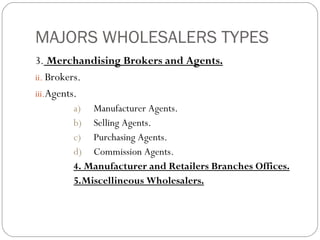
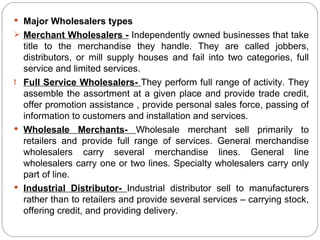
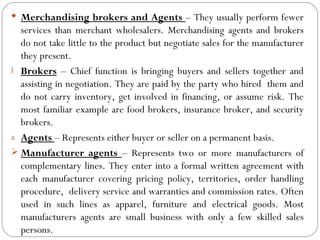
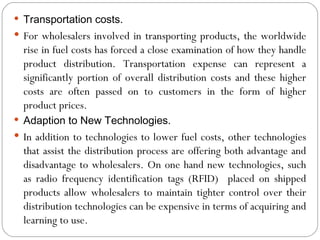
Wholesaling involves the sale of goods and services to retailers or commercial buyers for resale or business use. Wholesalers typically purchase goods in large quantities from manufacturers and sell in smaller quantities to retailers. They provide important services like warehousing, transportation, financing, market information, and risk bearing. New technologies and trends toward increased services are changing the wholesaling industry.