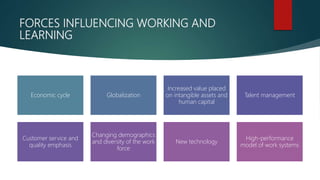
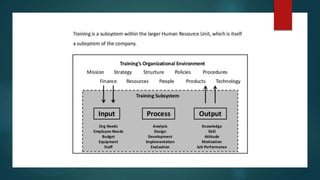
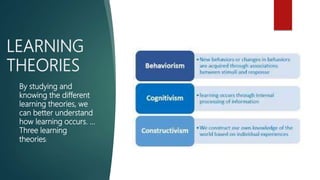
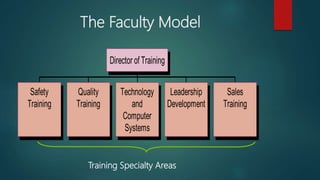
The document discusses training and development in organizations. It defines training and development, explaining that training focuses on current job skills while development focuses on future growth. It outlines the training process, including need assessment, program design, delivery, and evaluation. Challenges to effective training like employee schedules and technology changes are also examined. The role of training in organizations is to help them adapt to changes in the business environment, learn and implement new practices, and achieve excellence. An effective training system takes a systematic approach involving analyzing needs, designing the program, delivering instruction, and assessing outcomes.