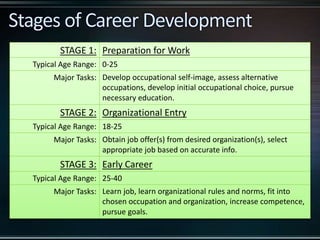
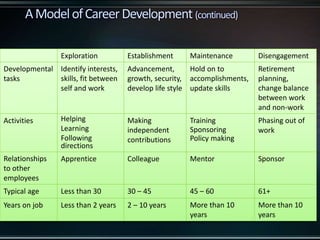
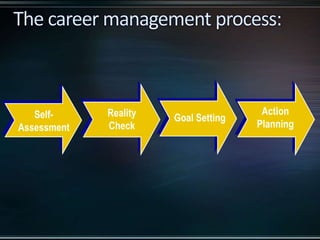
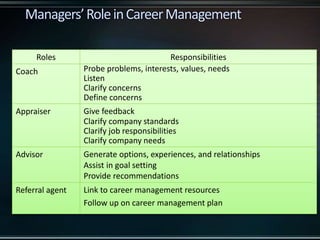
This document discusses career management and development. It covers traditional and protean career concepts, stages of career development including preparation, entry, early/mid/late career, and a four stage model of exploration, establishment, maintenance, and disengagement. The document also outlines the career management process, roles and responsibilities of managers, employees and HR in career development, and potential issues that can arise from a lack of career management.