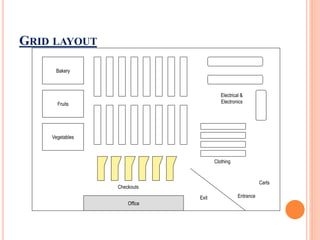
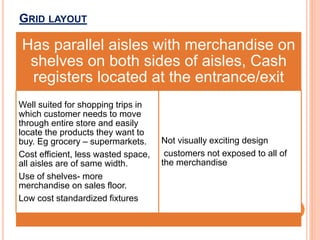
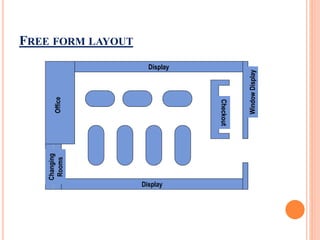
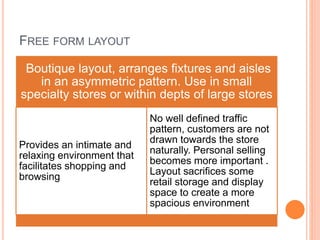
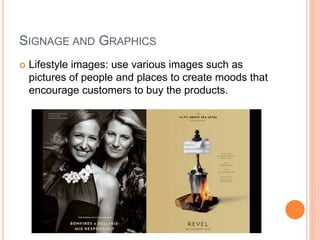
The document discusses store layout and design strategies. It outlines different layout types including grid, racetrack, and free-form and describes their advantages and disadvantages. Key aspects of store design covered include using the entrance, signage, lighting and floor plans to guide customers through their shopping experience and influence buying behavior. The objectives of store design are to implement the retailer's strategy, influence customers, provide flexibility, control costs and meet legal requirements.