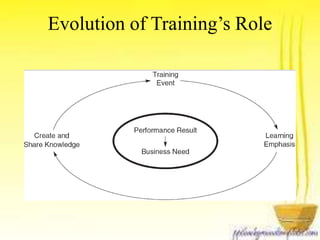
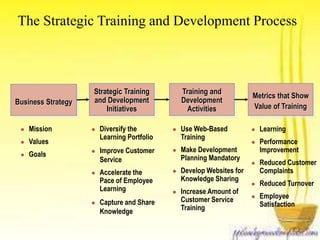
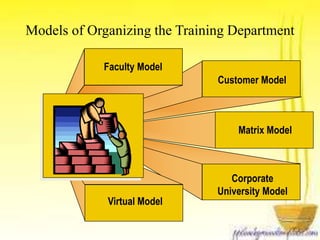
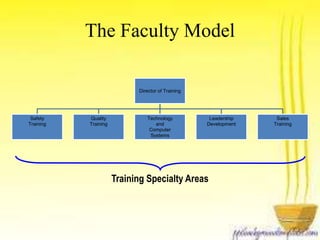
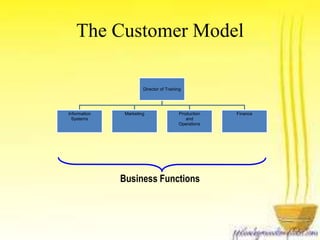
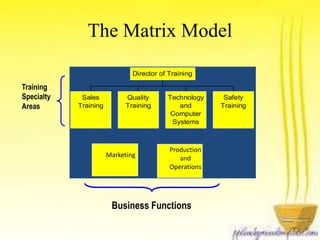
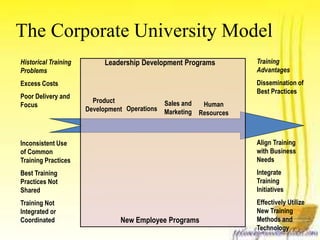
This document discusses how business strategy impacts organizational training. It outlines several models for structuring a training department, including faculty, customer, matrix, and corporate university models. Finally, it describes virtual training organizations, noting that they are customer-focused, provide customized solutions, and involve line managers in training direction and content. Employees have primary responsibility for learning, which occurs most effectively on the job rather than in classrooms.