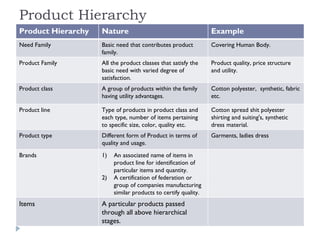
The document discusses the concept of products. It defines a product as anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. It then discusses the meaning, features, levels, and classification of products. Products can be classified based on tangibility, durability, user type as consumer or industrial goods, and social benefit. The document also discusses product mix decisions, product line appraisal, and product hierarchy.