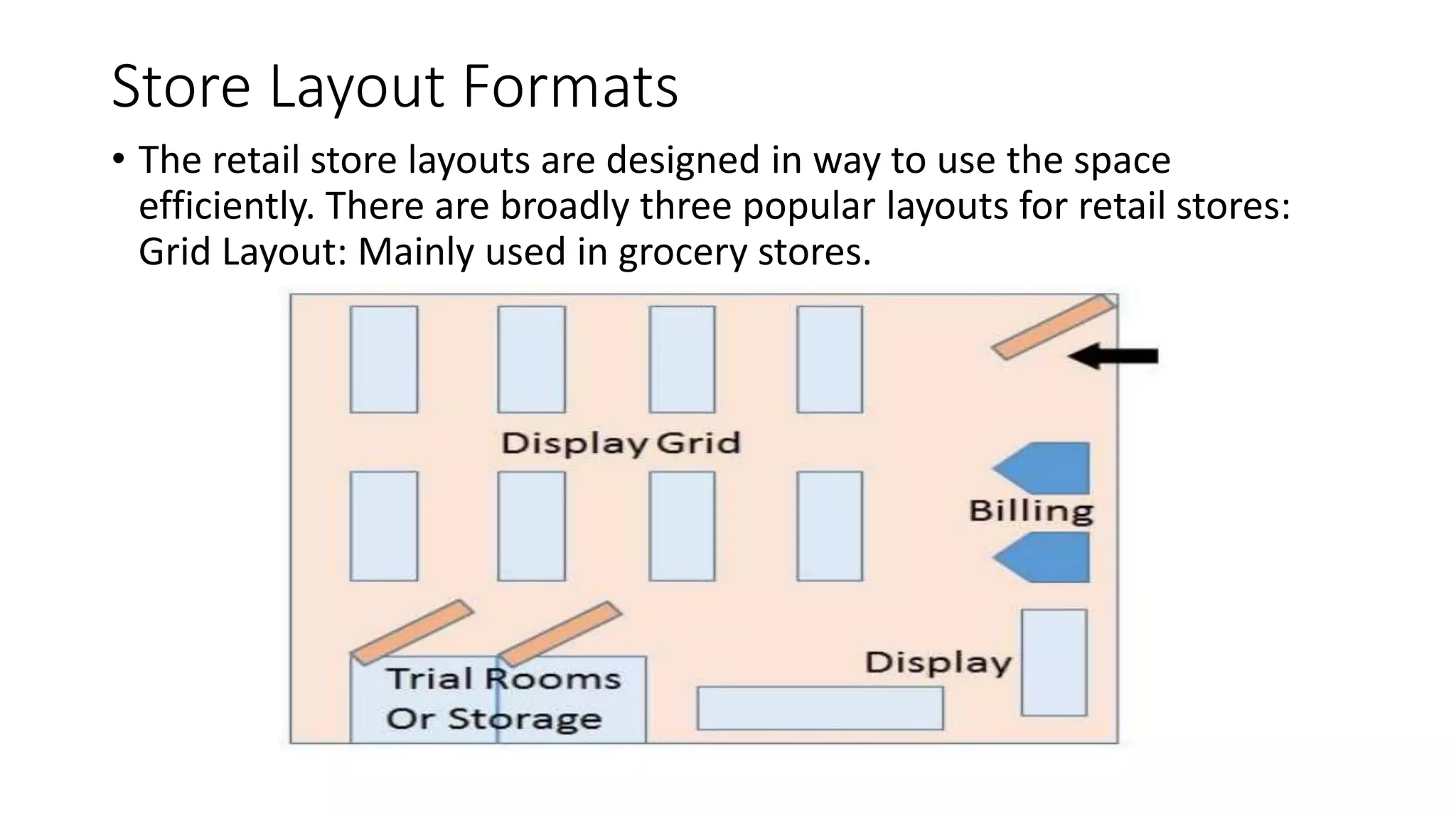
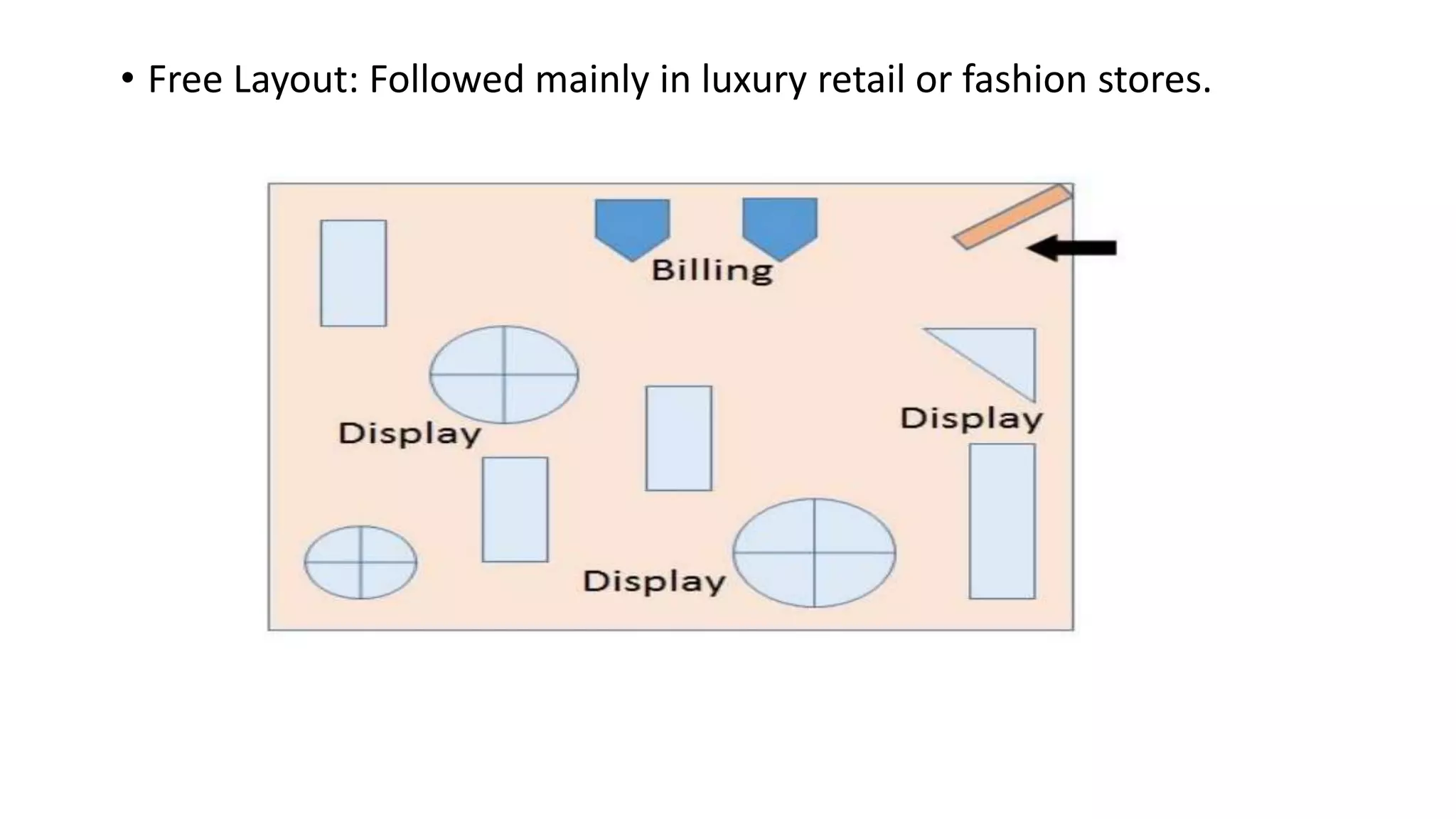
This document discusses retail space management. It defines space management as the process of managing floor space to facilitate customers and increase sales. Since store space is limited, it must be used wisely based on factors like product category, size, adjacencies, and life on the shelf. The steps for effective space use include measuring total area, dividing into selling and non-selling zones, creating a planogram, and allocating space logically. Store layout and design should attract customers, help them find products, encourage longer visits, and influence purchases. Common retail store layouts are grid, loop, and free formats.