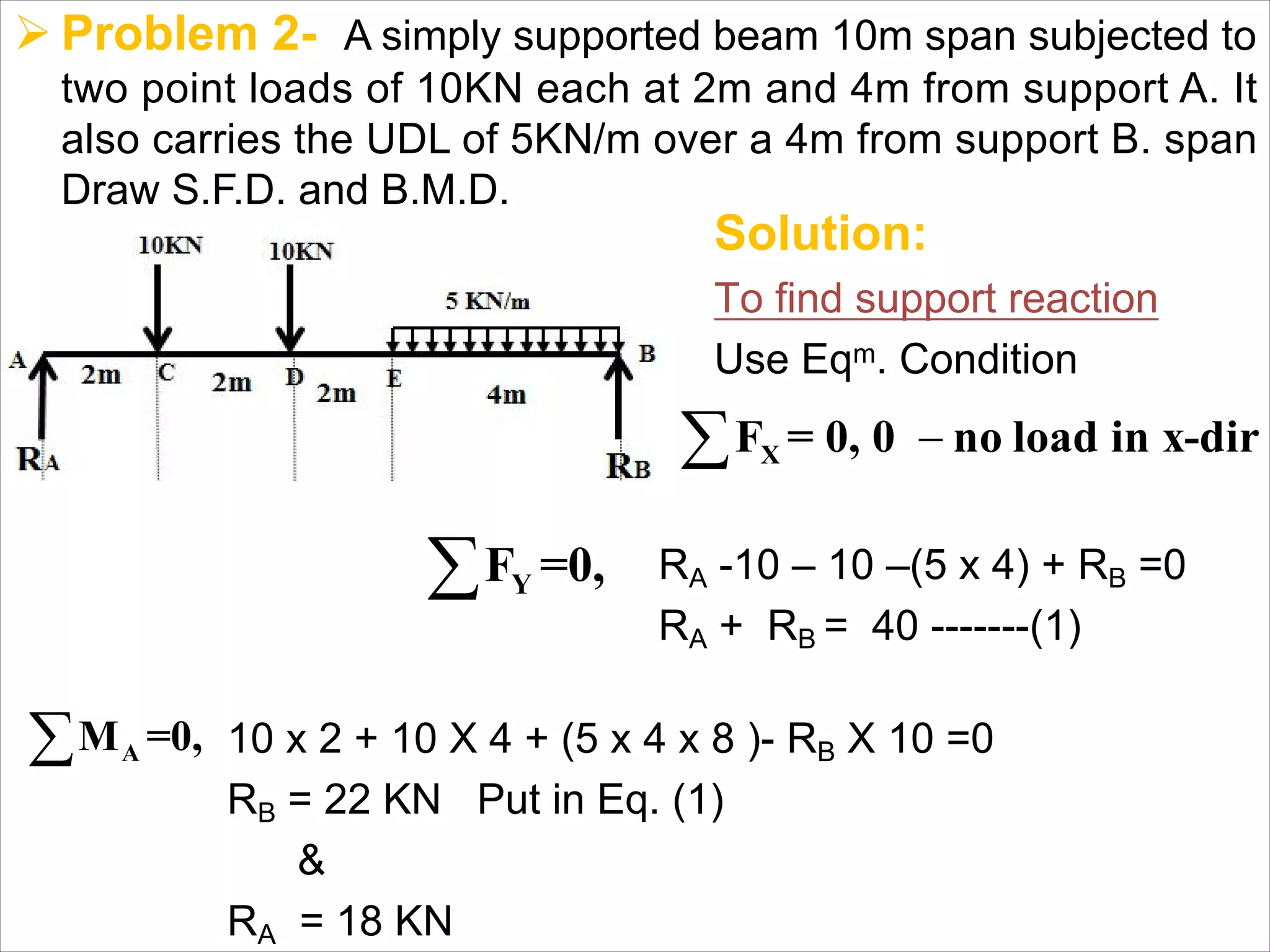
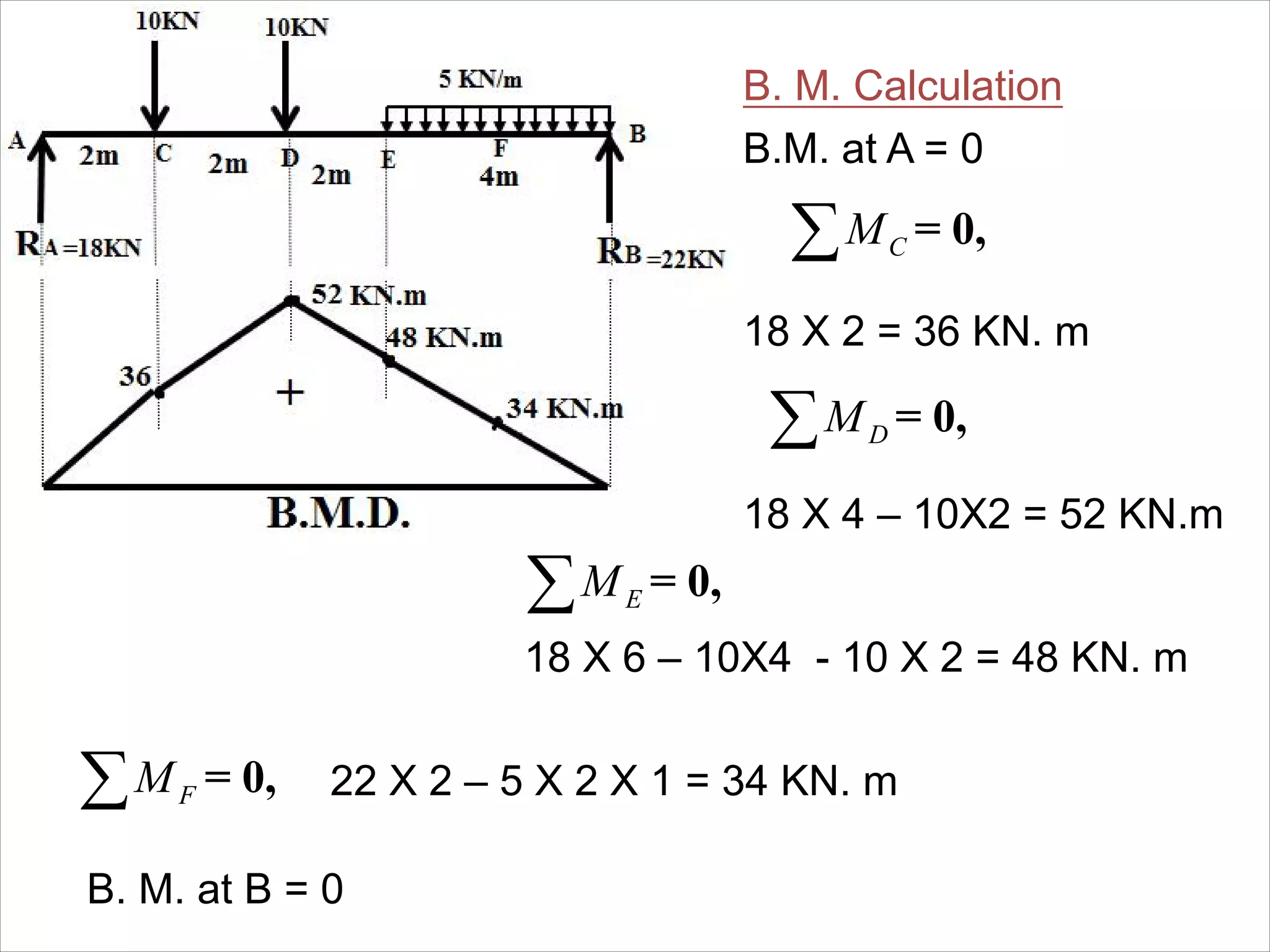
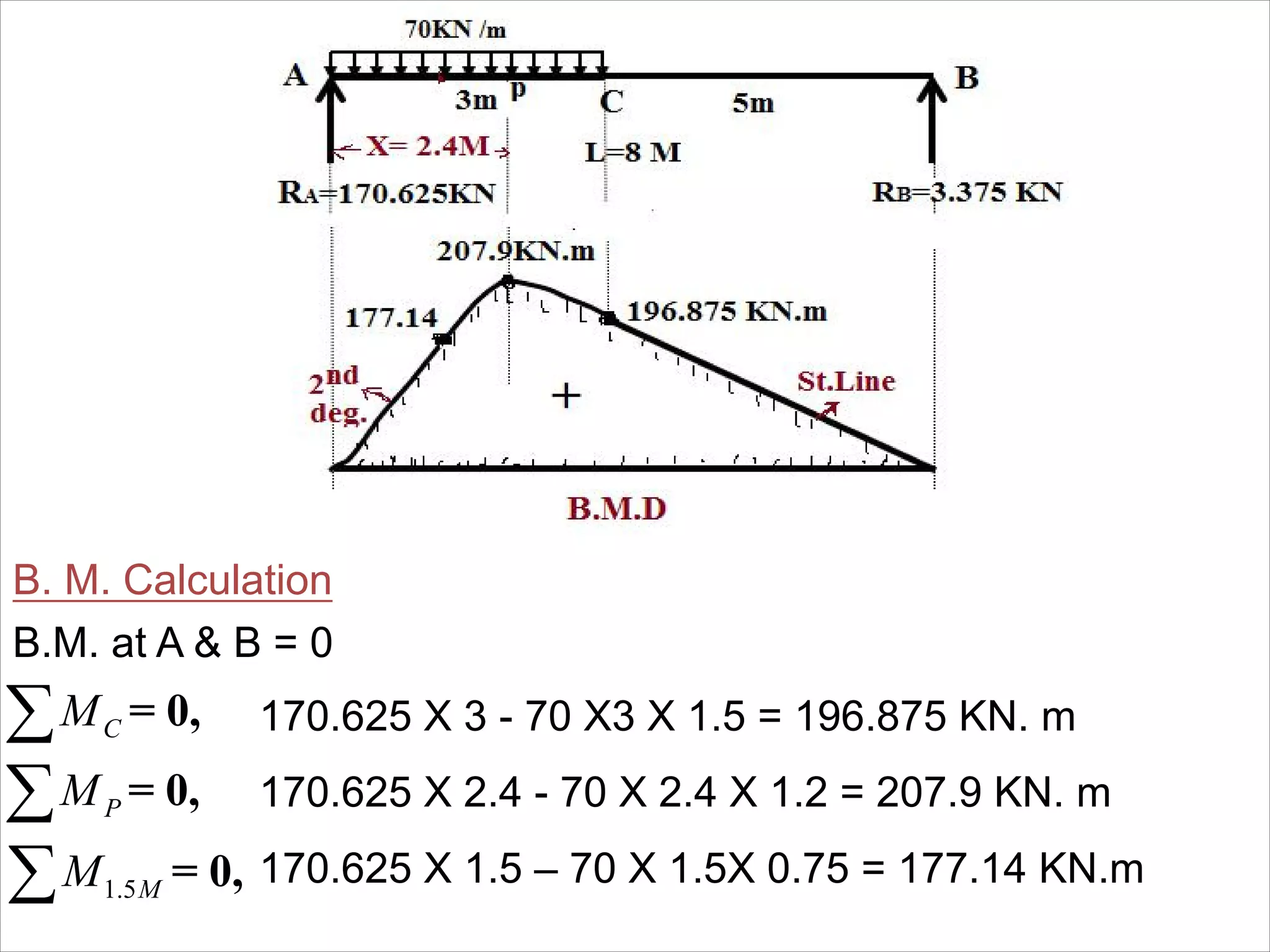
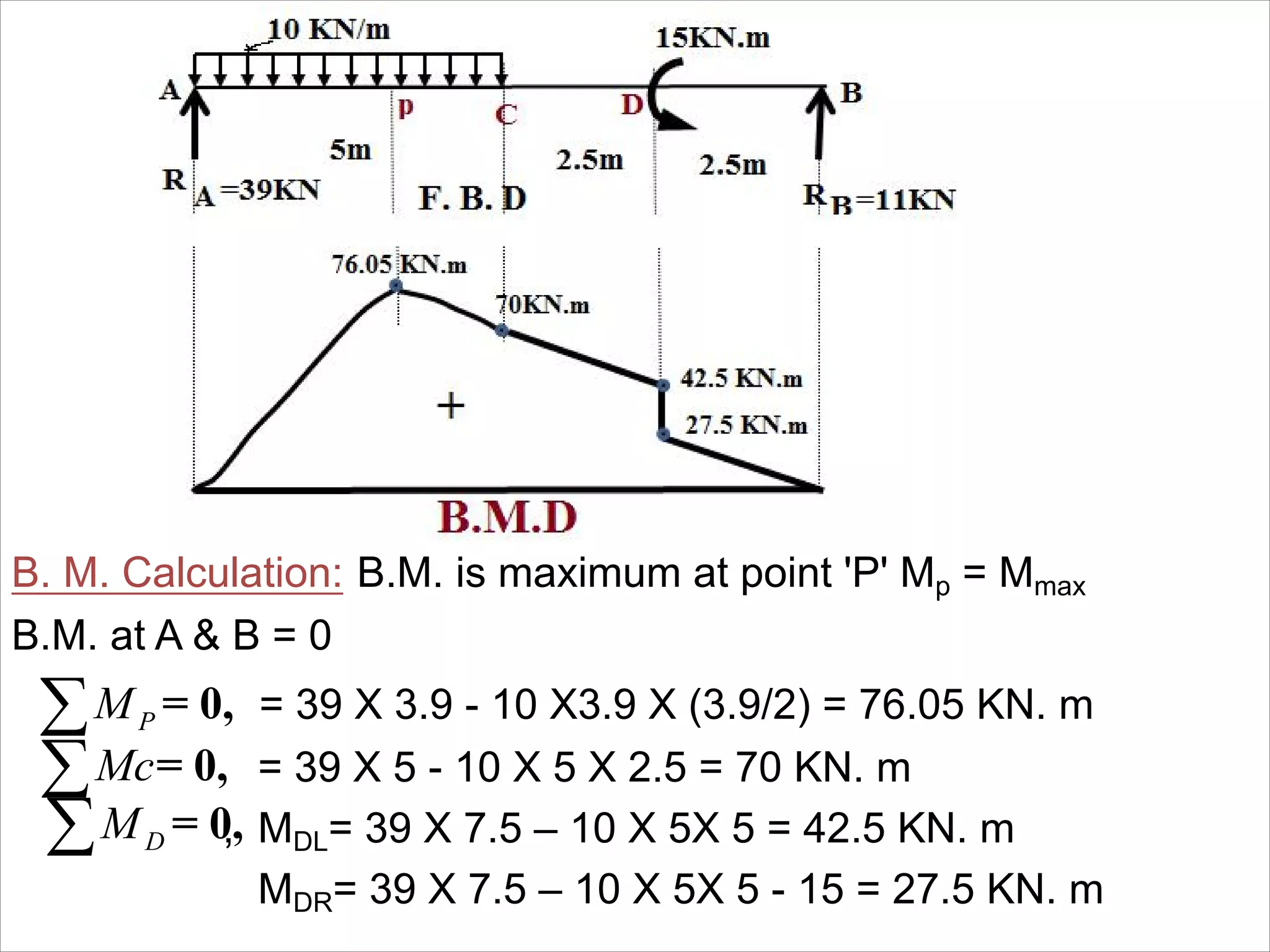
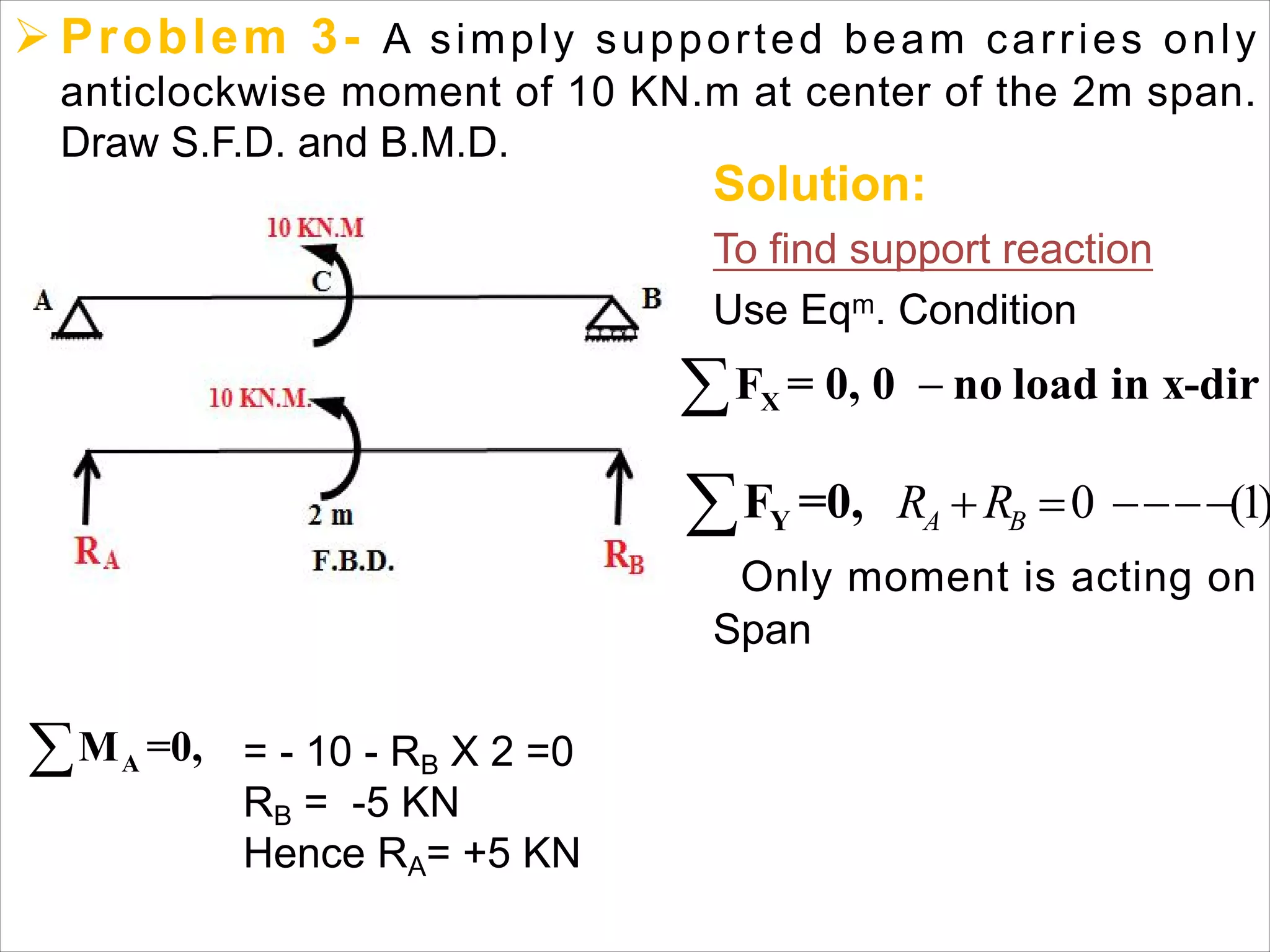
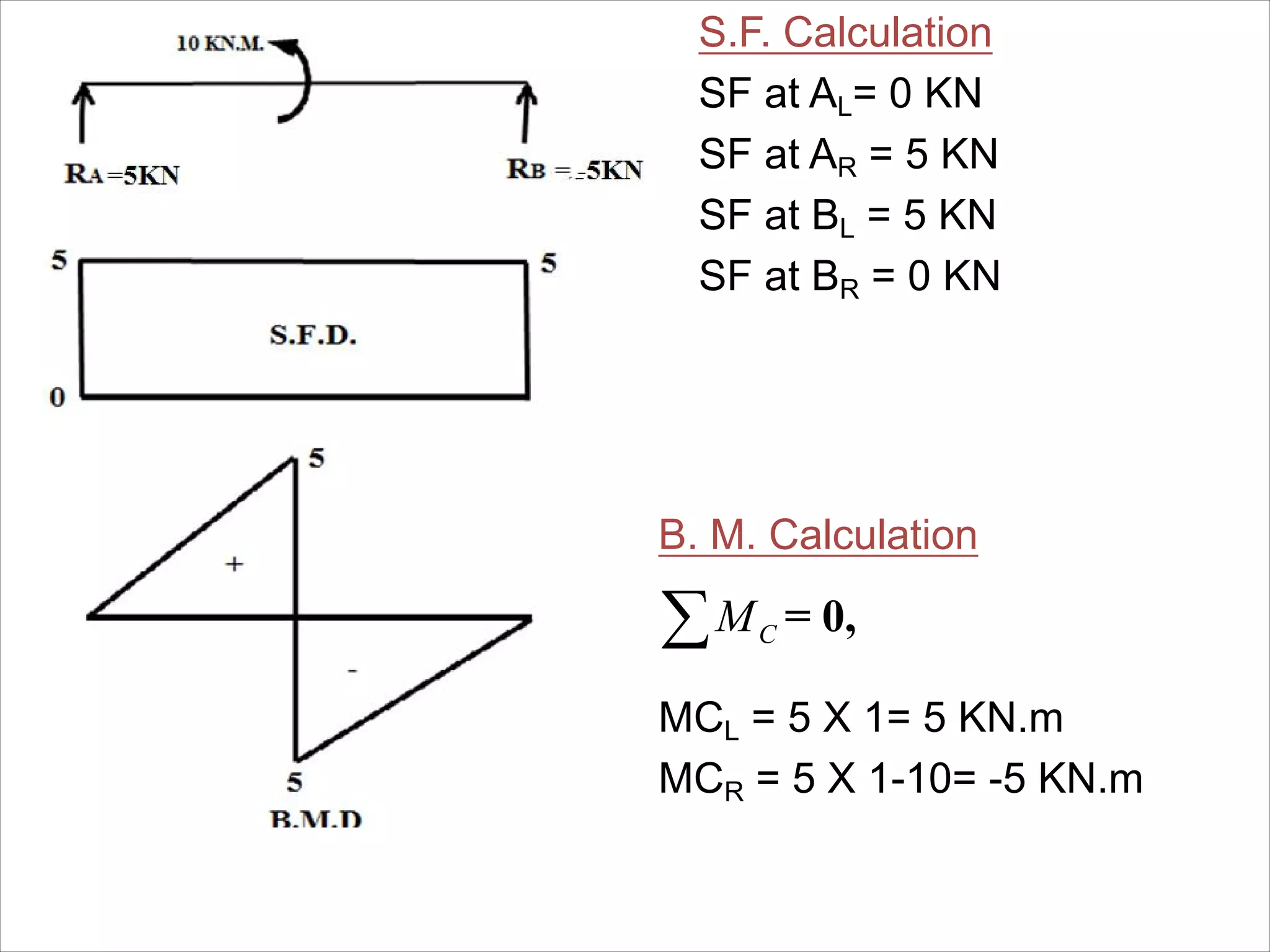
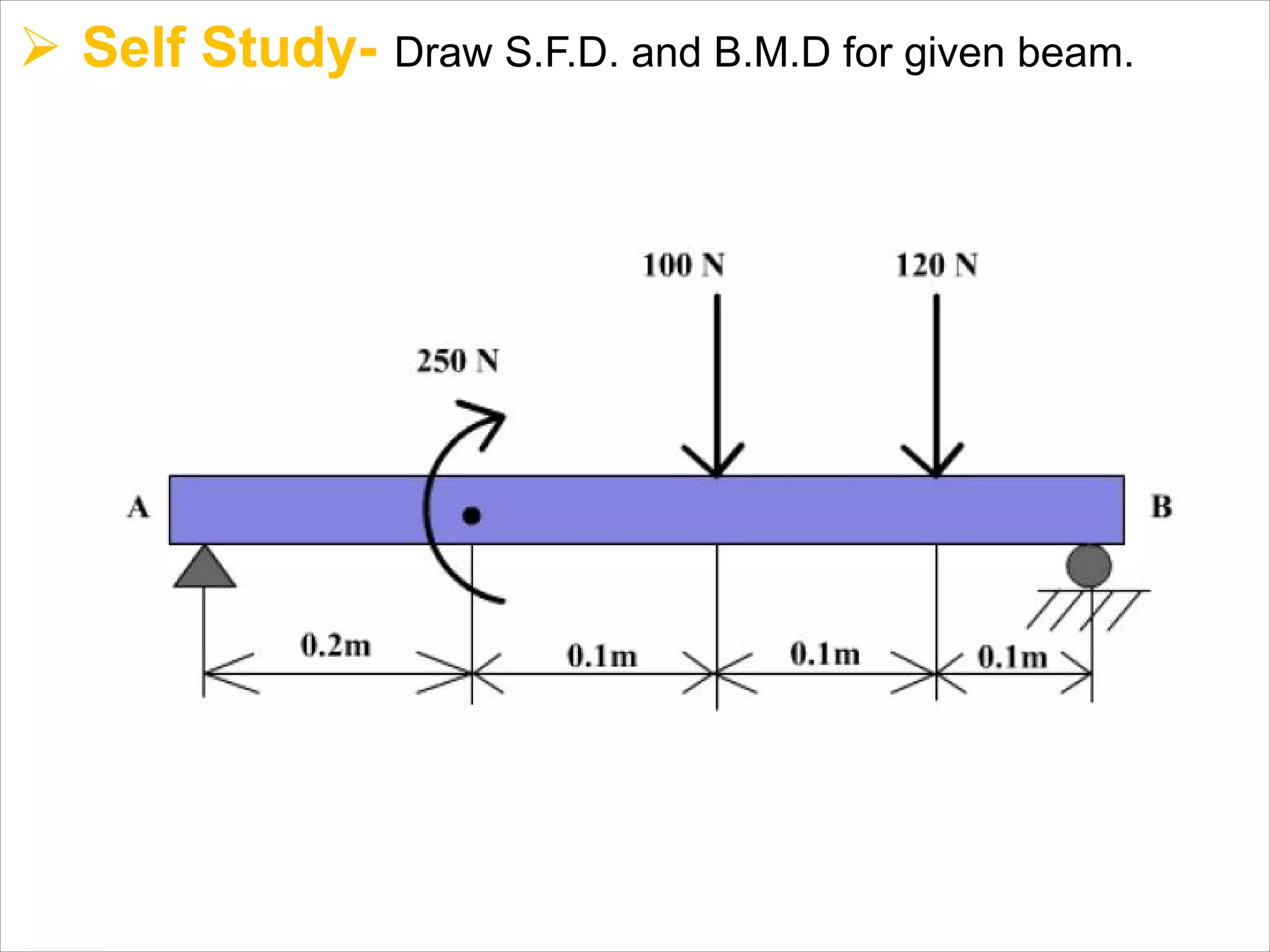
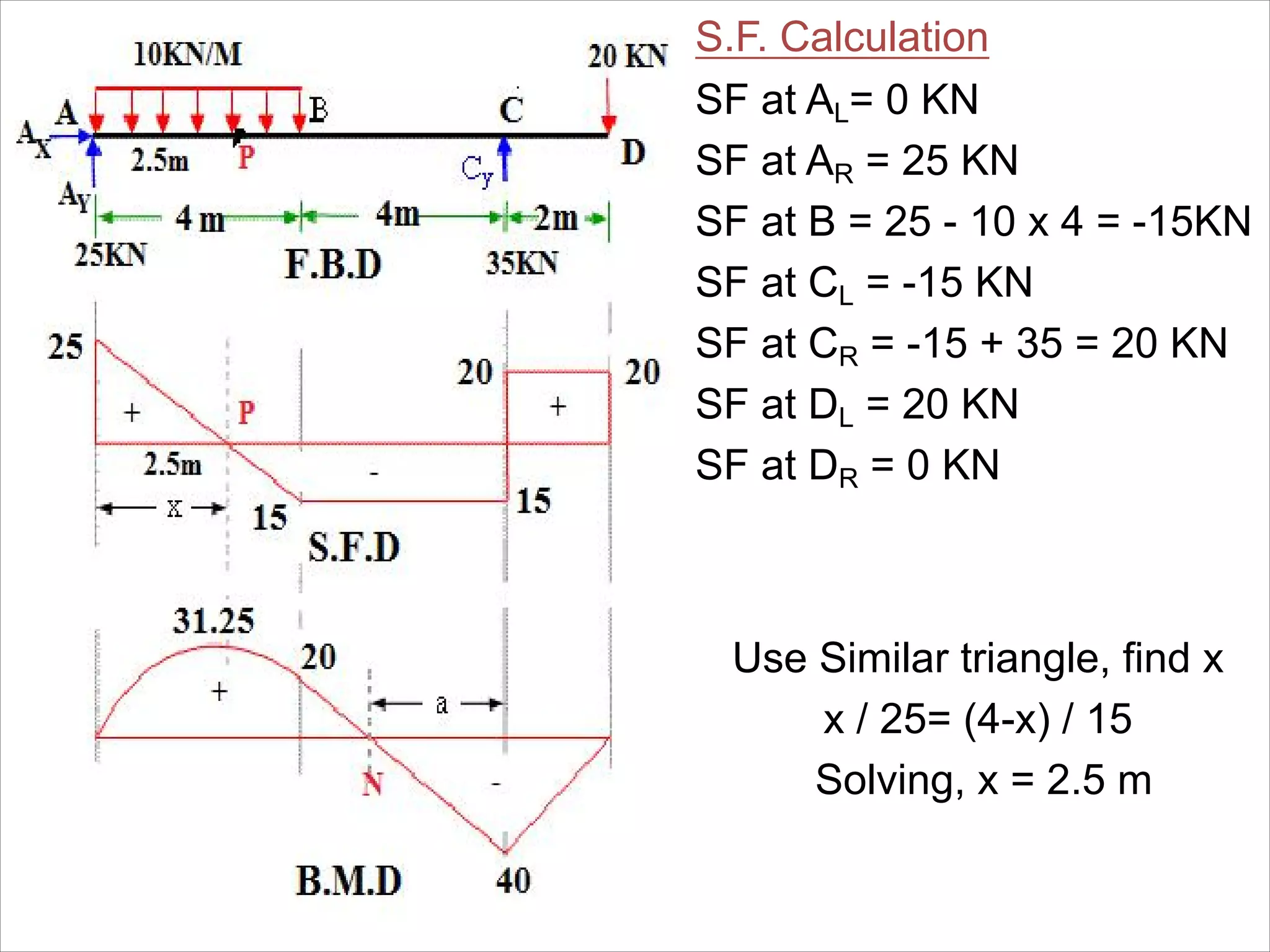
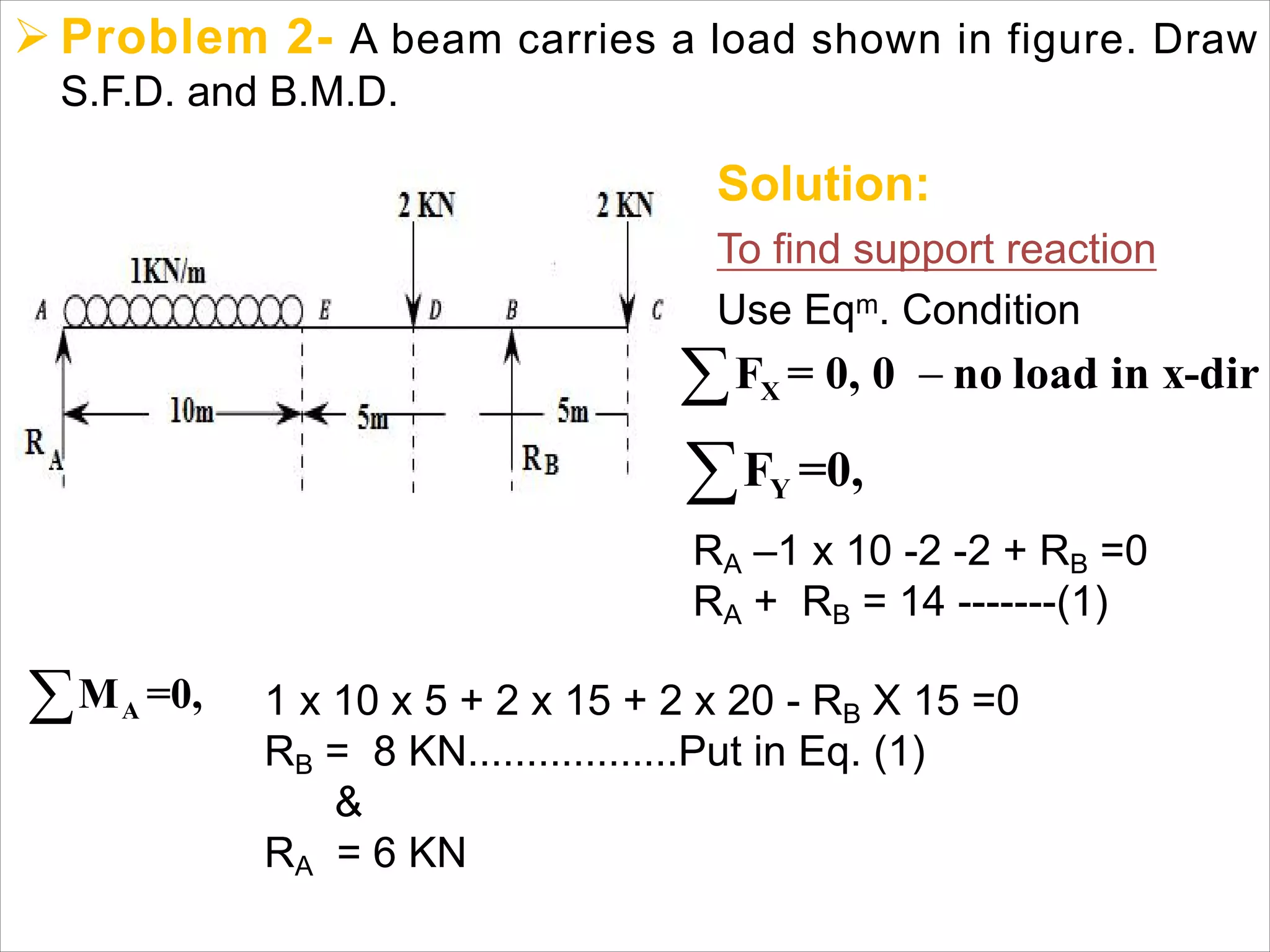
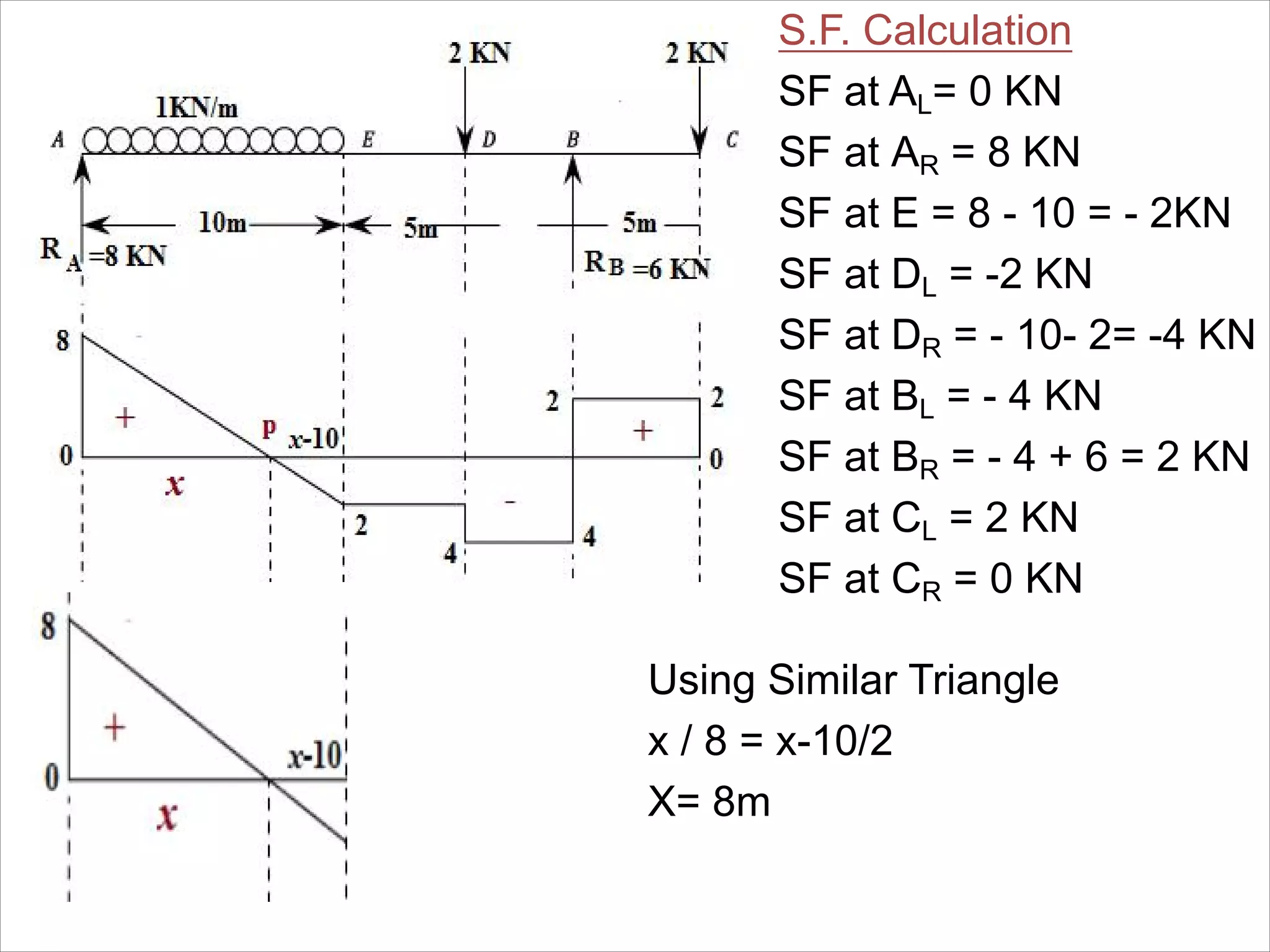
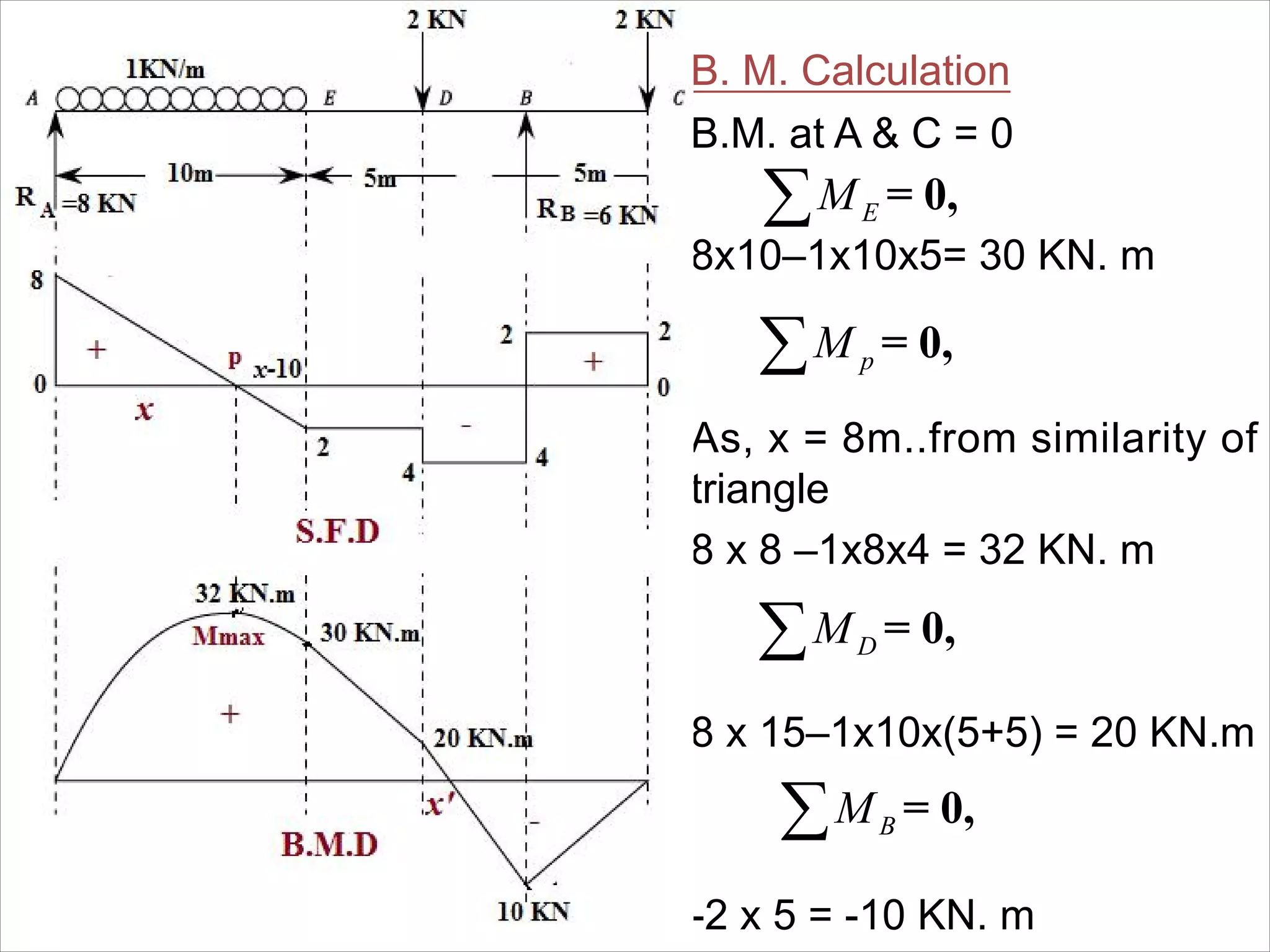
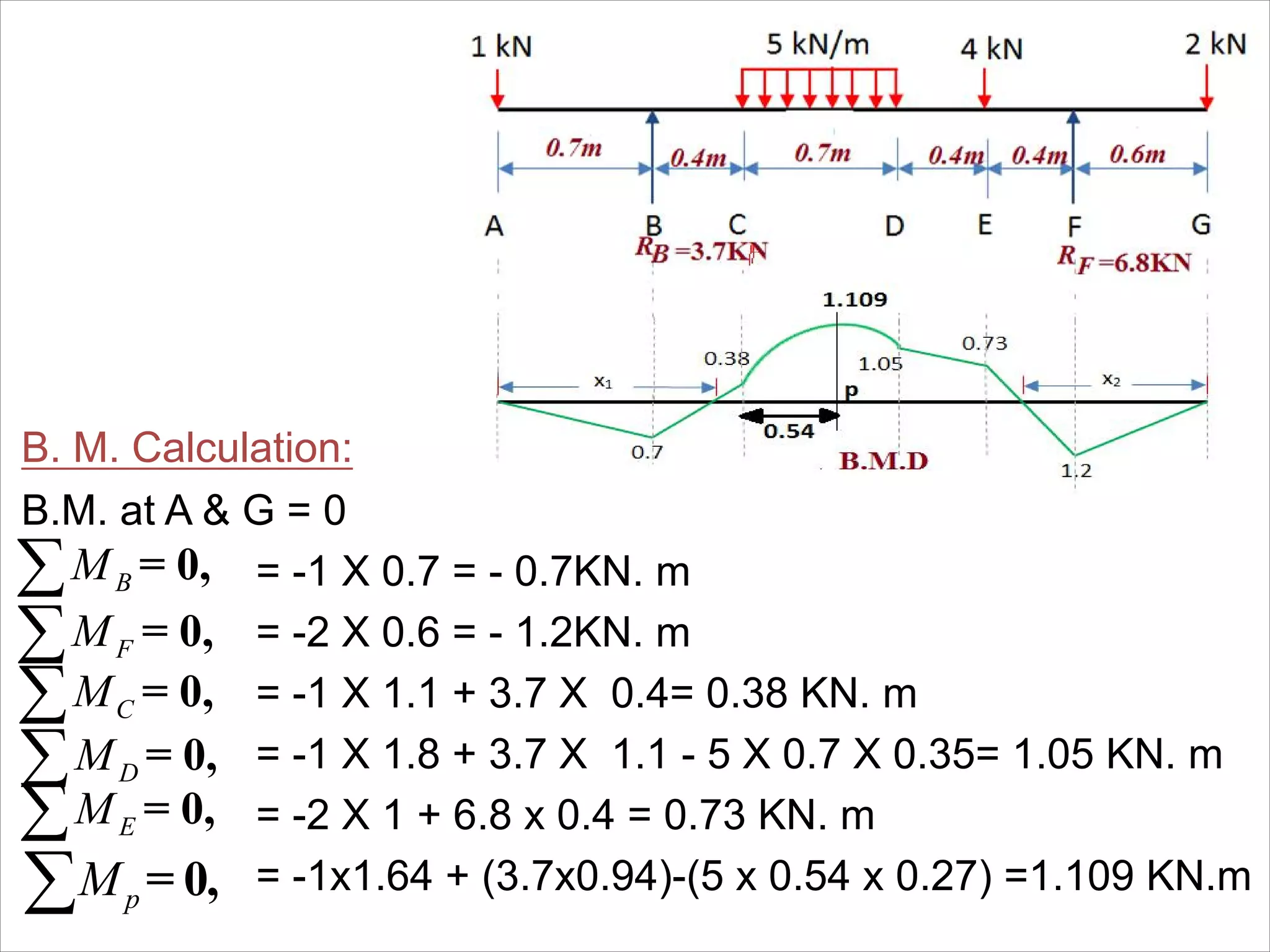
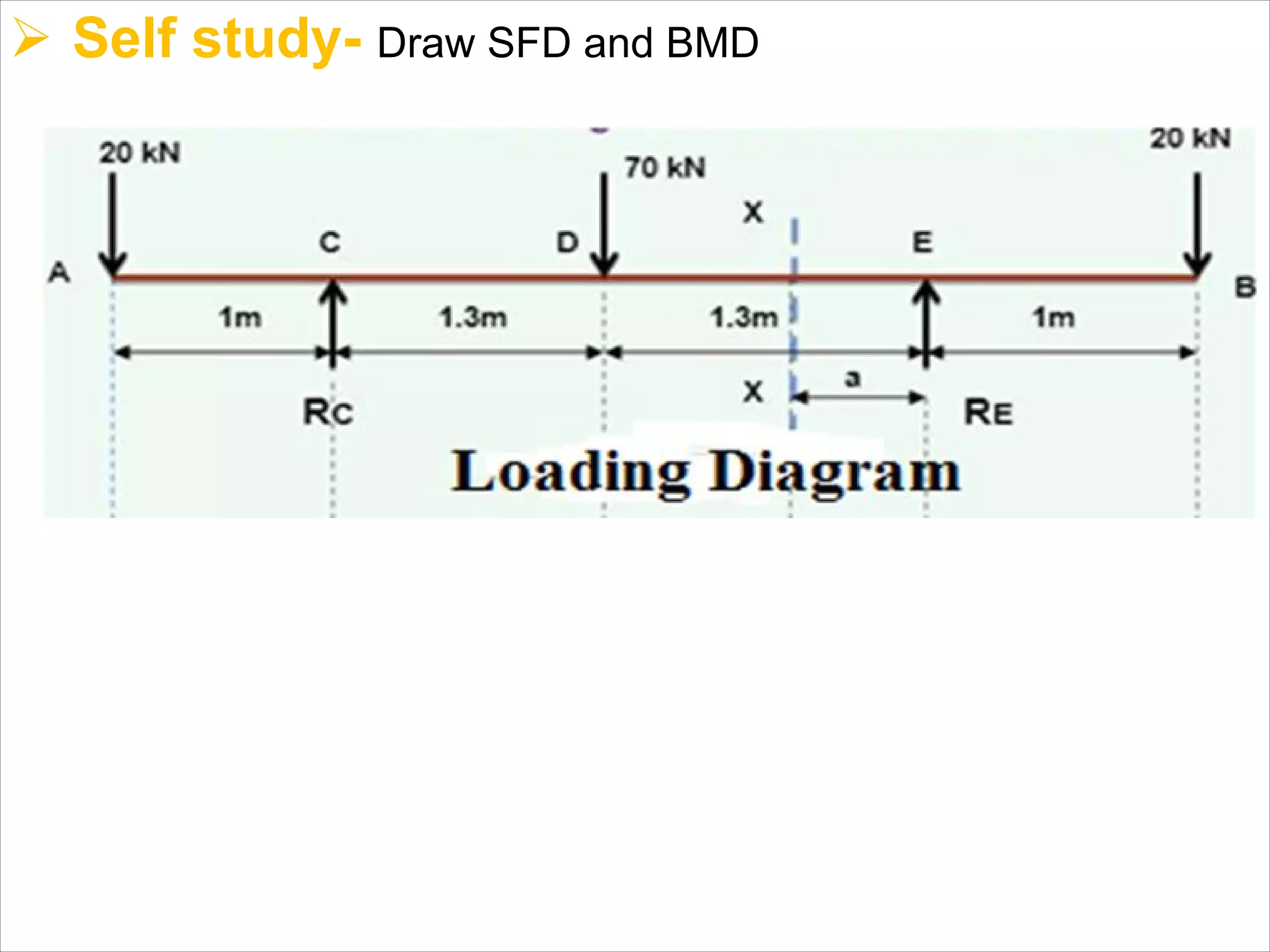
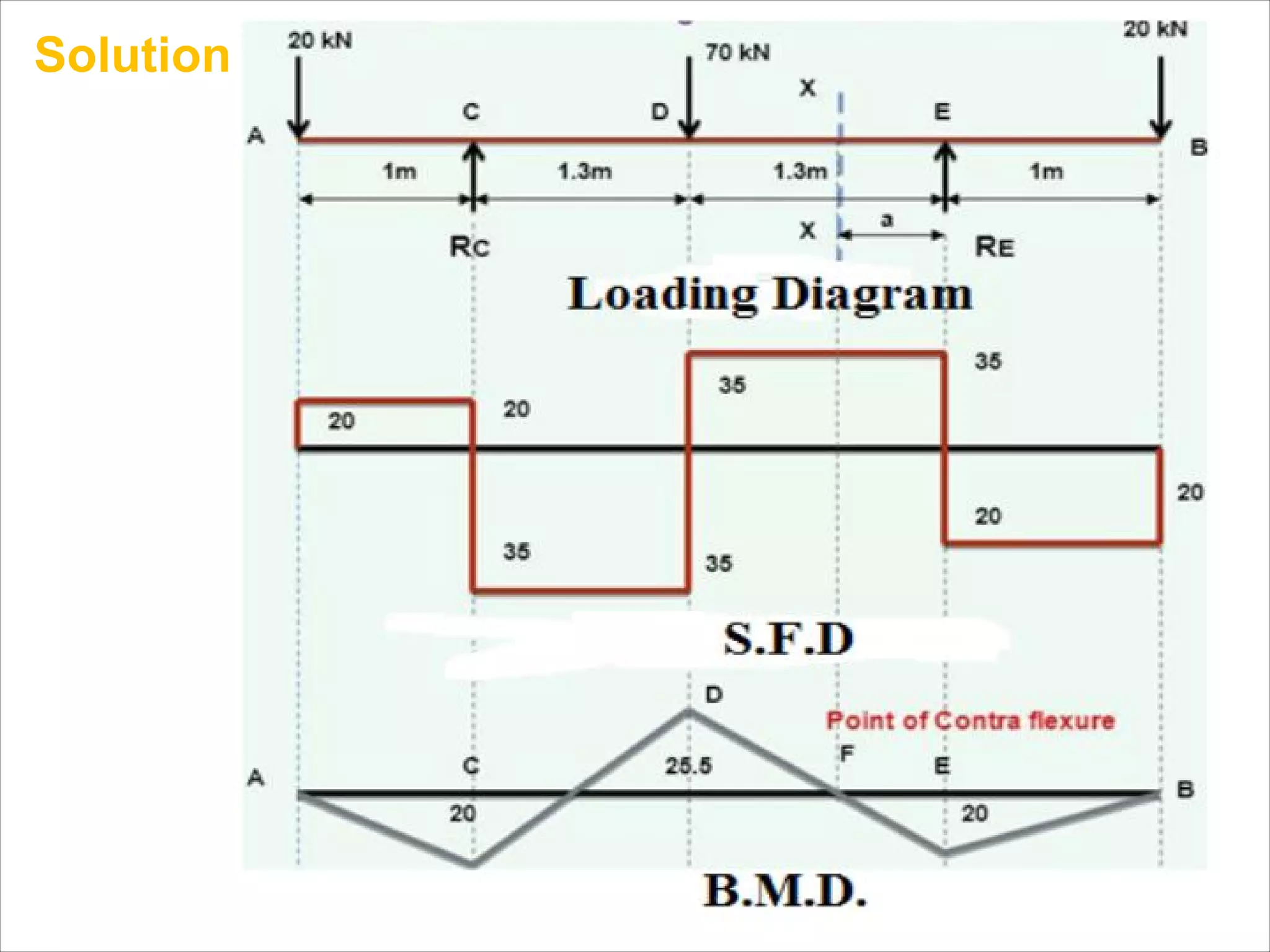
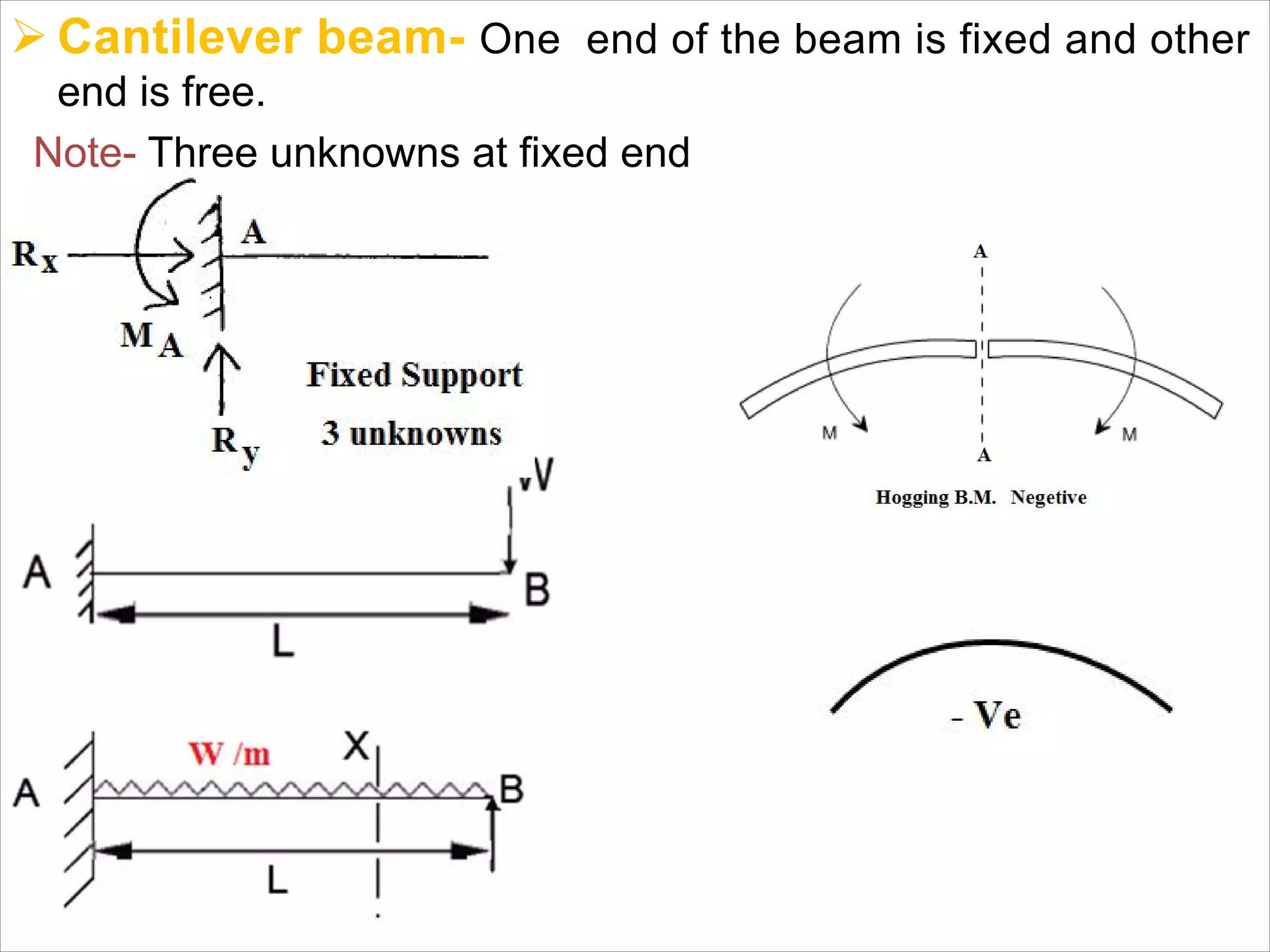
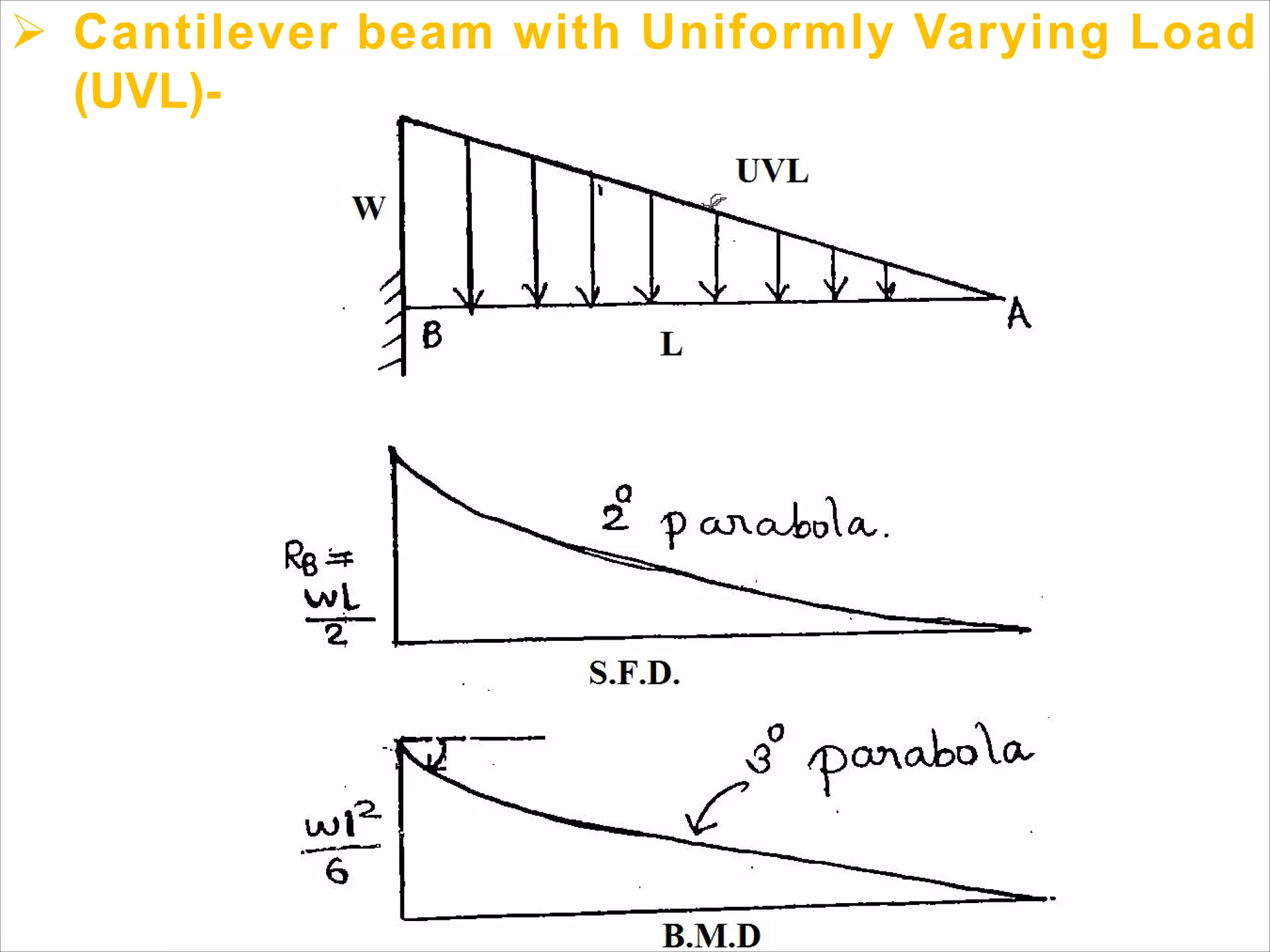
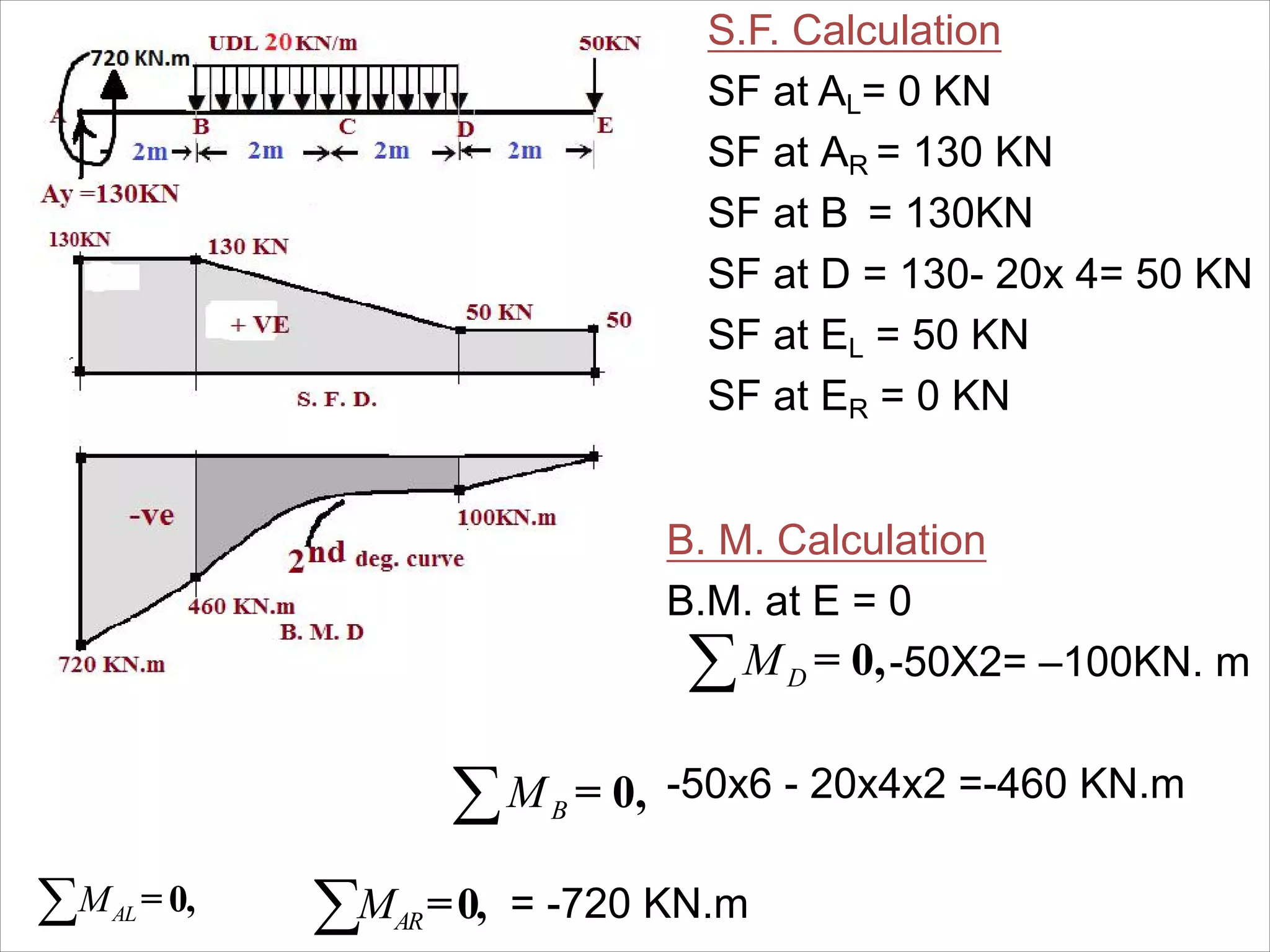
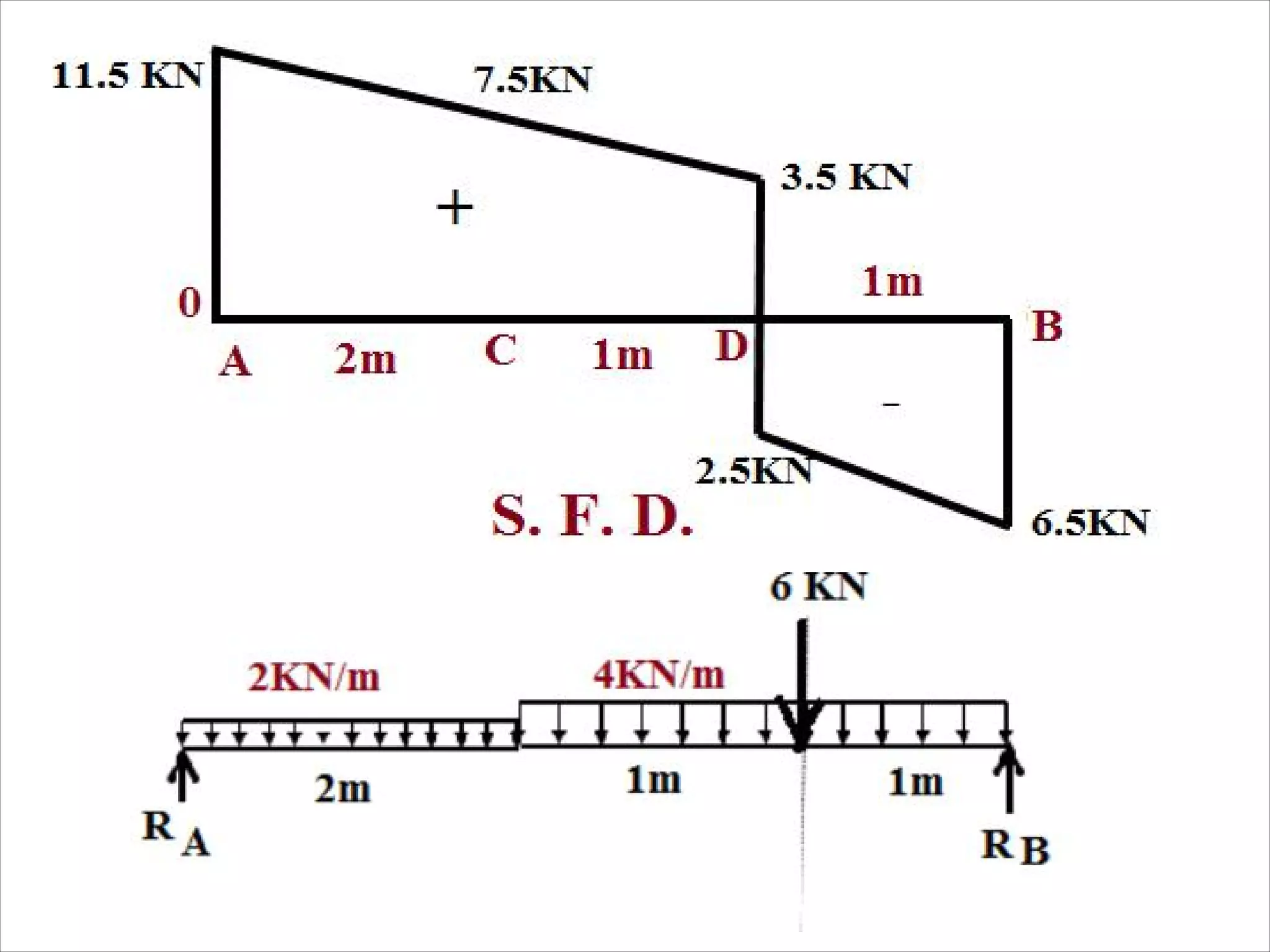
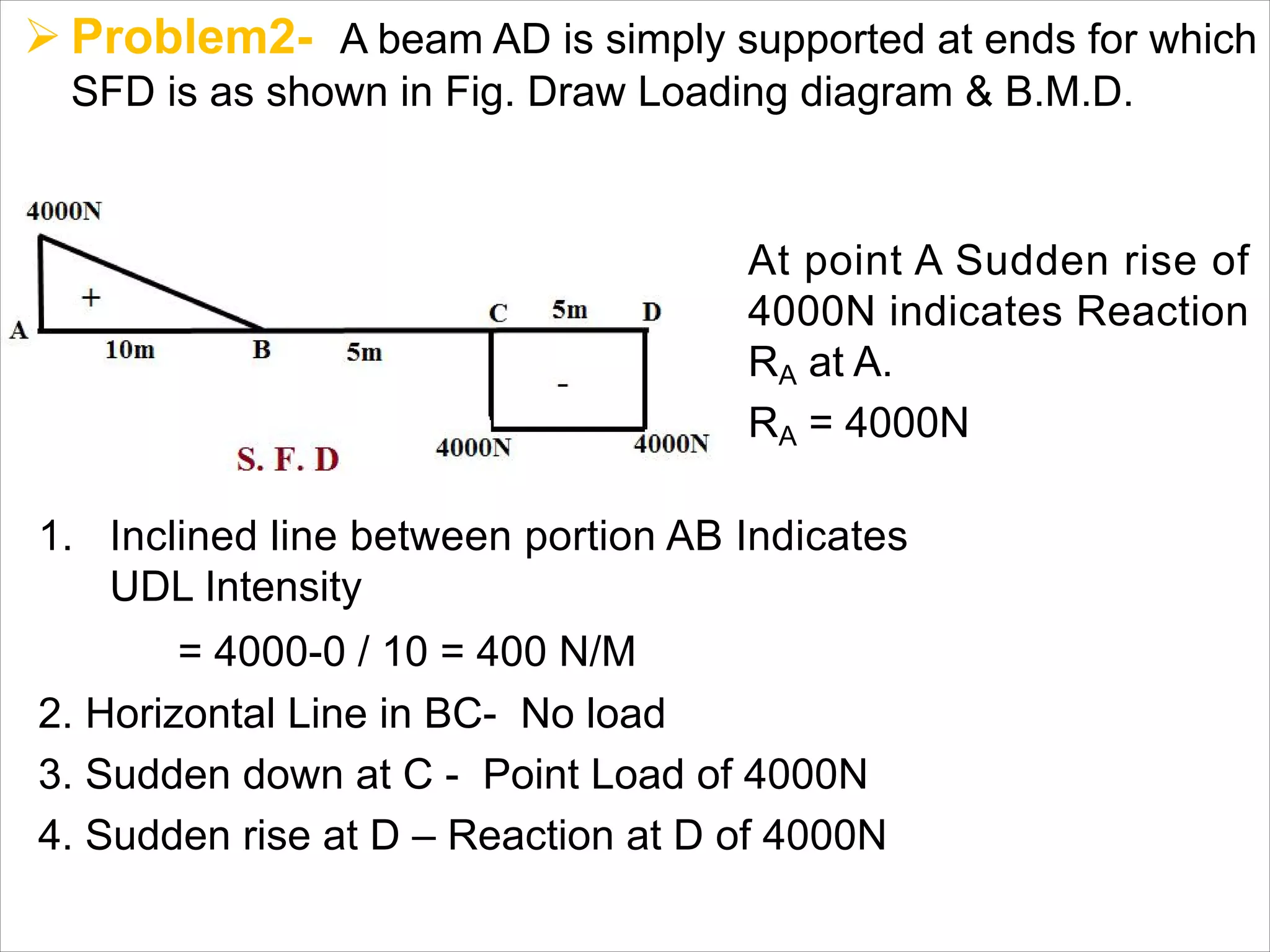
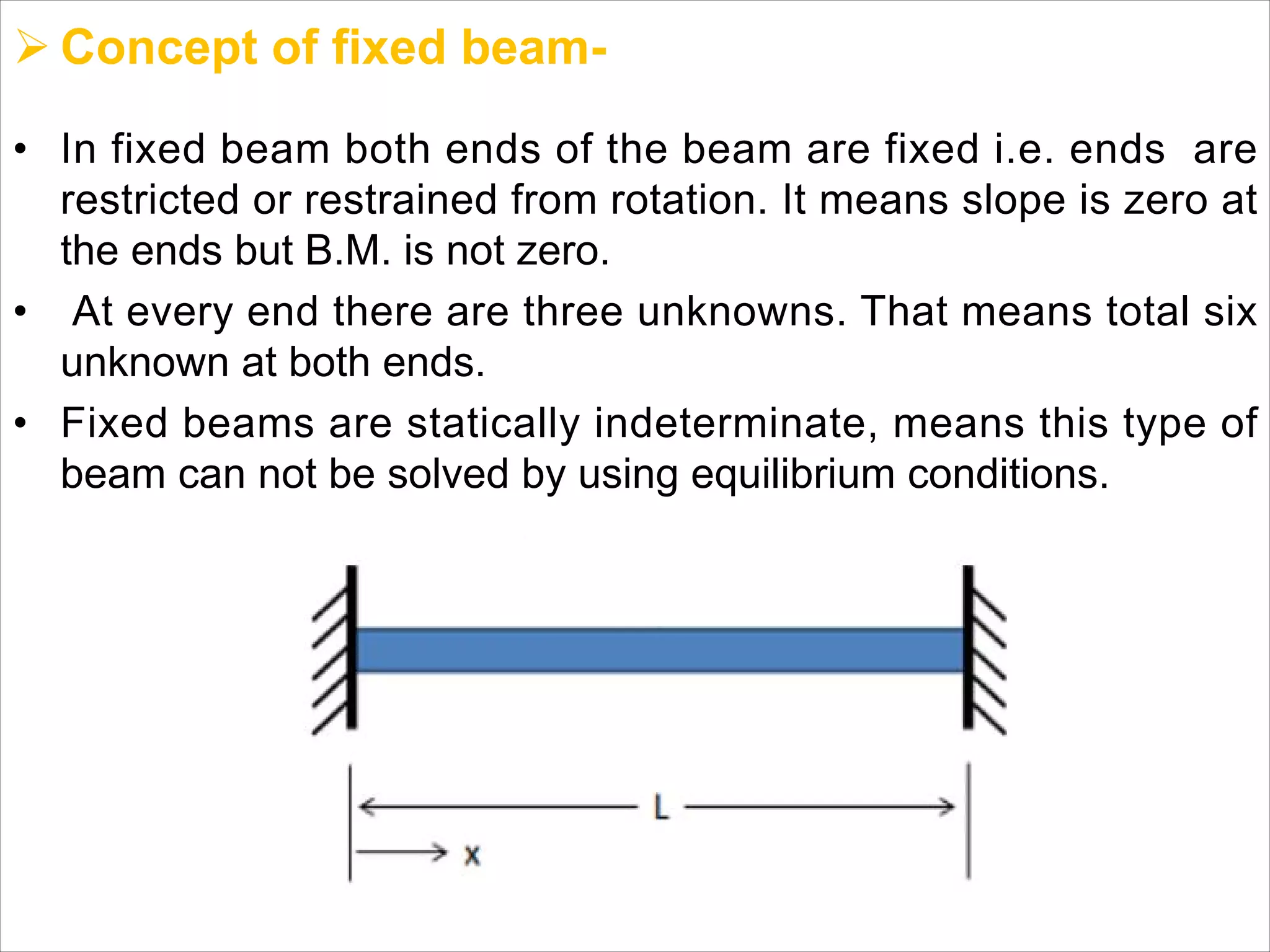
The document is a technical overview of beams in civil engineering, discussing their types, support systems, shear force, bending moment diagrams, and load analysis. It includes detailed explanations of concepts like determinate and indeterminate beams, alongside several examples of calculations for various loading scenarios. The author, Mr. Sumit S. Kolapkar, provides a structured approach to understanding beam behavior under different conditions, including the effects of point loads and uniformly distributed loads.