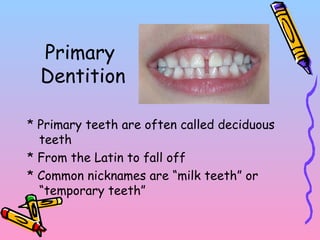
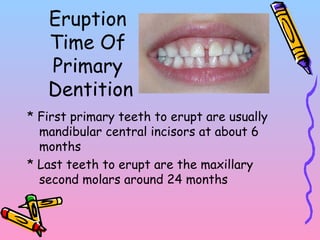
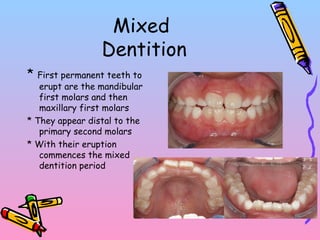
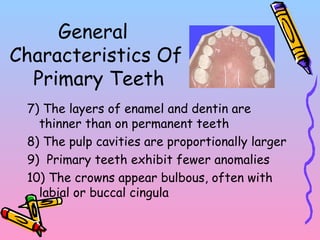
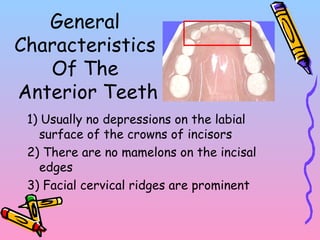
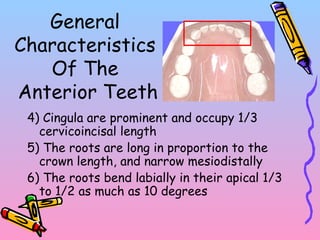
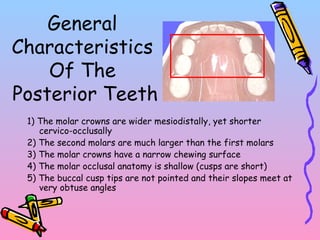
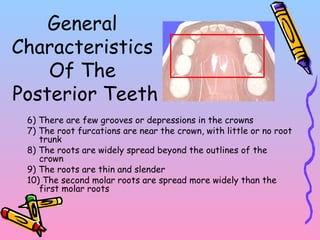
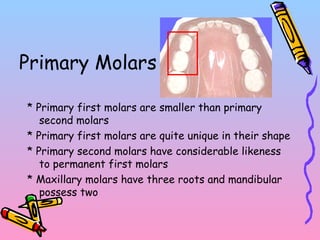
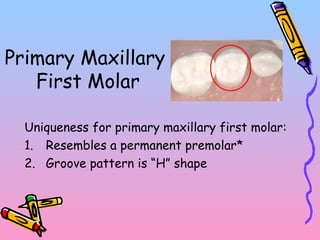
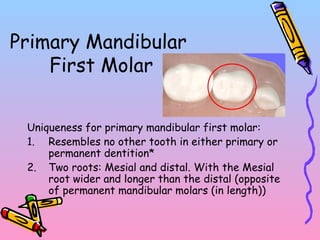
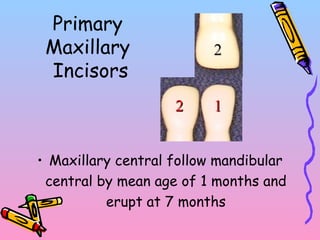
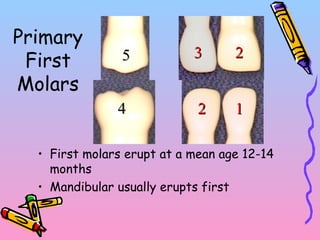
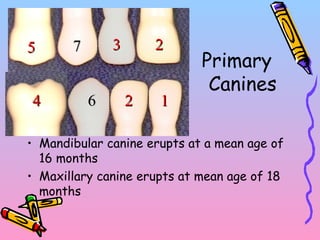
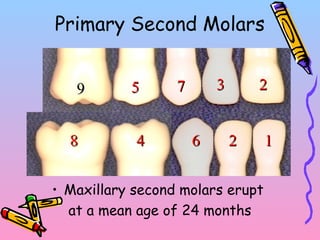
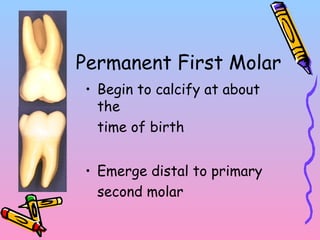
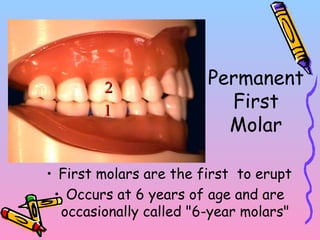
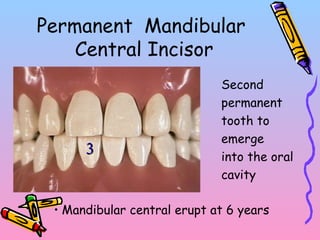
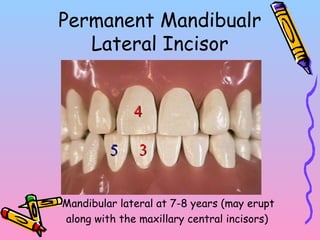
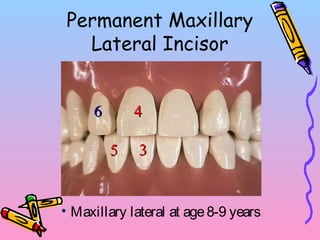
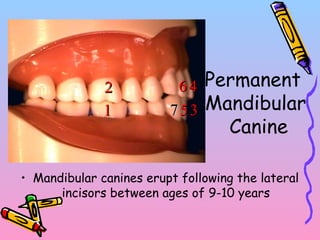
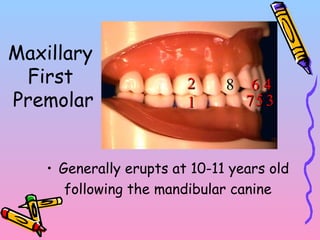
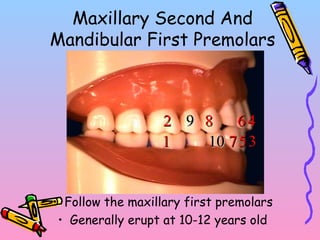
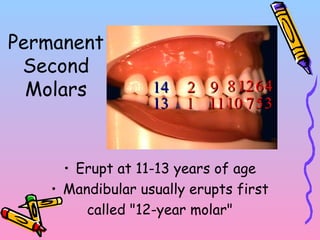
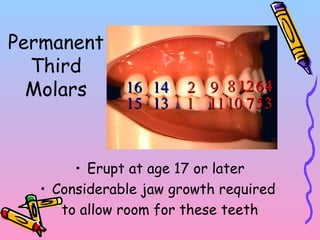
Primary teeth begin to emerge around 6 months of age and are gradually replaced by permanent teeth. The first primary teeth to erupt are usually the mandibular central incisors, while the last are the maxillary second molars around 24 months. Permanent first molars emerge around age 6 between the primary second molars and are occasionally called "6-year molars". The sequence of permanent tooth emergence continues with the mandibular central incisors at age 6, followed by other incisors and canines into the early teens.