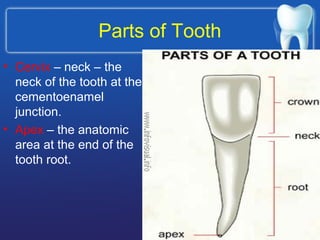
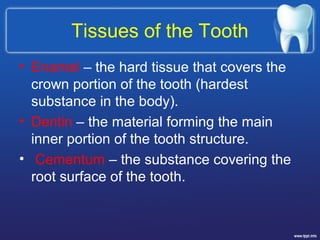
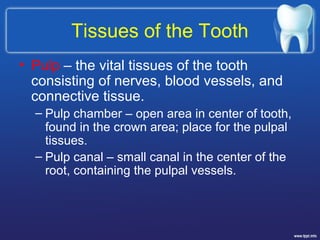
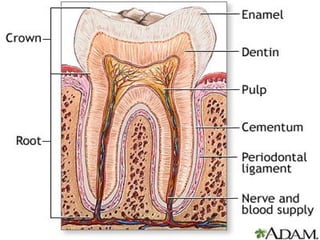
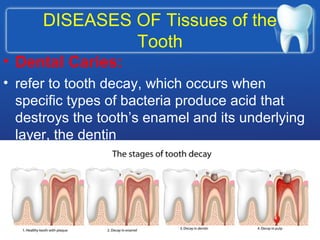
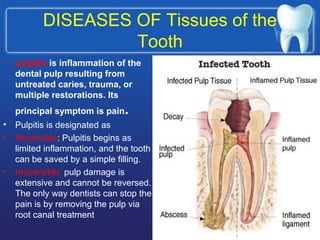
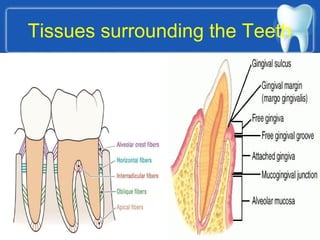
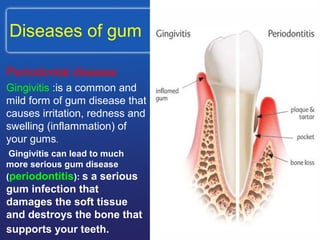
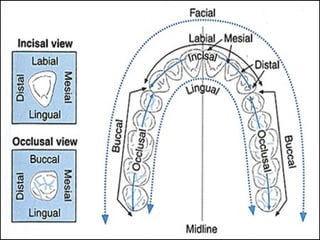
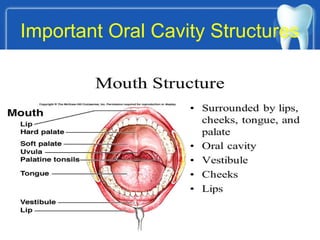
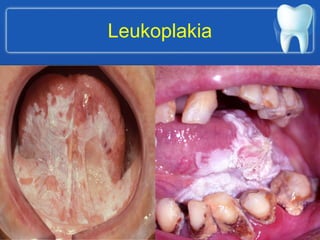
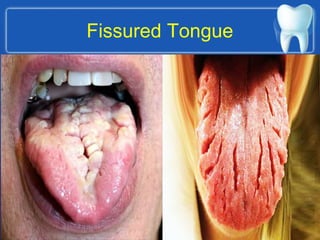
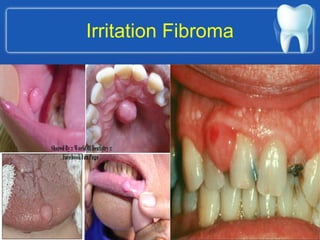
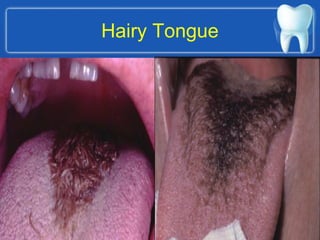
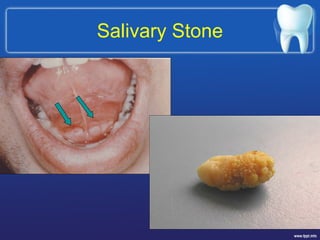
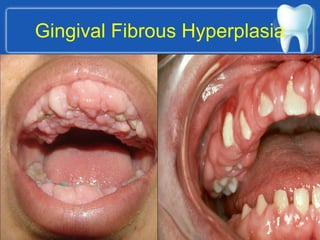
This document describes the structure and diseases of teeth. It discusses the parts of a tooth including the crown, root, and tissues like enamel, dentin, and cementum. It describes the tissues surrounding teeth like the alveolar process, bone, and periodontal ligament. Common dental diseases are also summarized such as dental caries, pulpitis, gingivitis and periodontitis. The surfaces and structures of teeth are defined including the facial, lingual, incisal edges and occlusal surfaces. Other oral cavity structures like leukoplakia, fissured tongue, fibroma and hairy tongue are also briefly mentioned.