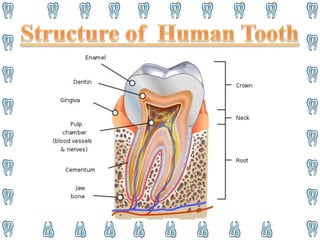
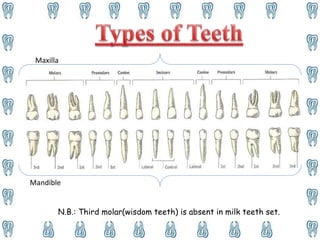
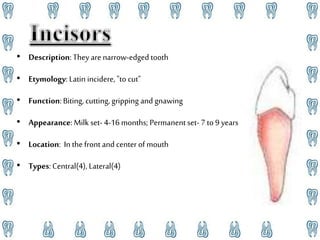
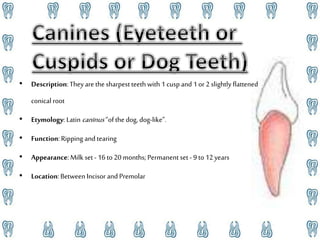
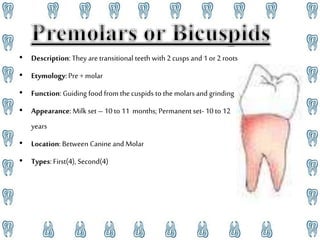
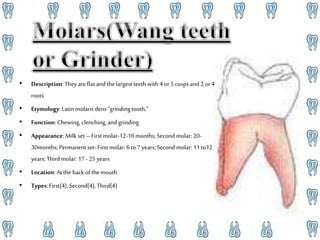
Human teeth have several functions including breaking down food through mastication, aiding in speech, and ingestion. Teeth are made up of multiple tissues and come in both primary and permanent sets according to dental formulas. The primary teeth formula is 2.1.0.2|2.1.0.2 and the permanent teeth formula is 2.1.2.3|2.1.2.3. Teeth are classified into incisors, canines, premolars, and molars depending on their shape and function in cutting, tearing, and grinding food. Proper dental hygiene including brushing, flossing, and checkups can prevent cavities and dental disease.