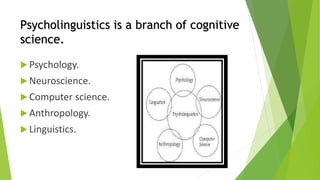
Psycholinguistics is the study of the psychological and neurobiological factors that enable humans to acquire, use, and understand language. It investigates the three primary processes of language comprehension, language production, and language acquisition. Psycholinguistics is a branch of cognitive science that draws from fields like psychology, neuroscience, linguistics and computer science to understand how humans perceive, learn, and produce language.