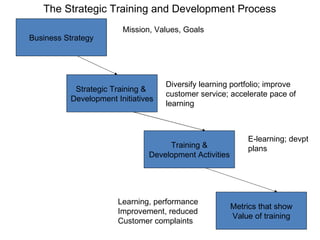
Training and development aims to improve employee performance by increasing skills and changing attitudes. It includes education, training, and development. Training provides specific skills while development helps employees grow. Training benefits include competitive advantage and improved productivity. The training process involves identifying needs, setting objectives, designing programs, implementing training, and assessing effectiveness. Various methods like lectures, simulations, and on-the-job training are used. Metrics help evaluate the impact of training on learning, behavior, and business results.