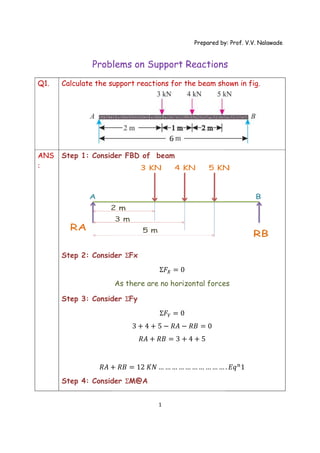
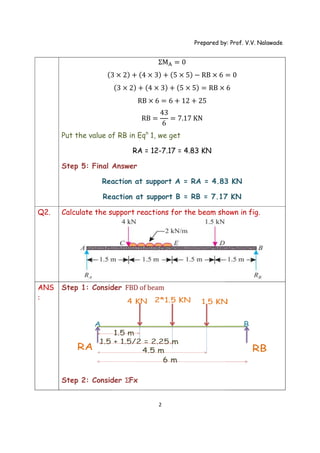
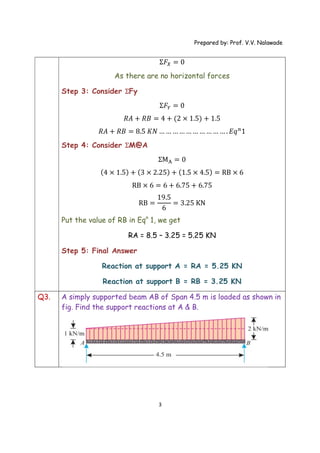
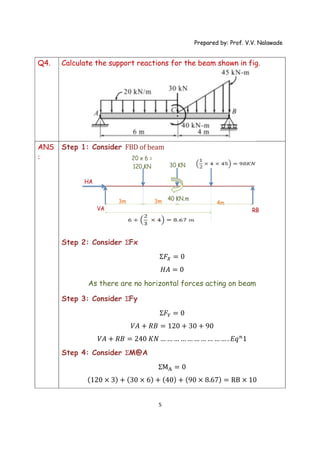
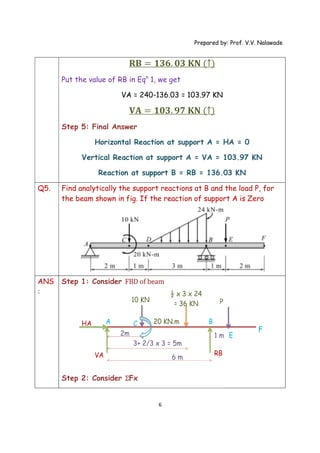
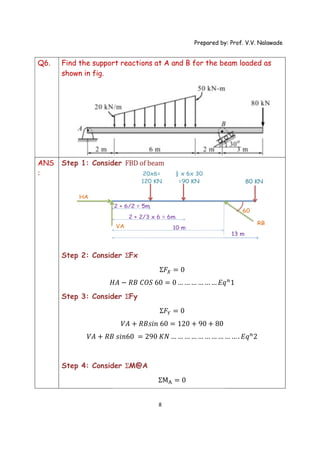
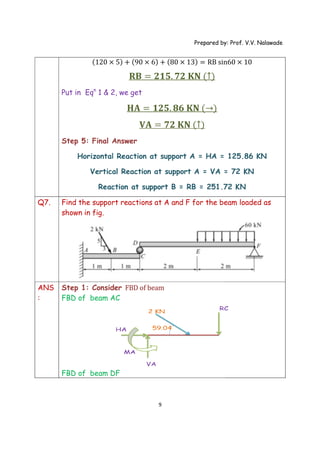
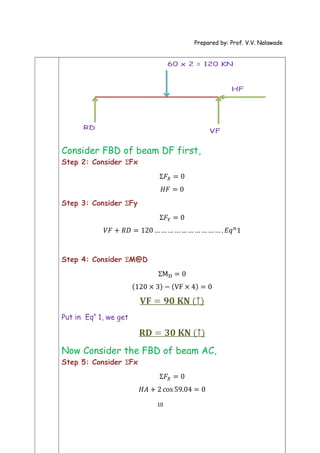
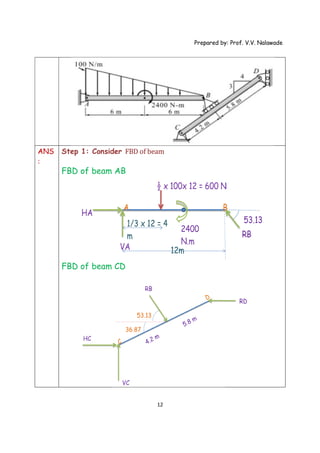
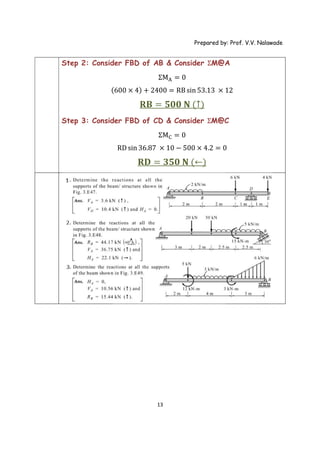
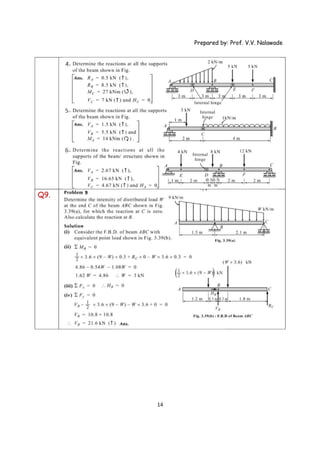
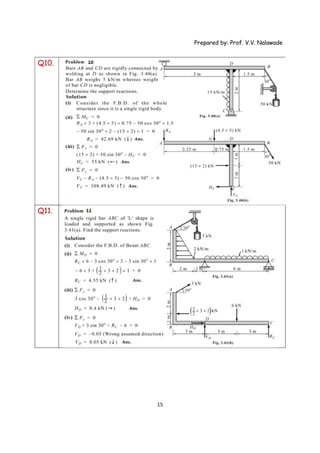
The document provides solutions to multiple problems involving calculating support reactions for beams. The problems involve drawing free body diagrams of beams, then applying equations for the sum of forces and sum of moments at the supports to solve for the unknown support reactions. Key steps include considering the absence of any horizontal forces, setting equations for the sum of vertical forces and moments equal to zero, and solving the resulting systems of equations to find the support reactions.