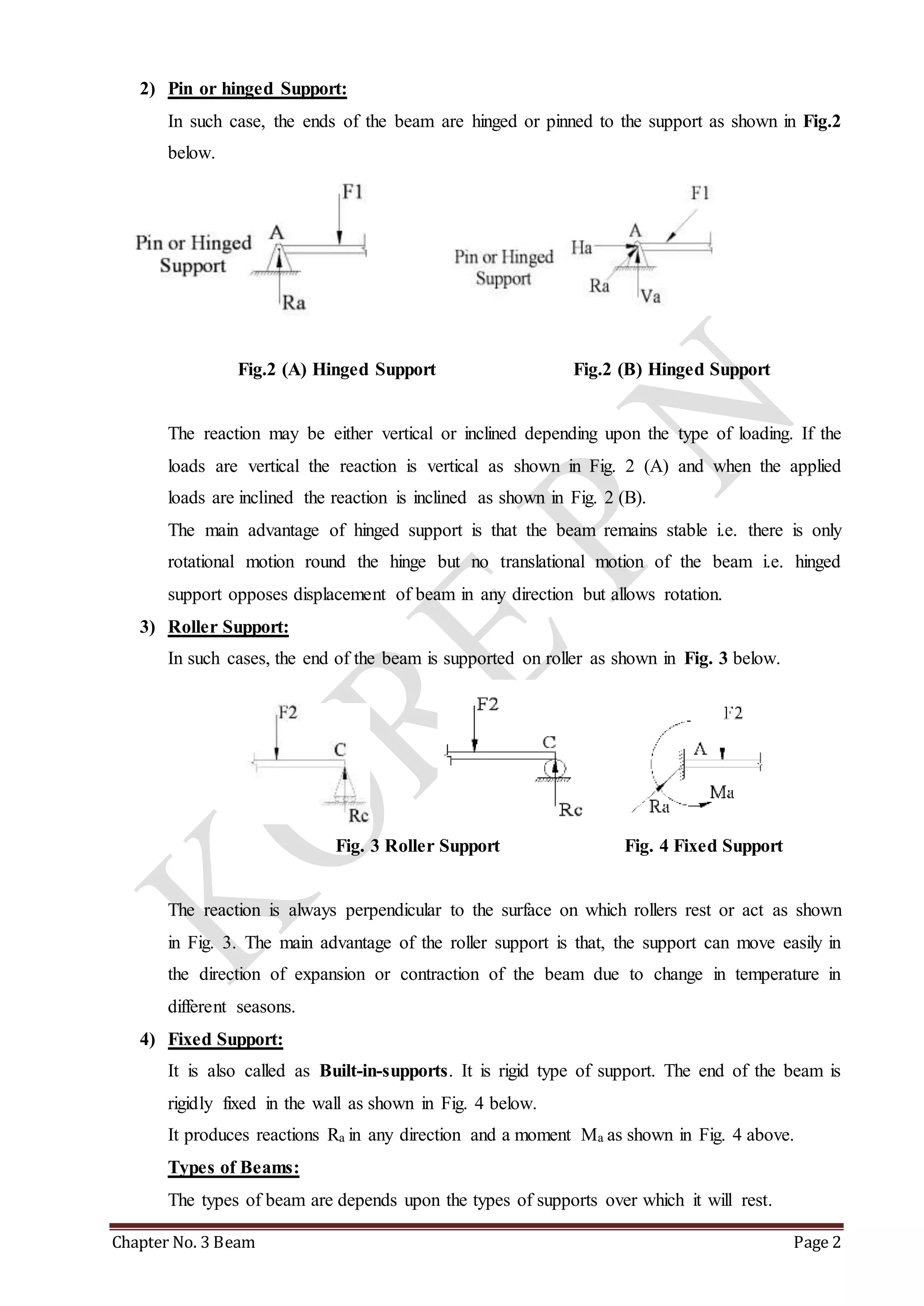
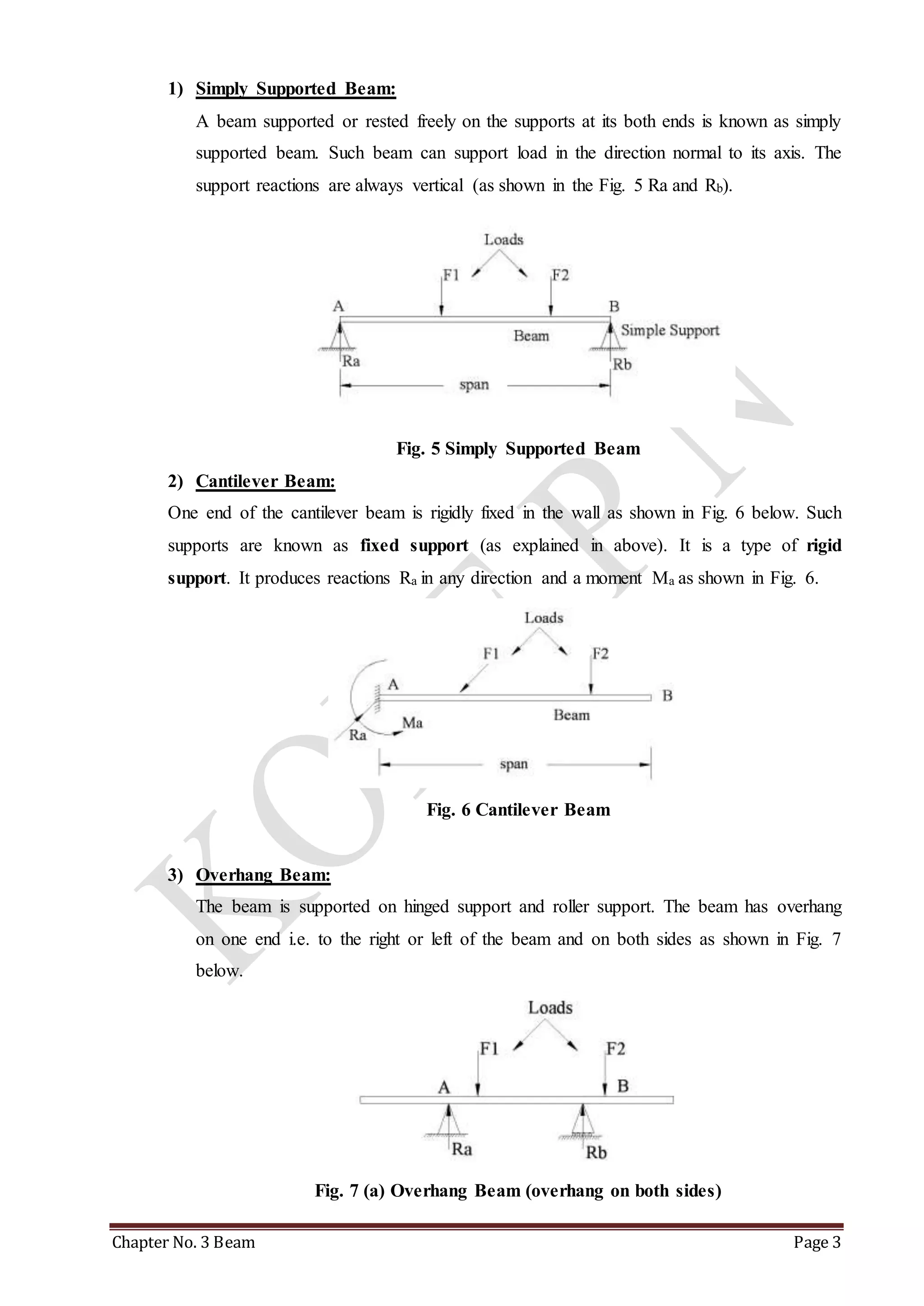
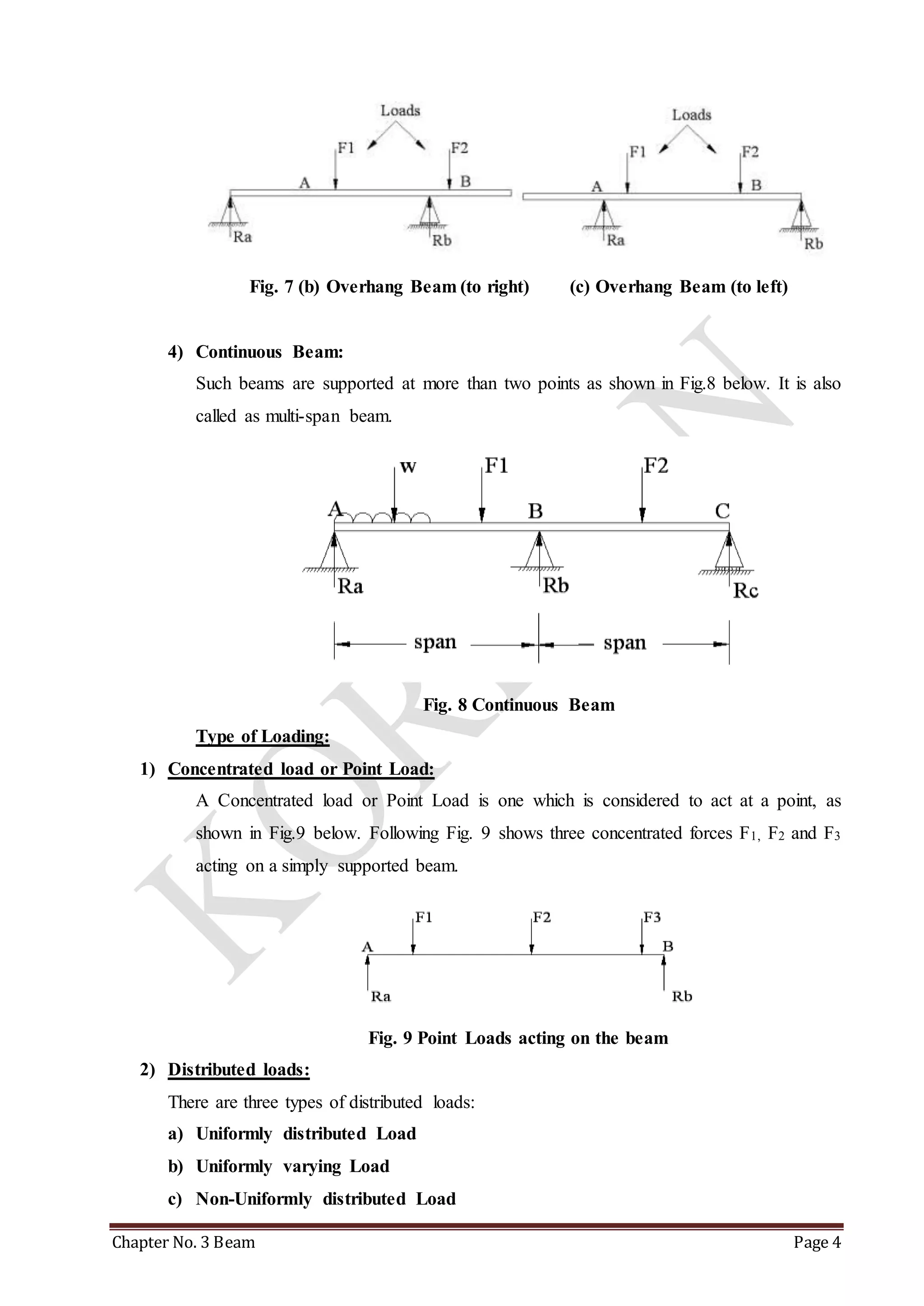
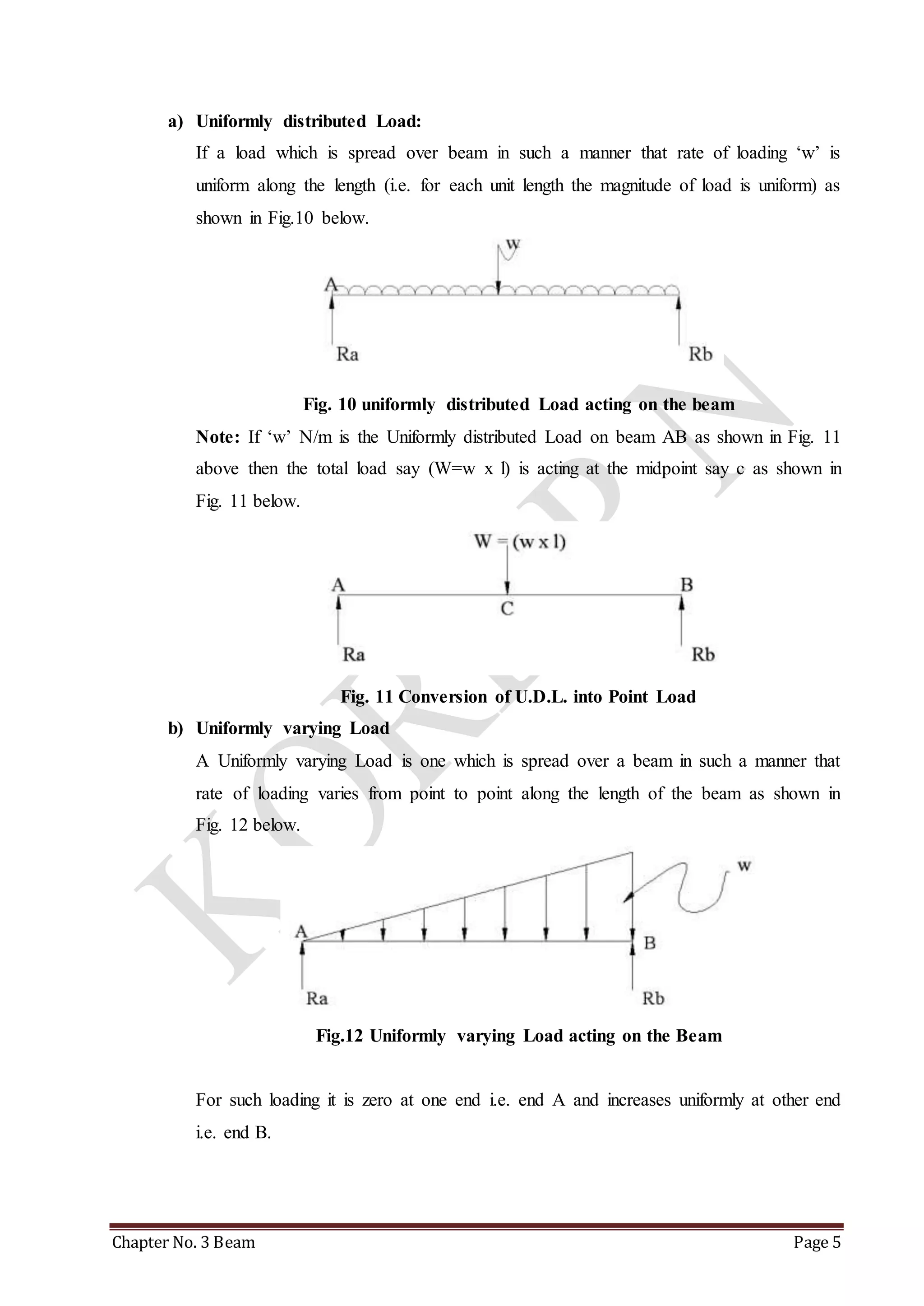
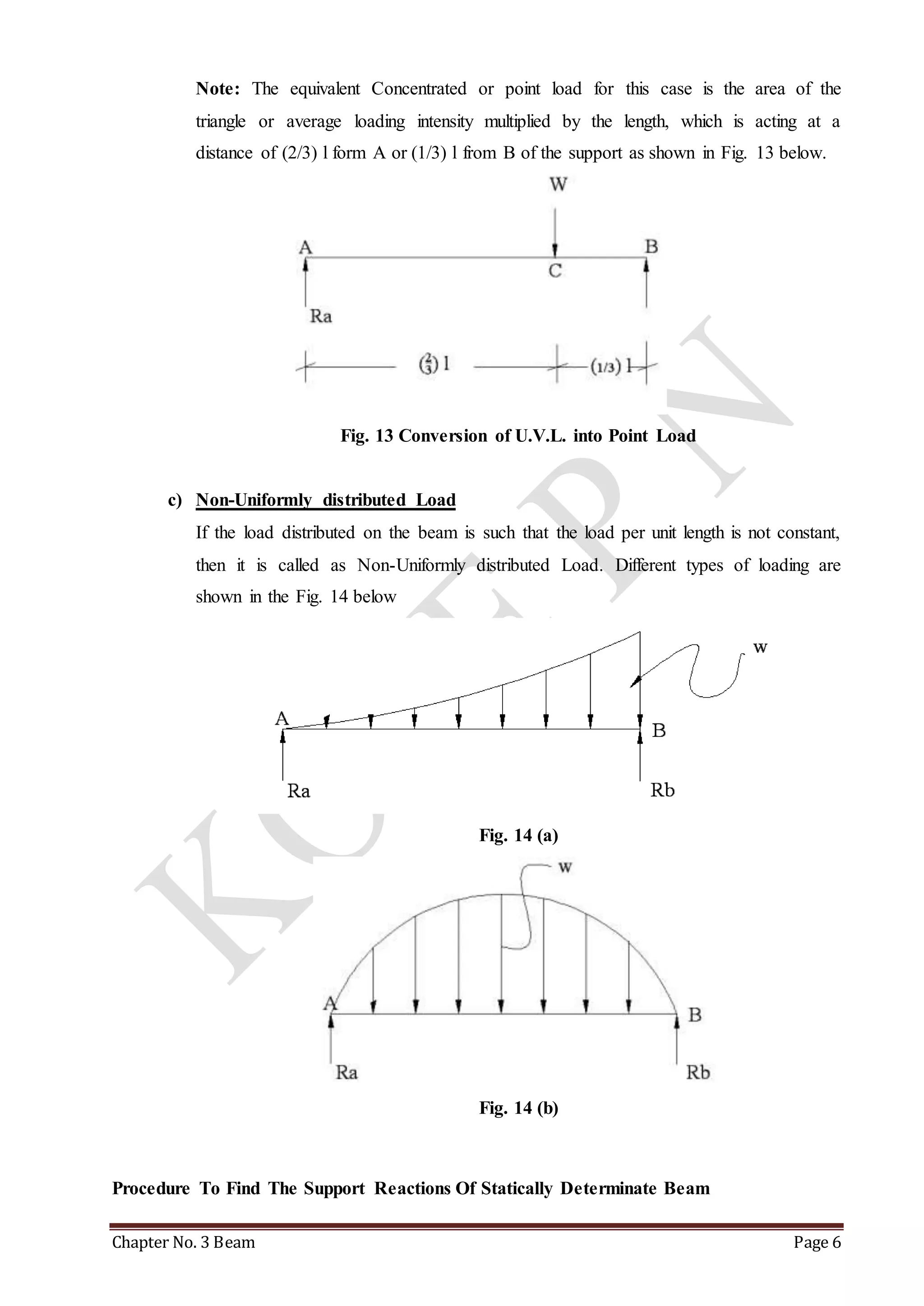
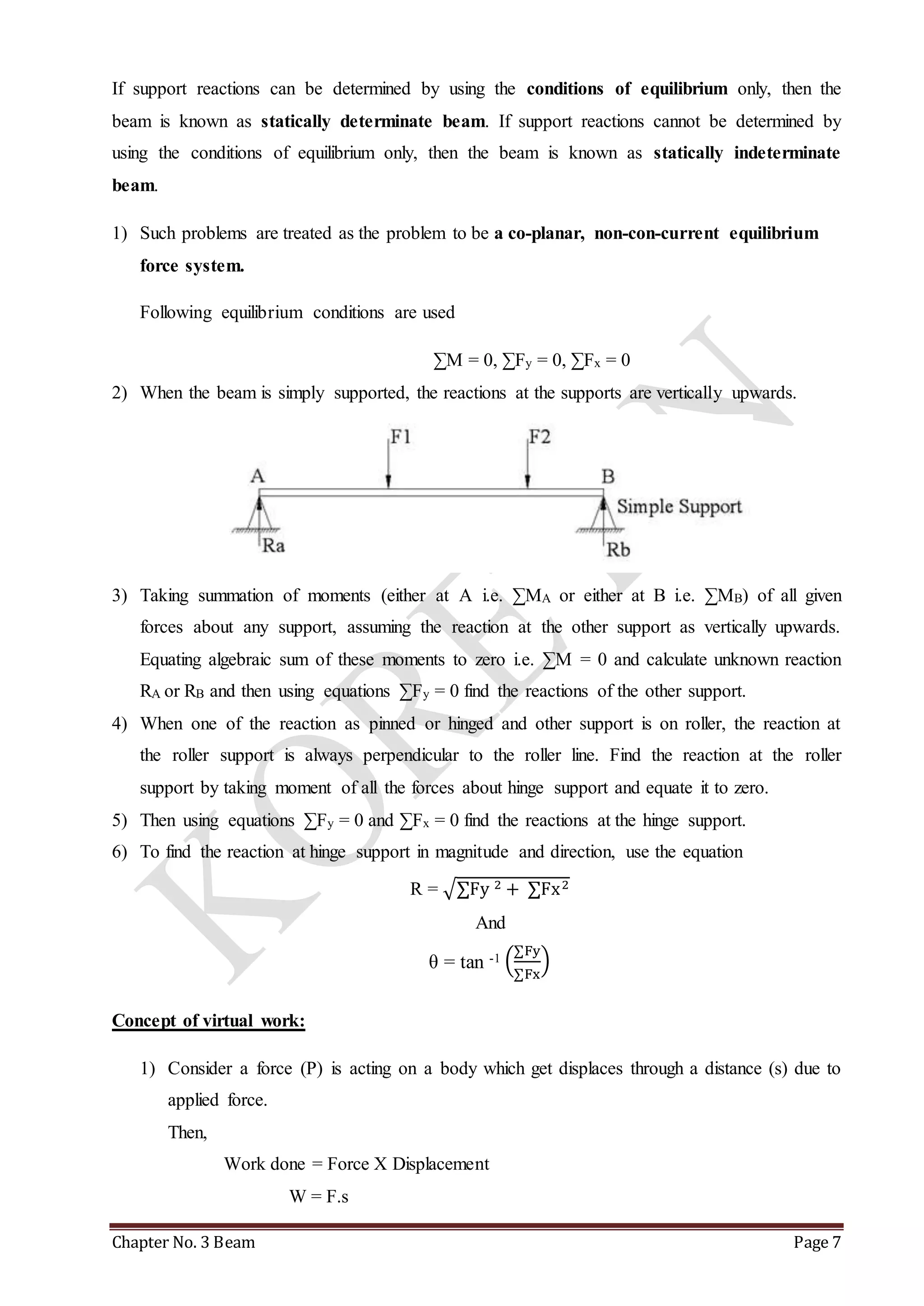
This chapter discusses beams and support reactions. It defines statically determinate beams and describes the following topics: types of beam supports including simple, pin/hinged, roller, and fixed supports; types of beams such as simply supported, cantilever, overhang, and continuous beams; types of loading including concentrated/point loads and distributed loads such as uniform, uniformly varying, and non-uniform loads; and the procedure to find support reactions of statically determinate beams using equilibrium conditions. It also discusses compound beams and the concept of virtual work.