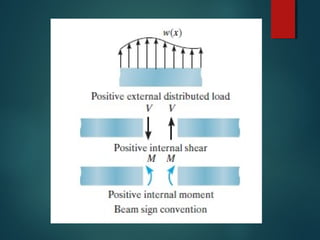
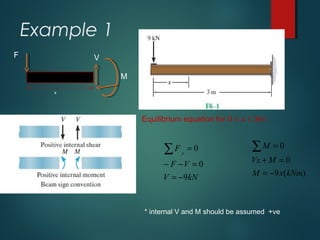
The document discusses different types of supports and loads that can act on beams. It describes:
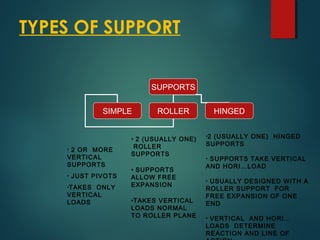
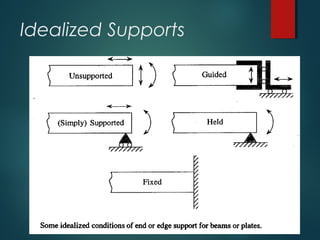
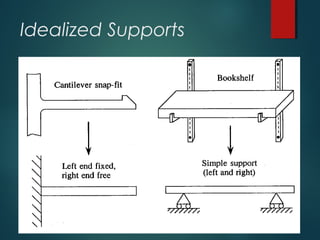
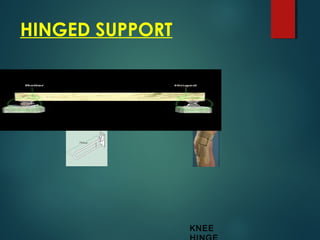
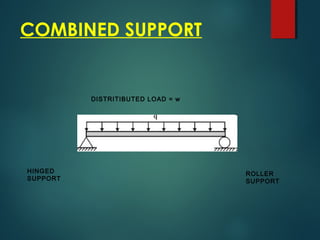
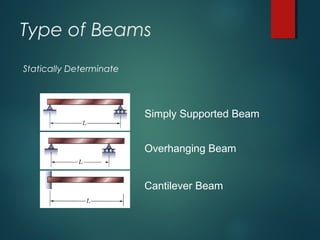
1) Types of supports including simple, roller, hinged, and combinations that determine reaction forces and the beam's equilibrium.
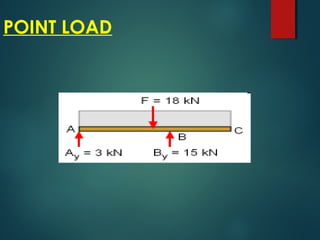
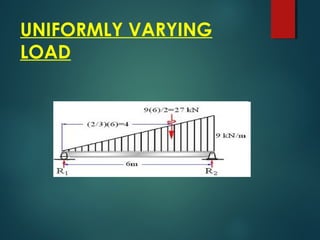
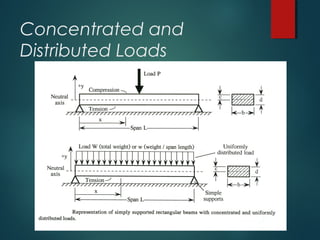
2) Types of loads such as concentrated point loads, uniformly distributed loads, and varying loads which can be represented as a single load at the center.
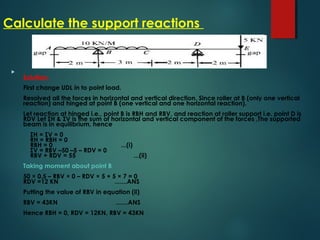
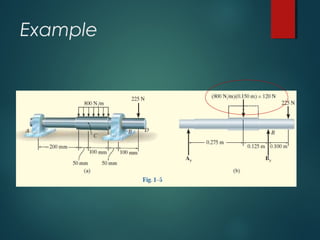
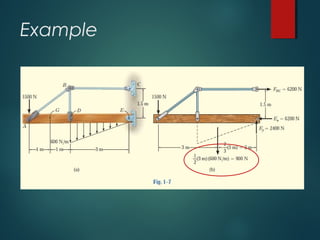
3) Examples of calculating support reactions and internal forces in beams under different loading conditions.