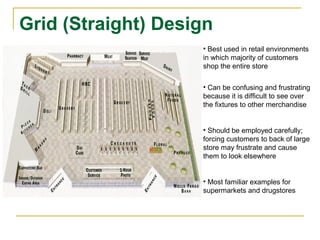
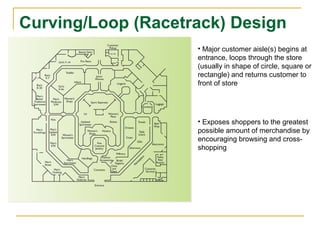
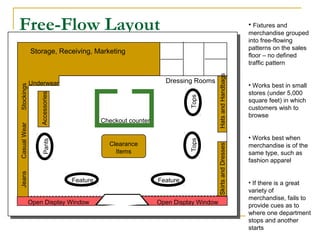
The document discusses objectives and strategies for effective store layout and design. The goals are to get customers into the store and convert them into buyers by exposing them to merchandise in an orderly manner. Key aspects covered include types of floor space, common layout designs like grid, loop and free-flow, principles for locating departments, using feature areas effectively, fixture types, merchandise display planning, and psychological factors to consider around value perception, sightlines, and color blocking. The overall aim is to influence customer behavior through a well-designed store environment.